Abstract
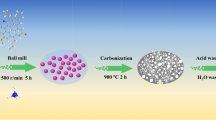
The artificial graphite materials were prepared by carbonizing coal tar pitch using two methods, namely, one- and two-step processes, and all sintered samples were graphitized at 2800 °C. Effects of different heat treatments on the performance of the samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), particle size analysis, polarized light microscopy, and charge–discharge measurements. All samples show a typical graphite crystalline structure; moreover, the degree of graphitization (g factor) and crystallite size along the c-axis (L c ) were calculated from (002) peak. The polarized light microscopy indicates that the coke with carbonization at 700 °C has an obvious wide domain (D) optical structure, while that with two-step sintering at 400 and 700 °C has a mixed optical structures of wide D, flow domains, and mosaics. TEM analysis revealed a number of irregular graphene layer images which are caused by the defects of graphite. EIS shows that the sample carbonized by two-step has a larger diffusion coefficient than the sample carbonized at 700 °C by one step. Higher carbonization temperature leads to better cycle performance as the temperature increasing from 500 to 700 °C in the one-step route. Specifically, the charge (Li+ extraction) capacity at the 50th cycle increases from 318 mA h g−1 to 357 mA h g−1. The results show that the rate performance of the artificial graphite is improved with the addition of the presintering at 400 °C.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kwak G, Park J, Lee J, Kim S, Jung I (2007) J Power Sources 174:484–492
Zhang HL, Liu SH, Li F, Bai S, Liu C, Tan J, Cheng HM (2006) Carbon 44:2212–2218
Ding YS, Li WN, Iaconetti S, Shen XF, DiCarlo J, Galasso FS, Suib SL (2006) Surf Coat Tech 200:3041–3048
Yoshio M, Wang H, Fukuda K, Hara Y, Adachi Y (2000) J Electrochem Soc 147:1245–1250
Liu SH, Zhe Y, Wang ZM, Li F, Bai S, Wen L (2008) New Carbon Mater 23:30–36
Jang SM, Miyawaki J, Tsuji M, Mochida I, Yoon SH, Kang FY (2010) New Carbon Mater 25:89–96
Jarvis CR, Lain MJ, Yakovleva MV, Gao Y (2006) J Power Sources 162:800–802
Jin YZ, Kim YJ, Gao C, Zhu YQ, Huczko A, Endo M, Kroto HW (2006) Carbon 44:724–729
Wang Q, Li H, Chen L, Huang X (2002) Solid State Ionics 152–153:43–50
Xing W, Bai P, Li ZF, Yu RJ, Yan ZF, Lu GQ, Lu LM (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:4626–4633
Yeh TS, Wu YS, Lee YH (2011) Mater Chem Phys 130:309–315
Wang DJ, Wang YL, Zhan L, XY Zg, Liu CF, Qiao WM, Ling LC (2011) J Inorg Mater 26:614–619
Wu YP, Rahm E, Holze R (2003) J Power Sources 114:228–236
Li HQ, Liu RL, Zhao DY, Xia YY (2007) Carbon 45:2628–2635
Takamura T, Endo K, Fu L, Wu Y, Lee KJ, Matsumoto T (2007) Electrochima Acta 53:1055–1061
Courtel FM, Niketic S, Duguay D, Abu-Lebdeh Y, Davidson IJ (2011) J Power Sources 196:2128–2134
Yuan C, Gao B, Su L, Zhang X (2008) Solid State Ionics 178:1859–1866
Li XK (1991) Carbon Tech 3:11–15
Gao Y, Song HH, Chen XH, Mao YL, Liu XL (2001) Nen Carbon Mater 16:32–35
Li TQ, Wang CY (2005) Nen Carbon Mater 20:278–285
Li HQ, Wang YG, Wang CX, Xia YY (2008) J Power Sources 185:1557–1562
Sung MG, Hattori K, Asai S (2009) Mater Design 30:387–390
Ren CQ, Li TH, Lin QL, Li H, Shun XY (2005) Mater Rev 19:50–56
Li X, Li Q (1995) Fuel 75:3–5
Chen JT, Zhou HH, Chang WB, Ci YX (2003) Acta Phys-Chim Sin 19:278–282
Lu JH, Li HJ, Liu H, Li KZ, Zhang MZ (2006) Acta Aeronautica Et Astronautica Sinica 27(5):969–972
Shenoudaa AY, Liu HK (2010) J Electrochem Soc 157:A1183–A1187
Liu QC, Xia JT, Zhou SM, Chen ZZ (2000) Carbon Tech 3:1–3
Zhang SS, Xu K, Jow TR (2006) Electrochim Acta 51:1636–1640
Morita T, Takami N (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:2591–2599
Zhang S, Shi PF (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:1475–1482
Mukhopadhyay I, Hoshino N, Kawasaki S, Okino F, Hsu WK, Touhara H (2002) J Electrochem Soc 149:A39–A44
Zhang GH, Yan ZX, Zou HL, Shen PK (2010) Electrochem 16:145–150
Acknowledgments
This work was financially sponsored by the Major Special Project of Science and Technology of Hunan Province (grant number 2011FJ1005) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant number 2010QZZD0101)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Guo, H., Li, X. et al. Carbonization and graphitization of pitch applied for anode materials of high power lithium ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 17, 1401–1408 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-013-2003-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-013-2003-9