Abstract
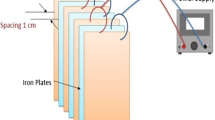
An intensified electrochemical process in an undivided cell using Cu–Zn alloy as cathode and Ti/IrO2–Pt as anode combined with bipolar iron particles (electro-iron system) has been developed. The performance of nitrate reduction was evaluated using synthetic groundwater. Results showed that the nitrate-N dropped rapidly from 50 to less than 10 mg/L within 100 min in the developed system at current densities in the range of 5–30 mA/cm2. Sodium chloride addition was found to have a positive effect on the system performance. No nitrite-N was detected during the electrolysis in the presence of sodium chloride. The concentration of total iron ion in the solutions was found to be less than 0.25 mg/L after 100 min electrolysis. Furthermore, the electrical energy consumption for nitrate reduction in the electro-iron system was saved by approximately 29.4–34.8 % at 5–30 mA/cm2. The developed system has been proved to promote electrochemical nitrate reduction and greatly improve the electrical energy efficiency.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nolan BT, Ruddy BC, Helsel DR (1999) Arch Environ Health 54:242–247
Wolfe AH, Patz JA (2002) Ambio 31:120–125
Cantor KP (1997) Cancer Cause Control 8:292–308
WHO (2004) Rolling revision of the WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality, nitrates and nitrites in drinking water. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Environmental Protection Agency US (1995) Drinking water regulations, health advisories. Office of Water, Washington, DC
Ghafari S, Hasan M, Aroua MK (2007) Bioresour Technol 99:3965–3974
Samatya S, Kabay N, Yüksel Ü, Rda M, Yüksel M (2006) React Funct Polym 66:1206–1214
Fernández-Nava Y, Maranon E, Soons J, Castrillón L (2008) Bioresour Technol 99:7976–7981
Murphy AP (1991) Nature 350:223–225
Li M, Feng CP, Zhang ZY, Lei XH, Chen RZ, Sugiura N (2009) J Hazard Mater 171:724–730
Taguchi S, Feliu JM (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:3626–3634
Reyter D, Bélanger D, Roué L (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:5977–5984
Li M, Feng CP, Zhang ZY, Sugiura N (2009) Electrochim Acta 54:4600–4606
Li H, Chambers JQ, Hobbs DT (1988) J Appl Electrochem 18:454–458
De Vooys ACA, Van Santen RA, Van Veen JAR (2000) J Mol Catal A Chem 154:203–215
Mácová Z, Bouzek K (2005) J Appl Electrochem 35:1203–1211
Li M, Feng CP, Zhang ZY, Shen ZL, Sugiura N (2009) Electrochem Commun 11:1853–1856
Talhi B, Monette F, Azzouz A (2011) Electrochem Acta 58:276–284
De D, Englehardt JD, Kalu EE (2000) J Electrochem Soc 147:4573–4579
Reyter D, Bélanger D, Roué L (2010) Water Res 44:1918–1926
Wang DM, Lin HY, Shah SI, Ni CY, Huang CP (2009) Sep Purif Technol 67:127–134
Kim KW, Kim YJ, Kim IT, Park GI, Lee EH (2005) Electrochim Acta 50:4356–4364
Vanlangendonck Y, Corbisier D, Lierde A (2005) Water Res 39:3028–3034
Kim KW, Kim YJ, Kim IT, Park GI, Lee EH (2006) Water Res 40:1431–1441
Phillips DH, Gu B, Watson DB, Roh Y, Liang L, Lee SY (2000) Environ Sci Technol 34:4169–4176
Tsai YJ, Chou FC, Cheng TC (2009) J Hazard Mater 163:743–747
Hwang YH, Kim DG, Shin HS (2011) J Hazard Mater 185:1513–1521
Weber EJ (1996) Environ Sci Technol 30:716–719
Choe S, Chang YY, Hwang KY, Khim J (2000) Chemosphere 41:1307–1311
Yang GCC, Lee HL (2005) Water Res 39:884–894
Liao CH, Kang SF, Hsu YW (2003) Water Res 37:4109–4118
Huang YH, Zhang TC (2002) J Environ Eng 128:604–611
Huang CP, Wang HW, Chiu PC (1998) Water Res 32:2257–2264
Chew CF, Zhang TC (1998) Water Sci Technol 38:135–142
Chew CF, Zhang TC (1999) Environ Eng Sci 16:389–401
Katsounaros I, Dortsiou M, Kyriacou G (2009) J Hazard Mater 171:323–327
Vlyssides AG, Karlis PK, Rori N, Zorpas AA (2002) J Hazard Mater 95:215–226
Katsounaros I, Kyriacou G (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:5477–5484
Czarnetzki LR, L. Janssen JJ (1992) J Appl Electrochem 22:315–324
Huang YH, Zhang TC (2004) Water Res 38:2631–2642
Cheng H, Scott K, Christensen PA (2005) Chem Eng J 108:257–268
Brylev O, Sarrazin M, Roué L, Bélanger D (2007) Electrochim Acta 52:6237–6247
Devkota LM, Williams DS, Matta JH, Albertson OE, Grasso D, Fox P (2000) Water Environ Res 72:610–617
Anand RK, Laws DR, Chow KF, Chang BY, Crooks JA, Crooks RM (2010) Anal Chem 82:8766–8774
Loan M, Newman OMG, Cooper RMG, Farrow JB, Parkinson GM (2006) Hydrometallurgy 81:104–129
WHO (2006) Water sanitation and health (WSH): guidelines for drinking-water quality, 3rd ed. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Acknowledgments
This was supported by National Natural Science Foundation (no. 31140082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Zhang, B., Li, M. et al. An electrochemical process intensified by bipolar iron particles for nitrate removal from synthetic groundwater. J Solid State Electrochem 17, 1013–1020 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1956-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1956-4