Abstract
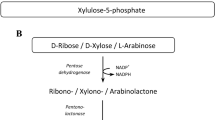
The pathway of l-arabinose degradation was studied in the haloarchaeon Haloferax volcanii. It is shown that l-arabinose is oxidatively degraded to α-ketoglutarate. During growth on l-arabinose, l-arabinose dehydrogenase (l-AraDH) was induced. The enzyme was purified as a 130 kDa homotetrameric protein catalyzing the oxidation of l-arabinose with both NADP+ and NAD+. The gene encoding l-AraDH was identified as HVO_B0032 and recombinant l-AraDH showed similar properties as the native enzyme. The l-AraDH deletion mutant did not grow on l-arabinose, but grew unaffected on glucose and d-xylose, indicating a specific involvement in l-arabinose degradation. Phylogenetic analyses attribute the first archaeal l-AraDH to the extended short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDRe) family, where it is part of a novel cluster and thus differs from known archaeal and bacterial pentose dehydrogenases. Further, cell extracts of H. volcanii catalyzed the NADP+-dependent conversion of l-arabinoate to α-ketoglutarate. The genes involved in that conversion were identified by analyses of transcripts and deletion mutants as HVO_B0038A, HVO_B0027 and HVO_B0039 recently reported to be involved in d-xylonate conversion to α-ketoglutarate in H. volcanii (Johnsen et al. 2009).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allers T, Ngo HP, Mevarech M, Lloyd RG (2004) Development of additional selectable markers for the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii based on the leuB and trpA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:943–953
Alphey MS, Burton A, Urbaniak MD, Boons GJ, Ferguson MA, Hunter WN (2006) Trypanosoma brucei UDP-galactose-4′-epimerase in ternary complex with NAD+ and the substrate analogue UDP-4-deoxy-4-fluoro-alpha-d-galactose. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 62:829–834
Amako K, Fujita K, Shimohata TA, Hasegawa E, Kishimoto R, Goda K (2006) NAD+-specific d-arabinose dehydrogenase and its contribution to erythroascorbic acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 580:6428–6434
Asada Y et al (2009) Biochemical and structural characterization of a short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase of Thermus thermophilus HB8: a hyperthermostable aldose-1-dehydrogenase with broad substrate specificity. Chem Biol Interact 178:117–126
Baroja-Mazo A et al (2005) Characterisation and biosynthesis of d-erythroascorbic acid in Phycomyces blakesleeanus. Fungal Genet Biol 42:390–402
Bitan-Banin G, Ortenberg R, Mevarech M (2003) Development of a gene knockout system for the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii by use of the pyrE gene. J Bacteriol 185:772–778
Brenneis M, Hering O, Lange C, Soppa J (2007) Experimental characterization of Cis-acting elements important for translation and transcription in halophilic archaea. PLoS Genet 3:e229
Brouns SJ et al (2006) Identification of the missing links in prokaryotic pentose oxidation pathways: evidence for enzyme recruitment. J Biol Chem 281:27378–27388
Brückner J (1955) Estimation of monosaccharides by the orcinol-sulphuric acid reaction. Biochem J 60:200–205
Chen YW, Dekker EE, Somerville RL (1995) Functional analysis of E. coli threonine dehydrogenase by means of mutant isolation and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta 1253:208–214
Chomczynski P, Mackey K (1995) Substitution of chloroform by bromo-chloropropane in the single-step method of RNA isolation. Anal Biochem 225:163–164
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Dambeck M, Soppa J (2008) Characterization of a Haloferax volcanii member of the enolase superfamily: deletion mutant construction, expression analysis, and transcriptome comparison. Arch Microbiol 190:341–353
Danner S, Soppa J (1996) Characterization of the distal promoter element of halobacteria in vivo using saturation mutagenesis and selection. Mol Microbiol 19:1265–1276
Hammelmann M, Soppa J (2008) Optimized generation of vectors for the construction of Haloferax volcanii deletion mutants. J Microbiol Methods 75:201–204
Johnsen U et al (2009) d-xylose degradation pathway in the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii. J Biol Chem 284:27290–27303
Kallberg Y, Oppermann U, Persson B (2010) Classification of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase superfamily using hidden Markov models. FEBS J 277:2375–2386
Kao YC, Davis L (1994) Purification and structural characterization of porcine l-threonine dehydrogenase. Protein Expr Purif 5:423–431
Kavanagh KL, Jörnvall H, Persson B, Oppermann U (2008) Medium- and short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase gene and protein families: the SDR superfamily: functional and structural diversity within a family of metabolic and regulatory enzymes. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:3895–3906
Kim ST, Huh WK, Kim JY, Hwang SW, Kang SO (1996) d-arabinose dehydrogenase and biosynthesis of erythroascorbic acid in Candida albicans. Biochim Biophys Acta 1297:1–8
Kuhn J, Binder S (2002) RT-PCR analysis of 5′ to 3′-end-ligated mRNAs identifies the extremities of cox2 transcripts in pea mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res 30:439–446
Marchler-Bauer A et al (2011) CDD: a conserved domain database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D225–D229. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1189
Meyer C, Schmid R, Scriba PC, Wehling M (1996) Purification and partial sequencing of high-affinity progesterone- binding site(s) from porcine liver membranes. Eur J Biochem 239:726–731
Persson B, Kallberg Y, Oppermann U, Jornvall H (2003) Coenzyme-based functional assignments of short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDRs). Chem Biol Interact 143–144:271–278
Pickl A, Johnsen U, Schonheit P (2012) Fructose degradation in the haloarchaeon Haloferax volcanii involves a bacterial type phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system, fructose-1-phosphate kinase, and class II fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. J Bacteriol 194:3088–3097. doi:10.1128/JB.00200-12
Sakuraba H, Kawai T, Yoneda K, Ohshima T (2011) Crystal structure of UDP-galactose 4-epimerase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrobaculum calidifontis. Arch Biochem Biophys 512:126–134
Sambrook S, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 2 edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Slupska MM, King AG, Fitz-Gibbon S, Besemer J, Borodovsky M, Miller JH (2001) Leaderless transcripts of the crenarchaeal hyperthermophile Pyrobaculum aerophilum. J Mol Biol 309:347–360
Stephens C, Christen B, Fuchs T, Sundaram V, Watanabe K, Jenal U (2007) Genetic analysis of a novel pathway for d-xylose metabolism in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol 189:2181–2185
Talaat AM, Lyons R, Howard ST, Johnston SA (2004) The temporal expression profile of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4602–4607. doi:10.1073/pnas.0306023101
Thoden JB, Frey PA, Holden HM (1996) Molecular structure of the NADH/UDP-glucose abortive complex of UDP-galactose 4-epimerase from Escherichia coli: implications for the catalytic mechanism. Biochemistry 35:5137–5144
Thoden JB, Wohlers TM, Fridovich-Keil JL, Holden HM (2000) Crystallographic evidence for Tyr 157 functioning as the active site base in human UDP-galactose 4-epimerase. Biochemistry 39:5691–5701
van de Werken HJ, Brouns SJ, Van der Oost J (2008) Pentose metabolism in archaea. In: Blum P (ed) Archaea. New models for prokaryotic biology. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, pp 71–94
Wagner M, Andreesen JR (1995) Purification and characterization of threonine dehydrogenase from Clostridium sticklandii. Arch Microbiol 163:286–290
Wanner C, Soppa J (2002) Functional role for a 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase in the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii. J Bacteriol 184:3114–3121
Watanabe S, Kodak T, Makino K (2006) Cloning, expression, and characterization of bacterial l-arabinose 1-dehydrogenase involved in an alternative pathway of l-arabinose metabolism. J Biol Chem 281:2612–2623
Weissbach A, Hurwitz J (1959) The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem 234:705–709
Yoneda K, Sakuraba H, Muraoka I, Oikawa T, Ohshima T (2010) Crystal structure of UDP-galactose 4-epimerase-like l-threonine dehydrogenase belonging to the intermediate short-chain dehydrogenase-reductase superfamily. FEBS J 277:5124–5132
Yoneda K, Sakuraba H, Araki T, Ohshima T (2012) Crystal structure of binary and ternary complexes of archaeal UDP-galactose 4-epimerase-like l-threonine dehydrogenase from Thermoplasma volcanium. J Biol Chem 287:12966–12974
Zaigler A, Schuster SC, Soppa J (2003) Construction and usage of a onefold-coverage shotgun DNA microarray to characterize the metabolism of the archaeon Haloferax volcanii. Mol Microbiol 48:1089–1105
Acknowledgments
We thank Roland Schmid (Osnabrück, Germany) for performing N-terminal amino acid sequencing. Thanks are also due to Jörg Soppa (Frankfurt, Germany) for providing the plasmid pSD1 and for supporting to establish the method for 5′-end and 3′-end determination of transcripts in our lab. This work was supported by grants of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SCHO 316/11-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by L. Huang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnsen, U., Sutter, JM., Zaiß, H. et al. l-Arabinose degradation pathway in the haloarchaeon Haloferax volcanii involves a novel type of l-arabinose dehydrogenase. Extremophiles 17, 897–909 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0572-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-013-0572-2