Abstract
Objective
To determine whether MTNR1B rs4753426 and rs10830963 polymorphisms are correlated with AIS.
Summary of background
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is the most common form of spinal deformity, while its etiology remains uncertain. Melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) gene polymorphisms have been found to be significantly associated with AIS risk; however, some of these results are controversial.
Methods
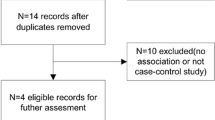
An systematic online search was performed using PubMed, EMBASE, Web of Science and the Cochrane Library to identify case–control studies investigating the relationship between MTNR1B rs4753426 and rs10830963 polymorphisms and the susceptibility of AIS. The pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95 % confidence interval (95 % CI) was calculated to assess the associations, and subgroup meta-analyses were performed according to the ethnicity of the study populations.
Results
A total of five studies involving 2395 cases and 3645 controls met the inclusion criteria after assessment by two reviewers. Overall, no significant associations were found between MTNR1B rs4753426 polymorphism and AIS risk (C vs. T: OR = 1.11, 95 % CI 0.94–1.30, P = 0.21; CC vs. TT: OR = 1.15, 95 % CI 0.97–1.36, P = 0.12; CT vs. TT: OR = 1.14, 95 % CI 0.97–1.35, P = 0.10; CC/CT vs. TT: OR = 1.14, 95 % CI 0.98–1.33, P = 0.09; CC vs. CT/TT: OR = 1.10, 95 % CI 0.84–1.45, P = 0.48), as well as the MTNR1B rs10830963 polymorphism (G vs. C: OR = 0.99, 95 % CI 0.88–1.12, P = 0.91; GG vs. CC: OR = 0.99, 95 % CI 0.74–1.33, P = 0.96; CG vs. CC: OR = 1.00, 95 % CI 0.84–1.18, P = 0.88; GG/CG vs. CC: OR = 0.99, 95 % CI 0.84–1.17, P = 0.93; GG vs. CG/CC: OR = 0.99, 95 % CI 0.75–1.30, P = 0.92). When stratified by ethnicity, there were no significant associations between MTNR1B rs4753426 and MTNR1B rs10830963 polymorphisms and AIS risk in either Asian or Caucasian populations.
Conclusion
MTNR1B rs4753426 and MTNR1B rs10830963 polymorphisms are not obviously associated with risk of AIS in either Asian populations or Caucasian populations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yagi M, Machida M, Asazuma T. Pathogenesis of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. JBJS Rev 2014;2(1)
Chen S, Zhao L, Roffey DM, Phan P, Wai EK. Association of rs11190870 near LBX1 with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in East Asians: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2014;14:2968–75.
Chan V, Fong GC, Luk KD, Yip B, Lee MK, Wong, Lu DD, Chan TK. A genetic locus for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis linked to chromosome 19p13. 3. Am J Hum Genet. 2002;71(2):401–6.
Miller NH, Justice CM, Marosy B, Swindle K, Kim Y, Roy-Gagnon MH, Sung H, Behneman D, Doheny KF, Pugh E, Wilson AF. Intra-familial tests of association between familial idiopathic scoliosis and linked regions on 9q31.3–q34.3 and 16p12.3-q22.2. Hum Hered. 2012;74(1):36–44.
Ji X, Yang Z, Yang X, Liu D, Ni H, Li M. Change of selenium in environment and risk of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a retrospective cohort study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(18):2499–503.
Zaina F, Donzelli S, Lusini M, Vismara L, Capodaglio P, Neri L, Negrini S. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and eating disorders: Is there a relation? Results of a cross-sectional study. Res Dev Disabil. 2013;34(4):1119–24.
Zhang Y, Gu Z, Qiu G. The Association study of calmodulin 1 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:168106.
Lao L-F, Shen J-X, Chen Z-G, Wang Y-P, Wen X-S, Qiu G-X. Uncoupled neuro-osseous growth in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? A preliminary study of 90 adolescents with whole-spine three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(7):1081–6.
Lu WW, Hu Y, Luk KD, Cheung KM, Leong JC. Paraspinal muscle activities of patients with scoliosis after spine fusion: an electromyographic study. Spine. 2002;27(11):1180–5.
Acaroglu E, Akel I, Alanay A, Yazici M, Marcucio R. Comparison of the melatonin and calmodulin in paravertebral muscle and platelets of patients with or without adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2009;34(18):E659–63.
Wise CA, Barnes R, Gillum J, Herring JA, Bowcock AM, Lovett M. Localization of susceptibility to familial idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2000;25(18):2372–80.
Salehi LB, Mangino M, De Serio S, De Cicco D, Capon F, Semprini S, Pizzuti A, Novelli G, Dallapiccola B. Assignment of a locus for autosomal dominant idiopathic scoliosis (IS) to human chromosome 17p11. Hum Genet. 2002;111(4–5):401–4.
Miller NH, Justice CM, Marosy B, Doheny KF, Pugh E, Zhang J, Dietz HC 3rd, Wilson AF. Identification of candidate regions for familial idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2005;30(10):1181–7.
Yang M, Li C, Li M. The estrogen receptor α gene (XbaI, PvuII) polymorphisms and susceptibility to idiopathic scoliosis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(5):713–21.
Takahashi Y, Kou I, Takahashi A, Johnson TA, Kono K, Kawakami N, Uno K, Ito M, Minami S, Yanagida H, Taneichi H, Tsuji T, Suzuki T, Sudo H, Kotani T, Watanabe K, Chiba K, Hosono N, Kamatani N, Tsunoda T, Toyama Y, Kubo M, Matsumoto M, Ikegawa S. A genome-wide association study identifies common variants near LBX1 associated with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Nat Genet. 2011;43:1237–40.
Ogura Y, Takahashi Y, Kou I, Nakajima M, Kono K, Kawakami N, Uno K, Ito M, Minami S, Yanagida H, Taneichi H, Yonezawa I, Tsuji T, Suzuki T, Sudo H, Kotani T, Watanabe K, Chiba K, Toyama Y, Matsumoto M, Ikegawa S. A replication study for association of 5 single nucleotide polymorphisms with curve progression of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Japanese patients. Spine. 2013;38(7):571–5.
Moreau A, Wang DS, Forget S, Azeddine B, Angeloni D, Fraschini F, Labelle H, Poitras B, Rivard CH, Grimard G. Melatonin signaling dysfunction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2004;29(16):1772–81.
Man GC, Wong JH, Wang WW, Sun GQ, Yeung BH, Ng TB, Lee SK, Ng BK, Qiu Y, Cheng JC. Abnormal melatonin receptor 1B expression in osteoblasts from girls with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Pineal Res. 2011;50(4):395–402.
Man GC, Wang WW, Yeung BH, Lee SK, Ng BK, Hung WY, Wong JH, Ng TB, Qiu Y, Cheng JC. Abnormal proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts from girls with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis to melatonin. J Pineal Res. 2010;49(1):69–77.
Qiu XS, Tang NL, Yeung HY, Lee KM, Hung VW, Ng BK, Ma SL, Kwok RH, Qin L, Qiu Y, Cheng JC. Melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) gene polymorphism is associated with the occurrence of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2007;32(16):1748–53.
Moon ES, Kim HS, Sharma V, Park JO, Lee HM, Moon SH, Chong HS. Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Korea: for personalized treatment. Yonsei Med J. 2013;54(2):500–9.
Mórocz M, Czibula A, Grózer ZB, Szécsényi A, Almos PZ, Raskó I, Illés T. Association study of BMP4, IL6, Leptin, MMP3, and MTNR1B gene promoter polymorphisms and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2011;36(2):E123–30.
Nelson LM, Ward K, Ogilvie JW. Genetic variants in melatonin synthesis and signaling pathway are not associated with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2011;36(1):37–40.
Takahashi Y, Matsumoto M, Karasugi T, Watanabe K, Chiba K, Kawakami N, Tsuji T, Uno K, Suzuki T, Ito M, Sudo H, Minami S, Kotani T, Kono K, Yanagida H, Taneichi H, Takahashi A, Toyama Y, Ikegawa S. Lack of association between adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and previously reported single nucleotide polymorphisms in MATN1, MTNR1B, TPH1, and IGF1 in a Japanese population. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(7):1055–8.
Bouatia-Naji N, Bonnefond A, Cavalcanti-Proença C, Sparsø T, Holmkvist J, Marchand M, Delplanque J, Lobbens S, Rocheleau G, Durand E, De Graeve F, Chèvre JC, Borch-Johnsen K, Hartikainen AL, Ruokonen A, Tichet J, Marre M, Weill J, Heude B, Tauber M, Lemaire K, Schuit F, Elliott P, Jørgensen T, Charpentier G, Hadjadj S, Cauchi S, Vaxillaire M, Sladek R, Visvikis-Siest S, Balkau B, Lévy-Marchal C, Pattou F, Meyre D, Blakemore AI, Jarvelin MR, Walley AJ, Hansen T, Dina C, Pedersen O, Froguel P. A variant near MTNR1B is associated with increased fasting plasma glucose levels and type 2 diabetes risk. Nat Genet. 2009;41(1):89–94.
Lai IC, Chen ML, Wang YC, Chen JY, Liao DL, Bai YM, Lin CC, Chen TT, Liou YJ. Analysis of genetic variations in the human melatonin receptor (MTNR1A, MTNR1B) genes and antipsychotics-induced tardive dyskinesia in schizophrenia. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2011;12(2):143–8.
de Jonghe A, de Rooij S, Tanck M, Sijbrands E, van Munster B. Polymorphisms in the melatonin receptor 1B gene and the risk of delirium. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2012;33(5):306–10.
Sparsø T, Bonnefond A, Andersson E, Bouatia-Naji N, Holmkvist J, Wegner L, Grarup N, Gjesing AP, Banasik K, Cavalcanti-Proença C, Marchand M, Vaxillaire M, Charpentier G, Jarvelin MR, Tichet J, Balkau B, Marre M, Lévy-Marchal C, Faerch K, Borch-Johnsen K, Jørgensen T, Madsbad S, Poulsen P, Vaag A, Dina C, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Froguel P. G-allele of Intronic rs10830963 in MTNR1B confers increased risk of impaired fasting glycemia and type 2 diabetes through an impaired glucose-stimulated insulin release studies involving 19,605 europeans. Diabetes. 2009;58(6):1450–6.
Vlassi M, Gazouli M, Paltoglou G, Christopoulos P, Florentin L, Kassi G, Mastorakos G. The rs10830963 variant of melatonin receptor MTNR1B is associated with increased risk for gestational diabetes mellitus in a Greek population. Hormones. 2012;11:70–6.
Li C, Shi Y, You L, Wang L, Chen Z-J. Association of rs10830963 and rs10830962 SNPs in the melatonin receptor (MTNR1B) gene among Han Chinese women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Mol Hum Reprod. 2011;17(3):193–8.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Yang, X. Wei and W. Yang contributed equally to this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, M., Wei, X., Yang, W. et al. The polymorphisms of melatonin receptor 1B gene (MTNR1B) (rs4753426 and rs10830963) and susceptibility to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Sci 20, 593–600 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-015-0725-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-015-0725-5