Abstract
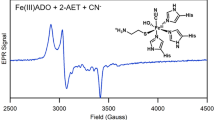
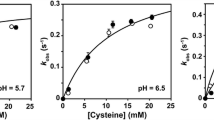
Sulfur metabolism has gained increasing medical interest over the last years. In particular, cysteine dioxygenase (CDO) has been recognized as a potential marker in oncology due to its altered gene expression in various cancer types. Human CDO is a non-heme iron-dependent enzyme, which catalyzes the irreversible oxidation of cysteine to cysteine sulfinic acid, which is further metabolized to taurine or pyruvate and sulfate. Several studies have reported a unique post-translational modification of human CDO consisting of a cross-link between cysteine 93 and tyrosine 157 (Cys-Tyr), which increases catalytic efficiency in a substrate-dependent manner. However, the reaction mechanism by which the Cys-Tyr cofactor increases catalytic efficiency remains unclear. In this study, steady-state kinetics were determined for wild type CDO and two different variants being either impaired or saturated with the Cys-Tyr cofactor. Cofactor formation in CDO resulted in an approximately fivefold increase in k cat and tenfold increase in k cat/K m over the cofactor-free CDO variant. Furthermore, iron titration experiments revealed an 18-fold decrease in K d of iron upon cross-link formation. This finding suggests a structural role of the Cys-Tyr cofactor in coordinating the ferrous iron in the active site of CDO in accordance with the previously postulated reaction mechanism of human CDO. Finally, we identified product-based inhibition and α-ketoglutarate and glutarate as CDO inhibitors using a simplified well plate-based activity assay. This assay can be used for high-throughput identification of additional inhibitors, which may contribute to understand the functional importance of CDO in sulfur amino acid metabolism and related diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CDO:
-
Cysteine dioxygenase
- Cys-Tyr cofactor:
-
Cysteine-tyrosine cofactor
- CSA:
-
Cysteine sulfinic acid
- GA:
-
Glutarate
- α-KG:
-
α-Ketoglutarate
References
Andine P, Orwar O, Jacobson I, Sandberg M, Hagberg H (1991) Extracellular acidic sulfur-containing amino acids and gamma-glutamyl peptides in global ischemia: postischemic recovery of neuronal activity is paralleled by a tetrodotoxin-sensitive increase in cysteine sulfinate in the CA1 of the rat hippocampus. J Neurochem 57:230–236
Belaidi AA, Arjune S, Santamaria-Araujo JA, Sass JO, Schwarz G (2012) Molybdenum cofactor deficiency: a new HPLC method for fast quantification of s-sulfocysteine in urine and serum. JIMD Rep 5:35–43. doi:10.1007/8904_2011_89
Bella DL, Hahn C, Stipanuk MH (1999a) Effects of nonsulfur and sulfur amino acids on the regulation of hepatic enzymes of cysteine metabolism. Am J Physiol 277:E144–E153
Bella DL, Hirschberger LL, Hosokawa Y, Stipanuk MH (1999b) Mechanisms involved in the regulation of key enzymes of cysteine metabolism in rat liver in vivo. Am J Physiol 276:E326–E335
Bradley H, Gough A, Sokhi RS, Hassell A, Waring R, Emery P (1994) Sulfate metabolism is abnormal in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Confirmation by in vivo biochemical findings. J Rheumatol 21:1192–1196
Brait M et al (2012) Cysteine dioxygenase 1 is a tumor suppressor gene silenced by promoter methylation in multiple human cancers. PLoS One 7:e44951. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044951
Chai SC, Jerkins AA, Banik JJ, Shalev I, Pinkham JL, Uden PC, Maroney MJ (2005) Heterologous expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant rat cysteine dioxygenase. J Biol Chem 280:9865–9869. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413733200
Chai SC, Bruyere JR, Maroney MJ (2006) Probes of the catalytic site of cysteine dioxygenase. J Biol Chem 281:15774–15779
Chung TK, Funk MA, Baker DH (1990) l-2-oxothiazolidine-4-carboxylate as a cysteine precursor: efficacy for growth and hepatic glutathione synthesis in chicks and rats. J Nutr 120:158–165
Cresenzi CL, Lee JI, Stipanuk MH (2003) Cysteine is the metabolic signal responsible for dietary regulation of hepatic cysteine dioxygenase and glutamate cysteine ligase in intact rats. J Nutr 133:2697–2702
Dominy JE Jr, Hirschberger LL, Coloso RM, Stipanuk MH (2006) Regulation of cysteine dioxygenase degradation is mediated by intracellular cysteine levels and the ubiquitin-26 S proteasome system in the living rat. Biochem J 394:267–273
Dominy JE Jr, Hwang J, Guo S, Hirschberger LL, Zhang S, Stipanuk MH (2008) Synthesis of amino acid cofactor in cysteine dioxygenase is regulated by substrate and represents a novel post-translational regulation of activity. J Biol Chem 283:12188–12201. doi:10.1074/jbc.M800044200
Dooley DM (1999) Structure and biogenesis of topaquinone and related cofactors. J Biol Inorg Chem 4:1–11
Emery P, Salmon M, Bradley H, Wordsworth P, Tunn E, Bacon PA, Waring R (1992) Genetically determined factors as predictors of radiological change in patients with early symmetrical arthritis. BMJ 305:1387–1389
Gordon C, Bradley H, Waring RH, Emery P (1992) Abnormal sulphur oxidation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 339:25–26 [pii]:0140-6736(92)90144-R
Heafield MT, Williams AC (1992) Parkinson’s disease: clinical and therapeutic aspects. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg 5:288–294
Heafield MT, Fearn S, Steventon GB, Waring RH, Williams AC, Sturman SG (1990) Plasma cysteine and sulphate levels in patients with motor neurone, Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 110:216–220 [pii]:0304-3940(90)90814-P
Imsand EM, Njeri CW, Ellis HR (2012) Addition of an external electron donor to in vitro assays of cysteine dioxygenase precludes the need for exogenous iron. Arch Biochem Biophys 521:10–17. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2012.03.006
Jahoor F, Jackson A, Gazzard B, Philips G, Sharpstone D, Frazer ME, Heird W (1999) Erythrocyte glutathione deficiency in symptom-free HIV infection is associated with decreased synthesis rate. Am J Physiol 276:E205–E211
Jeschke J et al (2013) Frequent inactivation of cysteine dioxygenase type 1 contributes to survival of breast cancer cells and resistance to anthracyclines. Clin Cancer Res 19:3201–3211. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3751
Lee JI, Londono M, Hirschberger LL, Stipanuk MH (2004) Regulation of cysteine dioxygenase and gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase is associated with hepatic cysteine level. J Nutr Biochem 15:112–122. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2003.10.005
Lehmann A, Hagberg H, Orwar O, Sandberg M (1993) Cysteine sulphinate and cysteate: mediators of cysteine toxicity in the neonatal rat brain? Eur J Neurosci 5:1398–1412
Li W, Blaesi EJ, Pecore MD, Crowell JK, Pierce BS (2013) Second-sphere interactions between the C93-Y157 cross-link and the substrate-bound Fe site influence the O(2) coupling efficiency in mouse cysteine dioxygenase. Biochemistry 52:9104–9119. doi:10.1021/bi4010232
Lyons J et al (2000) Blood glutathione synthesis rates in healthy adults receiving a sulfur amino acid-free diet. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5071–5076. doi:10.1073/pnas.090083297
McCoy JG, Bailey LJ, Bitto E, Bingman CA, Aceti DJ, Fox BG, Phillips GN Jr (2006) Structure and mechanism of mouse cysteine dioxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3084–3089
Montine TJ, Picklo MJ, Amarnath V, Whetsell WO Jr, Graham DG (1997) Neurotoxicity of endogenous cysteinylcatechols. Exp Neurol 148:26–33. doi:10.1006/exnr.1997.6662
Prabhu A et al (2014) Cysteine catabolism: a novel metabolic pathway contributing to glioblastoma growth. Cancer Res 74:787–796. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1423
Simmons CR, Hirschberger LL, Machi MS, Stipanuk MH (2006a) Expression, purification, and kinetic characterization of recombinant rat cysteine dioxygenase, a non-heme metalloenzyme necessary for regulation of cellular cysteine levels. Protein Expr Purif 47:74–81
Simmons CR, Liu Q, Huang Q, Hao Q, Begley TP, Karplus PA, Stipanuk MH (2006b) Crystal structure of mammalian cysteine dioxygenase. A novel mononuclear iron center for cysteine thiol oxidation. J Biol Chem 281:18723–18733
Stipanuk MH (1986) Metabolism of sulfur-containing amino acids. Annu Rev Nutr 6:179–209. doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.06.070186.001143
Stipanuk MH, Londono M, Lee JI, Hu M, Yu AF (2002) Enzymes and metabolites of cysteine metabolism in nonhepatic tissues of rats show little response to changes in dietary protein or sulfur amino acid levels. J Nutr 132:3369–3378
Stipanuk MH, Dominy JE, Ueki I, Hirschberger LL (2008) Measurement of cysteine dioxygenase activity and protein abundance. Curr Protoc Toxicol 38:6 15 11–16 15 25. doi:10.1002/0471140856.tx0615s38
Stipanuk MH, Ueki I, Dominy JE Jr, Simmons CR, Hirschberger LL (2009) Cysteine dioxygenase: a robust system for regulation of cellular cysteine levels. Amino Acids 37:55–63. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0202-y
Whittaker MM, Whittaker JW (2003) Cu(I)-dependent biogenesis of the galactose oxidase redox cofactor. J Biol Chem 278:22090–22101. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300112200
Wu G, Fang YZ, Yang S, Lupton JR, Turner ND (2004) Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J Nutr 134:489–492
Ye S, Wu X, Wei L, Tang D, Sun P, Bartlam M, Rao Z (2007) An insight into the mechanism of human cysteine dioxygenase. Key roles of the thioether-bonded tyrosine-cysteine cofactor. J Biol Chem 282:3391–3402
Acknowledgments
Technical assistance by Simona Jansen, Joana Stegemann and Monika Laurien (University of Cologne, Germany) is gratefully acknowledged. This work was supported by the Friedrich-Ebert-Foundation (to SA) and Center for Molecular Medicine Cologne (CMMC grant D05).
Conflict of interest
The authors do not declare a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arjune, S., Schwarz, G. & Belaidi, A.A. Involvement of the Cys-Tyr cofactor on iron binding in the active site of human cysteine dioxygenase. Amino Acids 47, 55–63 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1843-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1843-7