Abstract
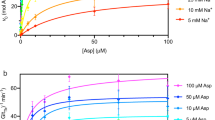
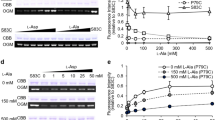
The kinetic mechanism of the transport catalyzed by the human glutamine/neutral amino acid transporter hASCT2 over-expressed in P. pastoris was determined in proteoliposomes by pseudo-bi-substrate kinetic analysis of the Na+-glutamineex/glutaminein transport reaction. A random simultaneous mechanism resulted from the experimental analysis. Purified functional hASCT2 was chemically cross-linked to a stable dimeric form. The oligomeric structure correlated well with the kinetic mechanism of transport. Half-saturation constants (Km) of the transporter for the other substrates Ala, Ser, Asn and Thr were measured both on the external and internal side. External Km were much lower than the internal ones confirming the asymmetry of the transporter. The electric nature of the transport reaction was determined imposing a negative inside membrane potential generated by K+ gradients in the presence of valinomycin. The transport reaction resulted to be electrogenic and the electrogenicity originated from external Na+. Internal Na+ exerted a stimulatory effect on the transport activity which could be explained by a regulatory, not a counter-transport, effect. Native and deglycosylated hASCT2 extracted from HeLa showed the same transport features demonstrating that the glycosyl moiety has no role in transport function. Both in vitro and in vivo interactions of hASCT2 with the scaffold protein PDZK1 were revealed.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C12E8 :
-
Octaethylene glycol monododecyl ether
- YPDS:
-
Yeast Extract Peptone Dextrose Sorbitol
- BMGY:
-
Buffered Glycerol-complex Medium
- DOC:
-
Na-deoxycholate
- NP-40:
-
Nonidet
- MeAIB:
-
Α-(methylamino)isobutyric acid
- BCH 2-aminobicyclo:
-
(2,2,1)-heptane-2-carboxylic acid
References
Adeva MM, Souto G, Blanco N, Donapetry C (2012) Ammonium metabolism in humans Metabolism 61:1495–1511 doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2012.07.007
Shimizu K et al (2014) ASC amino-acid transporter 2 (ASCT2) as a novel prognostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer. British J Cancer. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.88
Albers T, Marsiglia W, Thomas T, Gameiro A, Grewer C (2012) Defining substrate and blocker activity of alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2 (ASCT2) Ligands with Novel Serine Analogs. Mol Pharmacol 81:356–365. doi:10.1124/mol.111.075648
Avissar NE, Sax HC, Toia L (2008) In human entrocytes, GLN transport and ASCT2 surface expression induced by short-term EGF are MAPK, PI3 K, and Rho-dependent. Dig Dis Sci 53:2113–2125
Bode BP (2001) Recent molecular advances in mammalian glutamine transport. The Journal of nutrition 131:2475S–2485S (discussion 2486S-2477S)
Broer S (2011) Targeting tumour cells at the entrance. Biochem J 439:e1–e2. doi:10.1042/BJ20111484
Broer A, Brookes N, Ganapathy V, Dimmer KS, Wagner CA, Lang F, Broer S (1999) The astroglial ASCT2 amino acid transporter as a mediator of glutamine efflux. J Neurochem 73:2184–2194
Broer A, Wagner C, Lang F, Broer S (2000) Neutral amino acid transporter ASCT2 displays substrate-induced Na+ exchange and a substrate-gated anion conductance. Biochem J 346(Pt 3):705–710
Cleland WW (1970) The enzymes, kinetics and mechanism (vol II). Academic Press, London
Cynober LA (2002) Plasma amino acid levels with a note on membrane transport: characteristics, regulation, and metabolic significance. Nutrition 18:761–766
Dephoure N, Zhou C, Villen J, Beausoleil SA, Bakalarski CE, Elledge SJ, Gygi SP (2008) A quantitative atlas of mitotic phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:10762–10767. doi:10.1073/pnas.0805139105
Filippo CA, Ardon O, Longo N (2011) Glycosylation of the OCTN2 carnitine transporter: study of natural mutations identified in patients with primary carnitine deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:312–320. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.11.007
Fleysher L, Oesingmann N, Brown R, Sodickson DK, Wiggins GC, Inglese M (2013) Noninvasive quantification of intracellular sodium in human brain using ultrahigh-field MRI. NMR Biomed 26:9–19. doi:10.1002/nbm.2813
Flugge UI (1992) Reaction mechanism and asymmetric orientation of the reconstituted chloroplast phosphate translocator. Biochim Biophys Acta 1110:112–118
Fuchs BC, Bode BP (2005) Amino acid transporters ASCT2 and LAT1 in cancer: partners in crime? Semin Cancer Biol 15:254–266. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.04.005
Fuchs BC, Finger RE, Onan MC, Bode BP (2007) ASCT2 silencing regulates mammalian target-of-rapamycin growth and survival signaling in human hepatoma cells. Am J Cell Physiol 293:C55–C63. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00330.2006
Ganapathy V, Thangaraju M, Prasad PD (2009) Nutrient transporters in cancer: relevance to Warburg hypothesis and beyond. Pharmacol Ther 121:29–40. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.09.005
Giancaspero TA et al (2013) FAD synthesis and degradation in the nucleus create a local flavin cofactor pool. J Biol Chem 288:29069–29080. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.500066
Hu S et al (2009) Systematic analysis of a simple adaptor protein PDZK1: ligand identification, interaction and functional prediction of complex. Cell Physiol Biochem 24:231–242. doi:10.1159/000233258
Indiveri C, Dierks T, Kramer R, Palmieri F (1991) Reaction mechanism of the reconstituted oxoglutarate carrier from bovine heart mitochondria. Eur J Biochem 198:339–347
Indiveri C, Tonazzi A, De Palma A, Palmieri F (2001) Kinetic mechanism of antiports catalyzed by reconstituted ornithine/citrulline carrier from rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1503:303–313
Indiveri C, Galluccio M, Scalise M, Pochini L (2013) Strategies of bacterial over expression of membrane transporters relevant in human health: the successful case of the three members of OCTN subfamily. Mol Biotechnol 54:724–736. doi:10.1007/s12033-012-9586-8
Kato Y, Sai Y, Yoshida K, Watanabe C, Hirata T, Tsuji A (2005) PDZK1 directly regulates the function of organic cation/carnitine transporter OCTN2. Mol Pharmacol 67:734–743. doi:10.1124/mol.104.002212
Keller T, Schwarz D, Bernhard F, Dotsch V, Hunte C, Gorboulev V, Koepsell H (2008) Cell free expression and functional reconstitution of eukaryotic drug transporters. Biochemistry 47:4552–4564. doi:10.1021/bi800060w
Lee C et al (2013) A two-domain elevator mechanism for sodium/proton antiport. Nature 501:573–577. doi:10.1038/nature12484
Maddocks OD, Berkers CR, Mason SM, Zheng L, Blyth K, Gottlieb E, Vousden KH (2013) Serine starvation induces stress and p53-dependent metabolic remodelling in cancer cells. Nature 493:542–546. doi:10.1038/nature11743
Nicklin P et al (2009) Bidirectional transport of amino acids regulates mTOR and autophagy. Cell 136:521–534. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.044
Oppedisano F, Indiveri C (2008) Reconstitution into liposomes of the B degrees -like glutamine-neutral amino acid transporter from renal cell plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:2258–2265. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.05.01
Oppedisano F, Pochini L, Galluccio M, Cavarelli M, Indiveri C (2004) Reconstitution into liposomes of the glutamine/amino acid transporter from renal cell plasma membrane: functional characterization, kinetics and activation by nucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1667:122–131. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.09.007
Oppedisano F, Pochini L, Galluccio M, Indiveri C (2007) The glutamine/amino acid transporter (ASCT2) reconstituted in liposomes: transport mechanism, regulation by ATP and characterization of the glutamine/glutamate antiport. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:291–298. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.09.002
Oppedisano F, Galluccio M, Indiveri C (2010) Inactivation by Hg2 + and methylmercury of the glutamine/amino acid transporter (ASCT2) reconstituted in liposomes: prediction of the involvement of a CXXC motif by homology modelling. Biochem Pharmacol 80:1266–1273. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.032
Oppedisano F, Pochini L, Broer S, Indiveri C (2011) The B degrees AT1 amino acid transporter from rat kidney reconstituted in liposomes: kinetics and inactivation by methylmercury. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808:2551–2558. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.05.011
Oppedisano F et al (2012) Inactivation of the glutamine/amino acid transporter ASCT2 by 1,2,3-dithiazoles: proteoliposomes as a tool to gain insights in the molecular mechanism of action and of antitumor activity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 265:93–102. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2012.09.011
Palmieri F, Indiveri C, Bisaccia F, Iacobazzi V (1995) Mitochondrial metabolite carrier proteins: purification, reconstitution, and transport studies. Methods Enzymol 260:349–369
Pingitore P, Pochini L, Scalise M, Galluccio M, Hedfalk K, Indiveri C (2013) Large scale production of the active human ASCT2 (SLC1A5) transporter in Pichia pastoris–functional and kinetic asymmetry revealed in proteoliposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1828:2238–2246. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.05.034
Pochini L, Scalise M, Galluccio M, Indiveri C (2012) Regulation by physiological cations of acetylcholine transport mediated by human OCTN1 (SLC22A4). Implications in the non-neuronal cholinergic system. Life Sci 91:1013–1016. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2012.04.027
Pochini L, Scalise M, Galluccio M, Indiveri C (2013) OCTN cation transporters in health and disease: role as drug targets and assay development. J Biomol Screen 18:851–867. doi:10.1177/1087057113493006
Quick M, Wright EM (2002) Employing Escherichia coli to functionally express, purify, and characterize a human transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8597–8601. doi:10.1073/pnas.132266599
Scalise M, Pochini L, Giangregorio N, Tonazzi A, Indiveri C (2013) Proteoliposomes as tool for assaying membrane transporter functions and interactions with xenobiotics. Pharmaceutics 5:472–497. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics5030472
Stein WD (1989) Kinetics of transport: analyzing, testing, and characterizing models using kinetic approaches. Methods Enzymol 171:23–62
Sugiura T, Shimizu T, Kijima A, Minakata S, Kato Y (2011) PDZ adaptors: their regulation of epithelial transporters and involvement in human diseases. J Pharm Sci 100:3620–3635. doi:10.1002/jps.22575
Thingholm TE, Larsen MR, Ingrell CR, Kassem M, Jensen ON (2008) TiO(2)-based phosphoproteomic analysis of the plasma membrane and the effects of phosphatase inhibitor treatment. J Proteome Res 7:3304–3313. doi:10.1021/pr800099y
Tonikian R et al (2008) A specificity map for the PDZ domain family. PLoS Biol 6:e239. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060239
Torres-Zamorano V, Leibach FH, Ganapathy V (1998) Sodium-dependent homo- and hetero-exchange of neutral amino acids mediated by the amino acid transporter ATB degree. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 245:824–829
Utsunomiya-Tate N, Endou H, Kanai Y (1996) Cloning and functional characterization of a system ASC-like Na + -dependent neutral amino acid transporter. J Biol Chem 271:14883–14890
Vickers MF, Mani RS, Sundaram M, Hogue DL, Young JD, Baldwin SA, Cass CE (1999) Functional production and reconstitution of the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter (hENT1) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Interaction of inhibitors of nucleoside transport with recombinant hENT1 and a glycosylation-defective derivative (hENT1/N48Q). Biochem J 339(Pt 1):21–32
Yernool D, Boudker O, Jin Y, Gouaux E (2004) Structure of a glutamate transporter homologue from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Nature 431:811–818. doi:10.1038/nature03018
Zander CB, Albers T, Grewer C (2013) Voltage-dependent processes in the electroneutral amino acid exchanger ASCT2. J Gen Physiol 141:659–672. doi:10.1085/jgp.201210948
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funds from: Programma Operativo Nazionale [01_00937]-MIUR “Modelli sperimentali biotecnologici integrati per lo sviluppo e la selezione di molecole di interesse per la salute dell’uomo” to CI. The authors are grateful to Dr. Jean Jimenez for language revision.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scalise, M., Pochini, L., Panni, S. et al. Transport mechanism and regulatory properties of the human amino acid transporter ASCT2 (SLC1A5). Amino Acids 46, 2463–2475 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1808-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1808-x