Abstract
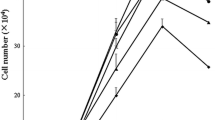
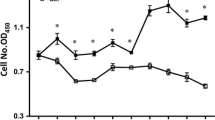
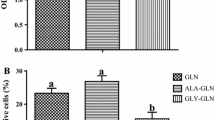
α-Ketoglutarate (AKG) is a key intermediate in glutamine metabolism. Emerging evidence shows beneficial effects of AKG on clinical and experimental nutrition, particularly with respect to intestinal growth and integrity. However, the underlying mechanisms are unknown. Intestinal porcine epithelial cells (IPEC-1) were used to test the hypothesis that AKG inhibits glutamine degradation and enhances protein synthesis. IPEC-1 cells were cultured for 3 days in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s-F12 Ham medium (DMEM-F12) containing 0, 0.2, 0.5 or 2 mM of AKG. At the end of the 3-day culture, cells were used to determine l-[U-14C]glutamine utilization, protein concentration, protein synthesis, and the total and phosphorylated levels of the mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR), ribosomal protein S6 kinase-1 (S6K1) and eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 4E-binding protein-1 (4E-BP1). Compared with 0 mM of AKG (control), 0.2 and 0.5 mM of AKG dose-dependently reduced (P < 0.05) glutamine degradation and the production of glutamate, alanine and aspartate in IPEC-1 cells. Addition of 0.5 and 2 mM of AKG to culture medium enhanced protein synthesis (P < 0.05) by 78 and 101% without affecting protein degradation, compared to the control group. Rapamycin (50 nM; a potent inhibitor of mTOR) attenuated the stimulatory effect of AKG on protein synthesis. Consistent with these metabolic data, the addition of 0.5 or 2 mM of AKG to culture medium increased (P < 0.05) the phosphorylated levels of mTOR, S6k1 and 4E-BP1 proteins. Collectively, these results indicate that AKG can spare glutamine and activate the mTOR signaling pathway to stimulate protein synthesis in intestinal epithelial cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKG:
-
α-Ketoglutarate
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DMEM-F12:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s F12 Ham medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- IPEC-1:
-
Intestinal porcine epithelial cells-1
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- 4E-BP1:
-
4E-Binding protein-1
- S6K1:
-
70-kDa Ribosomal protein S6 kinase-1
References
Bergen WG, Wu G (2009) Intestinal nitrogen recycling and utilization in health and disease. J Nutr 139:821–825
Blachier F, Boutry C, Bos C et al (2009) Metabolism and functions of l-glutamate in the epithelial cells of the small and large intestines. Am J Clin Nutr 90:814S–821S
Boutry C, Bos C, Matsumoto H et al (2011) Effects of monosodium glutamate supplementation on glutamine metabolism in rats. Front Biosci E3:279–290
Chen LX, Li P, Wang JJ et al (2009) Catabolism of nutritionally essential amino acids in developing porcine enterocytes. Amino Acids 37:143–152
Curthoys NP, Watford M (1995) Regulation of glutaminase activity and glutamine metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 15:133–159
Dai ZL, Zhang J, Wu G et al (2010) Utilization of amino acids by bacteria from the pig small intestine. Amino Acids 39:1201–1215
Dai ZL, Wu G, Zhu WY (2011) Amino acid metabolism in intestinal bacteria: links between gut ecology and host health. Front Biosci 16:1768–1786
Davis TA, Fiorotto ML, Burrin DG et al (2002) Stimulation of protein synthesis by both insulin and amino acids is unique to skeletal muscle in neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282:E880–E890
De Bandt JP, Coudray-Lucas C, Lioret N et al (1998) A randomized controlled trial of the influence of the mode of enteral ornithine α-ketoglutarate administration in burn patients. J Nutr 128:563–569
Dekaney CM, Wu G, Yin YL et al (2008) Regulation of ornithine aminotransferase gene expression and activity by all-trans retinoic acid in Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells. J Nutr Biochem 19:674–681
Duranton B, Schleiffer R, Gosse F et al (1998) Preventive administration of ornithine alpha-ketoglutarate improves intestinal mucosal repair after transient ischemia in rats. Crit Care Med 26:120–125
Flynn NE, Bird JG, Guthrie AS (2009) Glucocorticoid regulation of amino acid and polyamine metabolism in the small intestine. Amino Acids 37:123–129
Flynn NE, Patryak M, Seely J et al (2010) Glycine oxidation and conversion into amino acids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans. Amino Acids 39:605–608
Frank JW, Escobar J, Suryawan A et al (2006) Dietary protein and lactose increase translation initiation factor activation and tissue protein synthesis in neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E225–E233
Frank J, Escobar J, Nguyen HV et al (2007) Oral N-carbamylglutamate supplementation increases protein synthesis in skeletal muscle of piglets. J Nutr 137:315–319
Fu WJ, Stromberg AJ, Viele K (2010) Statistics and bioinformatics in nutritional sciences: analysis of complex data in the era of systems biology. J Nutr Biochem 21:561–572
Geng MM, Li TJ, Kong XF et al (2011) Reduced expression of intestinal N-acetylglutamate synthase in suckling piglets: a novel molecular mechanism for arginine as a nutritionally essential amino acid for neonates. Amino Acids 40:1513–1522
Haynes TE, Li P, Li XL et al (2009) l-Glutamine or l-alanyl-l-glutamine prevents oxidant- or endotoxin-induced death of neonatal enterocytes. Amino Acids 37:131–142
Hou YQ, Wang L, Ding BY et al (2010) Dietary α-ketoglutarate supplementation ameliorates intestinal injury in lipopolysaccharide-challenged piglets. Amino Acids 39:555–564
Hou YQ, Wang L, Ding BY et al (2011) Alpha-ketoglutarate and intestinal function. Front Biosci 16:1186–1196
Hu CA, Khalil S, Zhaorigetu S et al (2008) Human ∆1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase: function and regulation. Amino Acids 35:665–672
Hu Q, Hou Y, Ding B et al (2009) Effects of α-ketoglutarate on mucosal morphology and function of small intestine in piglets. J Anim Sci 87(E-Suppl 2):175 (Abstract)
Jobgen W, Fu WJ, Gao H et al (2009) High fat feeding and dietary l-arginine supplementation differentially regulate gene expression in rat white adipose tissue. Amino Acids 37:187–198
Junghans P, Dernoa M, Pierzynowski S et al (2006) Intraduodenal infusion of α-ketoglutarate decreases whole body energy expenditure in growing pigs. Clin Nutr 25:489–496
Kim JY, Song GH, Gao HJ et al (2008) Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) activates PI3K-AKT1 and MAPK cell signaling pathways and stimulates migration of ovine trophectoderm cells. Endocrinology 149:3085–3094
Ko TC, Beauchamp RD, Townsend CM Jr et al (1993) Glutamine is essential for epidermal growth factor-stimulated intestinal cell proliferation. Surgery 114:147–153
Kristensen NB, Jungvid H, Fernandez JA et al (2002) Absorption and metabolism of alpha-ketoglutarate in growing pigs. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 86:239–245
Lambert BD, Stoll B, Niinikoski H et al (2002) Net portal absorption of enterally fed a-ketoglutarate is limited in young pigs. J Nutr 132:3383–3386
Lambert BD, Filip R, Stoll B et al (2006) First-pass metabolism limits the intestinal absorption of enteral α-ketoglutarate in young pigs. J Nutr 136:2779–2784
Li P, Kim SW, Li XL et al (2008) Dietary supplementation with cholesterol and docosahexaenoic acid increases the activity of the arginine-nitric oxide pathway in tissues of young pigs. Nitric Oxide 19:259–265
Li XL, Bazer FW, Gao H et al (2009a) Amino acids and gaseous signaling. Amino Acids 37:65–78
Li P, Kim SW, Li XL et al (2009b) Dietary supplementation with cholesterol and docosahexaenoic acid affects concentrations of amino acids in tissues of young pigs. Amino Acids 37:709–716
Li XL, Rezaei R, Li P et al (2011) Composition of amino acids in feed ingredients for animal diets. Amino Acids 40:1159–1168
Odenlund M, Holmqvist B, Baldetorp B et al (2009) Polyamine synthesis inhibition induces S phase cell cycle arrest in vascular smooth muscle cells. Amino Acids 36:273–282
Palii SS, Kays CE, Deval C et al (2009) Specificity of amino acid regulated gene expression: analysis of gene subjected to either complete or single amino acid deprivation. Amino Acids 37:79–88
Papaconstantinou HT, Chung DH, Zhang W et al (2000) Prevention of mucosal atrophy: role of glutamine and caspases in apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. J Gastrointest Surg 4:416–423
Pierzynowski SG, Sjodin A (1998) Perspectives of glutamine and its derivatives as feed additives for farm animals. J Anim Feed Sci 7:79–91
Rhoads JM, Wu G (2009) Glutamine, arginine, and leucine signaling in the intestine. Amino Acids 37:111–122
Rhoads JM, Argenzio RA, Chen W et al (1997) l-Glutamine stimulates intestinal cell proliferation and activates mitogen-activated protein kinases. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 272:G943–G953
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sabatini DM (2005) Growing roles for the mTOR pathway. Curr Opin Cell Bio 17:596–603
Śliwa E (2006) Effect of simultaneous versus apart administration of dexamethasone and alpha-ketoglutarate on growth hormone cortisol and insulin-like growth factor-I in piglets. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 50:205–210
Stoll B, Burrin DG, Henry J et al (1999) Substrate oxidation by the portal drained viscera of fed piglets. Am J Physiol 277:E168–E175
Suryawan A, Davis TA (2011) Regulation of protein synthesis by amino acids in muscle of neonates. Front Biosci 16:1445–1460
Suryawan A, O’Connor PMJ, Bush JA et al (2009) Differential regulation of protein synthesis by amino acids and insulin in peripheral and visceral tissues of neonatal pigs. Amino Acids 37:97–110
Tan BE, Yin YL, Kong XF et al (2010) l-Arginine stimulates proliferation and prevents endotoxin-induced death of intestinal cells. Amino Acids 38:1227–1235
Wang JJ, Chen LX, Li P et al (2008) Gene expression is altered in piglet small intestine by weaning and dietary glutamine supplementation. J Nutr 138:1025–1032
Wang JJ, Wu G, Zhou HJ et al (2009a) Emerging technologies for amino acid nutrition research in the post-genome era. Amino Acids 37:177–186
Wang XQ, Ou DY, Yin JD et al (2009b) Proteomic analysis reveals altered expression of proteins related to glutathione metabolism and apoptosis in the small intestine of zinc oxide-supplemented piglets. Amino Acids 37:209–218
Wang XQ, Wu WZ, Lin G et al (2010) Temporal proteomic analysis reveals continuous impairment of intestinal development in neonatal piglets with intrauterine growth restriction. J Proteome Res 9:924–935
Wilson FA, Suryawan A, Orellana RA et al (2011) Differential effects of long-term leucine infusion on tissue protein synthesis in neonatal pigs. Amino Acids 40:157–165
Wu G (1995) Urea synthesis in enterocytes of developing pigs. Biochem J 312:717–723
Wu G (1997) Synthesis of citrulline and arginine from proline in enterocytes of postnatal pigs. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 272:G1382–G1390
Wu G (1998) Intestinal mucosal amino acid catabolism. J Nutr 128:1249–1252
Wu G (2009) Amino acids: metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids 37:1–17
Wu G (2010) Functional amino acids in growth, reproduction and health. Adv Nutr 1:31–37
Wu G, Flynn NE (1995) Regulation of glutamine and glucose metabolism by cell volume in lymphocytes and macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta 1243:343–350
Wu G, Knabe DA (1995) Arginine synthesis in enterocytes of neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 269:R621–R629
Wu G, Morris SM Jr (1998) Arginine metabolism: nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem J 336:1–17
Wu G, Thompson JR, Baracos VE (1991a) Glutamine metabolism in skeletal muscle from the broiler chick (Gallus domesticus) and the laboratory rat (Rattus norvegicus). Biochem J 274:769–774
Wu G, Field CJ, Marliss EB (1991b) Elevated glutamine metabolism in splenocytes from spontaneously diabetic BB rats. Biochem J 274:49–54
Wu G, Davis PK, Flynn NE et al (1997) Endogenous synthesis of arginine plays an important role in maintaining arginine homeostasis in postweaning growing pigs. J Nutr 127:2342–2349
Wu G, Knabe DA, Flynn NE (2005) Amino acid metabolism in the small intestine: biochemical bases and nutritional significance. In: Burrin DG, Mersmann HJ (eds) Biology of metabolism in growing animals. Elsevier Science, London, pp 107–126
Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA et al (2009) Arginine metabolism and nutrition in growth, health and disease. Amino Acids 37:153–168
Wu G, Bazer FW, Johnson GA et al (2011a) Important roles for l-glutamine in swine nutrition and production. J Anim Sci 89:2017–2030
Wu G, Bazer FW, Burghardt RC et al (2011b) Proline and hydroxyproline metabolism: implications for animal and human nutrition. Amino Acids 40:1053–1063
Xi PB, Jiang ZY, Zheng CT et al (2011) Regulation of protein metabolism by glutamine: implications for nutrition and health. Front Biosci 16:578–597
Yao K, Yin Y, Chu W et al (2008) Dietary arginine supplementation increases motor signaling activity in skeletal muscle of neonatal pigs. J Nutr 138:867–872
Yin YL, Yao K, Liu ZJ et al (2010a) Supplementing l-leucine to a low-protein diet increases tissue protein synthesis in weanling pigs. Amino Acids 39:1477–1486
Yin YL, Huang RL, Li TJ et al (2010b) Amino acid metabolism in the portal-drained viscera of young pigs: effects of dietary supplementation with chitosan and pea hull. Amino Acids 39:1581–1587
Acknowledgments
This research was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30901041, 30901040, 30928018, 30972156, 30871801, 30828024, 30828025, 30771558 and 30700581), National 863 Project (2008AA10Z316), National Basic Research Project (2009CB118800), the CAS/SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams, the Program for Innovative Research Groups of Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2007ABC009), Texas AgriLife Research, American Heart Association (10GRNT4480020) and the Thousand-People-Talent program at the China Agricultural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, K., Yin, Y., Li, X. et al. Alpha-ketoglutarate inhibits glutamine degradation and enhances protein synthesis in intestinal porcine epithelial cells. Amino Acids 42, 2491–2500 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1060-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1060-6