Abstract
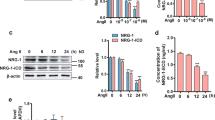
Apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) plays an important role in regulating vascular remodeling during cardiovascular diseases. Apelin is the endogenous ligand for the G-protein-coupled receptor APJ and plays an important role in the cardiovascular system. However, the mechanisms of apelin on apoptosis of VSMCs have not been elucidated. Using a culture of human VSMCs as a model for the study of apoptosis, the relationship between apelin and apoptosis of human VSMCs and the signal pathway involved were investigated. Using western blotting, we confirmed that VSMCs could express APJ. To evaluate the possible role of apelin in VSMC apoptosis, we assessed its effect on apoptosis of human VSMCs. The results showed that apelin inhibited human VSMCs apoptosis induced by serum deprivation. Suppression of APJ with small-interfering RNA (siRNA) abolished the anti-apoptotic activity of apelin. Apelin increased Bcl-2 protein expression, but decreased Bax protein expression. An increase in activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) and Akt (a downstream effector of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase) was shown after apelin stimulation. Suppression of APJ with siRNA abolished the apelin-induced activation of ERK and Akt. LY294002 (a PI3-K inhibitor) blocked apelin-induced activation of Akt and abolished the apelin-induced antiapoptotic activity. Our study suggests that apelin suppresses serum deprivation-induced apoptosis of human VSMCs, and that the anti-apoptotic action is mediated through the APJ/PI3-K/Akt signaling pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackah E, Yu J, Zoellner S, Iwakiri Y, Skurk C, Shibata R, Ouchi N, Easton RM, Galasso G, Birnbaum MJ, Walsh K, Sessa WC (2005) Akt1/protein kinase Balpha is critical for ischemic and VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. J Clin Invest 115:2119–2127
Bauriedel G, Hutter R, Welsch U, Bach R, Sievert H, Lüderitz B (1999) Role of smooth muscle cell death in advanced coronary primary lesions: implications for plaque instability. Cardiovasc Res 41:480–488
Boucher J, Masri B, Daviaud D, Gesta S, Guigné C, Mazzucotelli A, Castan-Laurell I, Tack I, Knibiehler B, Carpéné C, Audigier Y, Saulnier-Blache JS, Valet P (2005) Apelin, a newly identified adipokine up-regulated by insulin and obesity. Endocrinology 146:1764–1771
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296:1655–1657
Clarke MC, Littlewood TD, Figg N, Maguire JJ, Davenport AP, Goddard M, Bennett MR (2008) Chronic apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells accelerates atherosclerosis and promotes calcification and medial degeneration. Circ Res 102:1529–1538
Cox CM, D’Agostino SL, Miller MK, Heimark RL, Krieg PA (2006) Apelin, the ligand for the endothelial G-protein-coupled receptor, APJ, is a potent angiogenic factor required for normal vascular development of the frog embryo. Dev Biol 296:177–189
De Falco M, De Luca L, Onori N, Cavallotti I, Artigiano F, Esposito V, De Luca B, Laforgia V, Groeger AM, De Luca A (2002) Apelin expression in normal human tissues. In Vivo 16:333–336
De Mota N, Reaux-Le Goazigo A, El Messari S, Chartrel N, Roesch D, Dujardin C, Kordon C, Vaudry H, Moos F, Llorens-Cortes C (2004) Apelin, a potent diuretic neuropeptide counteracting vasopressin actions through inhibition of vasopressin neuron activity and vasopressin release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10464–10469
Degterev A, Boyce M, Yuan J (2003) A decade of caspases. Oncogene 22:8543–8567
Edinger AL, Hoffman TL, Sharron M, Lee B, Yi Y, Choe W, Kolson DL, Mitrovic B, Zhou Y, Faulds D, Collman RG, Hesselgesser J, Horuk R, Doms RW (1998) An orphan seven-transmembrane domain receptor expressed widely in the brain functions as a coreceptor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol 72:7934–7940
Eyries M, Siegfried G, Ciumas M, Montagne K, Agrapart M, Lebrin F, Soubrier F (2008) Hypoxia-induced apelin expression regulates endothelial cell proliferation and regenerative angiogenesis. Circ Res 103:432–440
Farkasfalvi K, Stagg MA, Coppen SR, Siedlecka U, Lee J, Soppa GK, Marczin N, Szokodi I, Yacoub MH, Terracciano CM (2007) Direct effects of apelin on cardiomyocyte contractility and electrophysiology. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:889–895
Fernández-Hernando C, József L, Jenkins D, Di Lorenzo A, Sessa WC (2009) Absence of Akt1 reduces vascular smooth muscle cell migration and survival and induces features of plaque vulnerability and cardiacd ysfunction during atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:2033–2040
Fredriksson R, Lagerstrom MC, Lundin LG, Schioth HB (2003) The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol 63:1256–1272
Habata Y, Fujii R, Hosoya M, Fukusumi S, Kawamata Y, Hinuma S, Kitada C, Nishizawa N, Murosaki S, Kurokawa T, Onda H, Tatemoto K, Fujino M (1999) Apelin, the natural ligand of the orphan receptor APJ, is abundantly secreted in the colostrum. Biochim Biophys Acta 1452:25–35
Henderson EL, Geng YJ, Sukhova GK, Whittemore AD, Knox J, Libby P (1999) Death of smooth muscle cells and expression of mediators of apoptosis by T lymphocytes in human abdominal aortic aneurysms. Circulation 99:96–104
Horn F, Weare J, Beukers MW, Horsch S, Bairoch A, Chen W, Edvardsen O, Campagne F, Vriend G (1998) GPCRDB: an information system for G protein-coupled receptors. Nucleic Acids Res 26:275–279
Hosoya M, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S (2000) Molecular and functional characteristics of APJ: tissue distribution of mRNA and interaction with the endogenous ligand apelin. J Biol Chem 275:21061–21067
Ishida J, Hashimoto T, Hashimoto Y, Nishiwaki S, Iguchi T, Harada S, Sugaya T, Matsuzaki H, Yamamoto R, Shiota N, Okunishi H, Kihara M, Umemura S, Sugiyama F, Yagami K, Kasuya Y, Mochizuki N, Fukamizu A (2004) Regulatory roles for APJ, a seven-transmembrane receptor related to angiotensin-type 1 receptor in blood pressure in vivo. J Biol Chem 279:26274–26279
Isner JM, Kearney M, Bortman S, Passeri J (1995) Apoptosis in human atherosclerosis and restenosis. Circulation 91:2703–2711
Jaszberenyi M, Bujdoso E, Telegdy G (2004) Behavioral, neuroendocrine and thermoregulatory actions of apelin-13. Neuroscience 129:811–816
Kasai A, Shintani N, Oda M, Kakuda M, Hashimoto H, Matsuda T, Hinuma S, Baba A (2004) Apelin is a novel angiogenic factor in retinal endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 325:395–400
Kawamata Y, Habata Y, Fukusumi S, Hosoya M, Fujii R, Hinuma S, Nishizawa N, Kitada C, Onda H, Nishimura O, Fujino M (2001) Molecular properties of apelin: tissue distribution and receptor binding. Biochim Biophys Acta 1538:162–171
Kidoya H, Ueno M, Yamada Y, Mochizuki N, Nakata M, Yano T, Fujii R, Takakura N (2008) Spatial and temporal role of the apelin/APJ system in the caliber size regulation of blood vessels during angiogenesis. EMBO J 27:522–534
Kleinz MJ, Davenport AP (2004) Immunocytochemical localization of the endogenous vasoactive peptide apelin to human vascular and endocardial endothelial cells. Regul Pept 118:119–125
Korsmeyer SJ, Shutter JR, Veis DJ, Merry DE, Oltvai ZN (1993) Bcl-2/bax: a rheostat that regulates an anti-oxidant pathway and cell death. Semin Cancer Biol 4:327–332
Leeper NJ, Tedesco MM, Kojima Y, Schultz GM, Kundu RK, Ashley EA, Tsao PS, Dalman RL, Quertermous T (2009) Apelin prevents aortic aneurysm formation by inhibiting macrophage inflammation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 296:H1329–H1335
Li F, Li L, Qin X, Pan W, Feng F, Chen F, Zhu B, Liao D, Tanowitz H, Albanese C, Chen L (2008) Apelin-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation: the regulation of cyclin D1. Front Biosci 13:3786–3792
Losano G, Penna C, Cappello S, Pagliaro P (2005) Activity of apelin and APJ receptors on myocardial contractility and vasomotor tone. Ital Heart J Suppl 6:272–278
Masri B, Lahlou H, Mazarguil H, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y (2002) Apelin (65–77) activates extracellular signal-regulated kinases via a PTX-sensitive G protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:539–545
Masri B, Morin N, Cornu M, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y (2004) Apelin (65–77) activates p70 S6 kinase and is mitogenic for umbilical endothelial cells. FASEB J 18:1909–1911
O’Dowd BF, Heiber M, Chan A, Heng HH, Tsui LC, Kennedy JL, Shi X, Petronis A, George SR, Nguyen T (1993) A human gene that shows identity with the gene encoding the angiotensin receptor is located on chromosome 11. Gene 136:355–360
Okura T, Watanabe S, Jiang Y, Nakamura M, Takata Y, Yang ZH, Kohara K, Kitami Y, Hiwada K (2002) Soluble Fas ligand and atherosclerosis in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 20:895–898
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, bax, that accelerates programed cell death. Cell 74:609–619
Reaux A, de Mota N, Skultetyova I, Lenkei Z, El Messari S, Gallatz K, Corvol P, Palkovits M, Llorens-Cortès C (2001) Phisiological role of a novel neuropeptide, apelin, and its receptor in the rat brain. J Neurochem 77:1085–1096
Shiojima I, Sato K, Izumiya Y, Schiekofer S, Ito M, Liao R, Colucci WS, Walsh K (2005) Disruption of coordinated cardiac hypertrophy and angiogenesis contributes to the transition to heart failure. J Clin Invest 115:2108–2118
Somanath PR, Razorenova OV, Chen J, Byzova TV (2006) Akt1 in endothelial cell and angiogenesis. Cell Cycle 5:512–518
SorhedeWinzell M, Magnusson C, Ahren B (2005) The APJ receptor is expressed in pancreatic islets and its ligand, apelin, inhibits insulin secretion in mice. Regul Pept 131:12–17
Sunter D, Hewson AK, Dickson SL (2003) Intracerebroventricular injection of apelin-13 reduces food intake in the rat. Neurosci Lett 353:1–4
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R, Kakegawa T, Zou MX, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Hinuma S, Kitada C, Kurokawa T, Onda H, Fujino M (1998) Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251:471–476
Wang G, Anini Y, Wei W, Qi X, OCarroll AM, Mochizuki T, Wang HQ, Hellmich MR, Englander EW, Greeley GH Jr (2004) Apelin, a newenteric peptide: localization in the gastrointestinal tract, ontogeny, and stimulation of gastric cell proliferation and of cholecystokinin secretion. Endocrinology 145:1342–1348
Wei L, Hou X, Tatemoto K (2005) Regulation of apelin mRNA expression by insulin and glucocorticoids in mouse 3T3–L1 adipocytes. Regul Pept 132:27–32
Whiteman EL, Cho H, Birnbaum MJ (2002) Role of Akt/protein kinase B in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13:444–451
Xie H, Tang SY, Cui RR, Huang J, Ren XH, Yuan LQ, Lu Y, Yang M, Zhou HD, Wu XP, Luo XH, Liao EY (2006) Apelin and its receptor are expressed in human osteoblasts. Regul Pept 134:118–125
Yuan LQ, Liu YS, Luo XH, Guo LJ, Xie H, Lu Y, Wu XP, Liao EY (2007) Recombinant tissue metalloproteinase inhibitor-3 protein induces apoptosis of murine osteoblast MC3T3–E1. Amino Acids 35:123–127
Yuan LQ, Liu W, Cui RR, Wang D, Meng JC, Xie H, Wu XP, Zhou HD, Lu Y, Liao EY (2009) Taurine inhibits osteoclastogenesis through the taurine transporter. Amino Acids [Epub ahead of print]
Zeng XJ, Zhang LK, Wang HX, Lu LQ, Ma LQ, Tang CS (2009) Apelin protects heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat. Peptides 30:1144–1152
Zou MX, Liu HY, Haraguchi Y, Soda Y, Tatemoto K, Hoshino H (2000) Apelin peptides block the entry of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). FEBS Lett 473(1):15–18
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funding from The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30801174 and 30900622), the Ph. D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No.200805331017), and clinic medicine special research fund-endocrinology disease research fund (10020040226).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Rong-Rong Cui, Ding-An Mao and Lu Yi contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, RR., Mao, DA., Yi, L. et al. Apelin suppresses apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells via APJ/PI3-K/Akt signaling pathways. Amino Acids 39, 1193–1200 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0555-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0555-x