Summary.
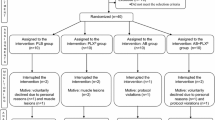
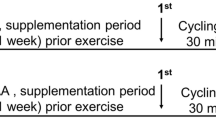
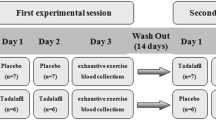
To evaluate the protective effects of taurine supplementation on exercise-induced oxidative stress and exercise performance, eleven men aged 18–20 years were selected to participate in two identical bicycle ergometer exercises until exhaustion. Single cell gel assay (SCG assay) was used to study DNA damage in white blood cells (WBC). Pre-supplementation of taurine, a significant negative correlation was found between plasma taurine concentration before exercise and plasma thiobaribituric-acid reactive substance (TBARS) 6 hr after exercise (r=−0.642, p<0.05). WBC showed a significant increase in DNA strand breakage 6 hr and 24 hr after exercise. Seven-day taurine supplementation reduced serum TBARS before exercise (p<0.05) and resulted in a significantly reduced DNA migration 24 hr after exercise (p<0.01). Significant increases were also found in VO2max, exercise time to exhaustion and maximal workload in test with taurine supplementation (p<0.05). After supplementation, the change in taurine concentration showed positive correlations with the changes in exercise time to exhaustion and maximal workload. The results suggest that taurine may attenuate exercise-induced DNA damage and enhance the capacity of exercise due to its cellular protective properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Izumi, I., Kagamimori, S. et al. Role of taurine supplementation to prevent exercise-induced oxidative stress in healthy young men. Amino Acids 26, 203–207 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-003-0002-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-003-0002-3