Abstract
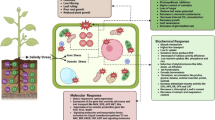
Nitric oxide (NO) and glutathione (GSH) regulate a variety of physiological processes and stress responses; however, their involvement in mitigating Cu toxicity in plants has not been extensively studied. This study investigated the interactive effect of exogenous sodium nitroprusside (SNP) and GSH on Cu homeostasis and Cu-induced oxidative damage in rice seedlings. Hydroponically grown 12-day-old seedlings were subjected to 100 μM CuSO4 alone and in combination with 200 μM SNP (an NO donor) and 200 μM GSH. Cu exposure for 48 h resulted in toxicity symptoms such as stunted growth, chlorosis, and rolling in leaves. Cu toxicity was also manifested by a sharp increase in lipoxygenase (LOX) activity, lipid peroxidation (MDA), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), proline (Pro) content, and rapid reductions in biomass, chlorophyll (Chl), and relative water content (RWC). Cu-caused oxidative stress was evident by overaccumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS; superoxide (O2 •–) and H2O2). Ascorbate (AsA) content decreased while GSH and phytochelatin (PC) content increased significantly in Cu-stressed seedlings. Exogenous SNP, GSH, or SNP + GSH decreased toxicity symptoms and diminished a Cu-induced increase in LOX activity, O2 •–, H2O2, MDA, and Pro content. They also counteracted a Cu-induced increase in superoxide dismutase (SOD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), glutathione reductase (GR), monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDHAR), and glyoxalase I and glyoxalase II activities, which paralleled changes in ROS and MDA levels. These seedlings also showed a significant increase in catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR), glutathione S-transferase (GST) activities, and AsA and PC content compared with the seedlings stressed with Cu alone. Cu analysis revealed that SNP and GSH restricted the accumulation of Cu in the roots and leaves of Cu-stressed seedlings. Our results suggest that Cu exposure provoked an oxidative burden while reduced Cu uptake and modulating the antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems by adding SNP and GSH play an important role in alleviating Cu toxicity. Furthermore, the protective action of GSH and SNP + GSH was more efficient than SNP alone.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anjum NA, Ahmad I, Mohmood I, Pacheco M, Duarte AC, Pereira E, Umar S, Ahmad A, Khan NA, Iqbal M, Prasad MNV (2012) Modulation of glutathione and its related enzymes in plants’ responses to toxic metals and metalloids — a review. Environ Exp Bot 75:307–324
Arnon DT (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated Chloroplast polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Beligni MV, Lamattina L (2002) Nitric oxide interferes with plant photooxidative stress by detoxifying reactive oxygen species. Plant Cell Environ 25:737–748
Bhuiyan MAH, Islam MA, Dampare SB, Parvez L, Suzuki S (2010) Evaluation of hazardous metal pollution in irrigation and drinking water systems in the vicinity of a coal mine area of northwestern Bangladesh. J Hazard Mater 179:1065–1077
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Burkhead JL, Reynolds KAG, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM, Pilon M (2009) Copper homeostasis. New Phytol 182:799–816
Cai Y, Cao F, Cheng W, Zhang G, Wu F (2010) Modulation of exogenous glutathione in phytochelatins and photosynthetic performance against Cd stress in the two rice genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:1159–1173
Chen CT, Chen TH, Lo KF, Chiu CY (2004) Effects of proline on copper transport in rice seedlings under excess copper stress. Plant Sci 166:103–111
Chen F, Wang F, Wu FB, Mao WH, Zhang GP, Zhou M (2010a) Modulation of exogenous GSH on antioxidant defense system against Cd stress in two barley genotypes differing in Cd tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:663–672
Chen WW, Yang JL, Qin C, Jin CW, Mo JH, Ye T, Zheng SJ (2010b) Nitric oxide acts downstream of auxin to trigger root ferric-chelate reductase activity in response to iron deficiency in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 154:810–819
Chino M (1981) Metal stress in rice plants. In: Kitagishi K, Yamane I (eds) Heavy metal pollution in soils of Japan. Japan Scientific Societies Press, Tokyo, pp 65–80
Choudhary SP, Oral HV, Bhardwaj R, Yu JQ, Tran LSP (2012) Interaction of brassinosteroids and polyamines enhances copper stress tolerance in Raphanus sativus. J Exp Bot 63:5659–5675
Cobbett CS, Goldsbrough P (2002) Phytochelatins and metallothioneins: roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:159–182
Contreras L, Mella D, Moenne A, Correa JA (2009) Differential responses to copper-induced oxidative stress in the marine macroalgae Lessonia nigrescens and Scytosiphon lomentaria (Phaeophyceae). Aquat Toxicol 94:94–102
De Vos RCH, Vonk MJ, Vooijs R, Schat H (1992) Glutathione depletion due to copper-induced phytochelatin synthesis causes oxidative stress in Silene cucubalus. Plant Physiol 98l:853–858
Demirevska-Kepova K, Simova-Stoilova L, Stoyanova Z, Hölzer R, Feller U (2004) Biochemical changes in barley plants after excessive supply of copper and manganese. Environ Exp Bot 52:253–266
Doderer A, Kokkelink I, van der Veen S, Valk B, Schram A, Douma A (1992) Purification and characterization of two lipoxygenase isoenzymes from germinating barley. Biochim Biophys Acta 112:97–104
Dutilleul C, Driscoll S, Cornic G, De Paepe R, Foyer CH, Noctor G (2003) Functional mitochondrial complex I is required by tobacco leaves for optimal photosynthetic performance in photorespiratory conditions and during transients. Plant Physiol 131:264–275
El-Shabrawi H, Kumar B, Kaul T, Reddy MK, Singla-Pareek SL, Sopory SK (2010) Redox homeostasis, antioxidant defense, and methylglyoxal detoxification as markers for salt tolerance in Pokkali rice. Protoplasma 245:85–96
Elia AC, Galarini R, Taticchi MI, Dorr AJM, Mantilacci L (2003) Antioxidant responses and bioaccumulation in Ictalurus melas under mercury exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 55:162–167
Foyer CH, Halliwell B (1976) The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: a proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism. Planta 133:21–25
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Graziano M, Lamattina L (2007) Nitric oxide accumulation is required for molecular and physiological responses to iron deficiency in tomato roots. Plant J 52:949–960
Griffiths OW (1980) Determination of glutathione and glutathione disulphide using glutathione reductase and 2-vinylpyridine. Anal Biochem 106:207–212
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. Kinetics and stochiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Hoque TS et al (2012) Methylglyoxal-induced stomatal closure accompanied by peroxidase-mediated ROS production in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 169:979–986
Hossain MA, Hasanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2010) Up-regulation of antioxidant and glyoxalase systems by exogenous glycinebetaine and proline in mung bean confer tolerance to cadmium stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plant 26:259–272
Hossain MA, Hossain MZ, Fujita M (2009) Stress induced changes of methylglyoxal level and Glyoxalase I activity in pumpkin seedlings and cDNA cloning of glyoxalase I gene. Aust J Crop Sci 3:53–64
Hossain MA, Mostofa MG, Fujita M (2013a) Cross protection by cold-shock to salinity and drought stress-induced oxidative stress in mustard (Brassica campestris L.) seedlings. Mol Plant Breed 4:50–70
Hossain MA, Mostofa MG, Fujita M (2013b) Heat-shock positively modulates oxidative protection of salt and drought-stressed mustard (Brassica campestris L.) seedlings. J Plant Sci Mol Breed 2:1–14
Hossain MA, Nakano Y, Asada K (1984) Monodehydroascorbate reductase in spinach chloroplasts and its participation in the regeneration of ascorbate for scavenging hydrogen peroxide. Plant Cell Physiol 25:385–395
Hossain MA, Piyatida P, da Silva JAT, Fujita M (2012) Molecular mechanism of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance in plants: central role of glutathione in detoxification of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal and in heavy metal chelation. J Bot 2012:1–37
Jones JB (1998) The micronutrients. In: Jones JB Jr (ed) Plant nutrition manual. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 55–76
Jozefczak M, Remans T, Vangronsveld J, Cuypers A (2012) Glutathione is a key player in metal-induced oxidative stress defenses. Int J Mol Sci 13:3145–3175
Kang YJ, Enger MD (1987) Effect of cellular glutathione depletion on cadmium induced cytotoxicity in human lung carcinoma cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 3:347–360
Kazemi N, Khavari-Nejad RA, Fahimi H, Saadatmand S, Nejad-Sattari T (2010) Effects of exogenous salicylic acid and nitric oxide on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities in leaves of Brassica napus L. under nickel stress. Sci Hortic 126:402–407
Kholodova V, Volkov K, Abdeyeva A, Kuznetsov V (2011) Water status in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum under heavy metal stress. Environ Exp Bot 71:382–389
Laspina NV, Groppa MD, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2005) Nitric oxide protects sunflower leaves against Cd-induced oxidative stress. Plant Sci 169:323–330
Li Y, Song YP, Shi GJ, Wang JJ, Hou XL (2009) Response of antioxidant activity to excess copper in two cultivars of Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis Makino. Acta Physiol Plant 31:55–162
Lippard SJ, Berg JM (1994) Principles of bioinorganic chemistry. University Science Books, Mill Valley
Marschner P (2012) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press, Elsevier, London
Metwally A, Finkemeier I, Georgi M, Dietz KJ (2003) Salicylic acid alleviates the cadmium toxicity in barley seedlings. Plant Physiol 132:272–281
Mishra A, Choudhuri MA (1999) Effects of salicylic acid on heavy metal-induced membrane deterioration mediated by lipoxygenase in rice. Biol Plant 42:409–415
Mostofa MG, Fujita M (2013) Salicylic acid alleviates copper toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by up-regulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems. Ecotoxicology 22:959–973
Mostofa MG, Yoshida N, Fujita M (2013) Spermidine pretreatment enhances heat tolerance in rice seedlings through modulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems. Plant Growth Regul. doi:10.1007/s10725-013-9865-9
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Noctor G, Gomez L, Vanacker H, Foyer CH (2002) Interactions between biosynthesis, compartmentation, and transport in the control of glutathione homeostasis and signaling. J Exp Bot 53:1283–1304
Panda P, Nath S, Chanu TT, Sharma GD, Panda SK (2011) Cadmium stress-induced oxidative stress and role of nitric oxide in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Physiol Plant 33:1737–1747
Saito R, Yamamoto H, Makino A, Sugimoto T, Miyake C (2011) Methylglyoxal functions as Hill oxidant and stimulates the photoreduction of O2 at photosystem I: a symptom of plant diabetes. Plant Cell Environ 34:1454–1464
Siddiqui MH, Al-Whaibi MH, Basalah MO (2011) Role of nitric oxide in tolerance of plants to abiotic stress. Protoplasma 248:447–455
Singh HP, Batish DR, Kaur G, Arora K, Kohli RK (2008) Nitric oxide (as sodium nitroprusside) supplementation ameliorates Cd toxicity in hydroponically grown wheat roots. Environ Exp Bot 63:158–167
Singh HP, Kaur S, Batish DR, Sharma VP, Sharma N, Kohli RK (2009) Nitric oxide alleviates arsenic toxicity by reducing oxidative damage in the roots of Oryza sativa (rice). Nitric Oxide 20:289–297
Singh VP, Srivastava PK, Prasad SM (2013) Nitric oxide alleviates arsenic-induced toxic effects in ridged Luffa seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 71:155–163
Singla-Pareek SL, Yadav SK, Pareek A, Reddy MK, Sopory SK (2006) Transgenic tobacco overexpressing Glyoxalase pathway enzymes grow and set viable seeds in zinc-spiked soils. Plant Physiol 140:613–623
Sun B, Jing Y, Chen K, Song L, Chen F, Zhang L (2007) Protective effect of nitric oxide on iron deficiency induced oxidative stress in maize (Zea mays). J Plant Physiol 164:536–543
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Mazumdar P, Kumar D, Sharma GD, Sahoo L, Panda SK (2012) Excess copper induced oxidative stress and responses of antioxidants in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 53:33–39
Thounaojam TC, Panda P, Choudhury S, Patra HK, Panda SK (2013) Zinc ameliorates copper-induced oxidative stress in developing rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Protoplasma. doi:10.1007/s00709-013-0525-8
Wang L, Yang L, Yang F, Li X, Song Y, Wang X, Hu X (2010) Involvements of H2O2 and metallothionein in NO-mediated tomato tolerance to Cu toxicity. J Plant Physiol 167:1298–1306
Wang YS, Yang ZM (2005) Nitric oxide reduces aluminum toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in the roots of Cassia tora L. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1915–1923
Wendehenne D, Gould K, Lamotte O, Durner J, Vandelle E, Lecourieux D, Courtois C, Barnavon L, Bentejac M, Pugin A (2005) NO signaling functions in the biotic and abiotic stress responses. BMC Plant Biol 5 (Suppl. 1) S35, doi:10.1186/1471-2229-5-S1-S35
Xiong J, Fu G, Tao L, Zhu C (2010) Roles of nitric oxide in alleviating heavy metal toxicity in plants. Arch Biochem Biophys 497:13–20
Yadav SK, Singla-Pareek SL, Reddy MK, Sopory SK (2005) Methylglyoxal detoxification by glyoxalase system: a survival strategy during environmental stresses. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 11:1–11
Yruela I (2005) Copper in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:145–156
Yruela I (2009) Copper in plants: acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct Plant Biol 36:409–430
Yu CC, Hung KT, Kao CH (2005) Nitric oxide reduces Cu toxicity and Cu-induced NH4 + accumulation in rice leaves. J Plant Physiol 162:319–330
Zhang H, Li YH, Hu LY, Wang SH, Zhang FQ, Hu KD (2008) Effects of exogenous nitric oxide donor on antioxidant metabolism in wheat leaves under aluminum stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 55:469–474
Acknowledgements
M. G. Mostofa thankfully acknowledges the financial support from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Néstor Carrillo
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Supplementary material table T1 Effect of exogenous 0.2 mM sodium ferrocyanide (SF) and 0.2 mM sodium nitroprusside (SNP) on visual appearances in 0.1 mM copper (Cu) -treated rice seedlings. Supplementary material Fig. S1 Effect of exogenous SNP (A), GSH (B), and SNP+GSH (C) on visual appearances in Cu-treated rice seedlings. Supplementary material Fig. S2 Effect of exogenous 0.2 mM sodium ferrocyanide (SF) and 0.2 mM sodium nitroprusside (SNP) on visual appearances in 0.1 mM copper (Cu) -treated rice seedlings. (PDF 522 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mostofa, M.G., Seraj, Z.I. & Fujita, M. Exogenous sodium nitroprusside and glutathione alleviate copper toxicity by reducing copper uptake and oxidative damage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Protoplasma 251, 1373–1386 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0639-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0639-7