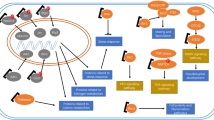
Abstract
Protein phosphorylation is essential for many aspects of plant growth and development. To fully modulate the activity of specific proteins after phosphorylation, interaction with members of the 14-3-3 family is necessary. 14-3-3 Proteins are important for many processes because they “assist” a wide range of target proteins with divergent functions. In this review, we will describe how plant 14-3-3 proteins are as spiders in a web of phosphorylation: they act as sensors for phospho-motifs, they themselves are phosphorylated with unknown consequences and they have kinases as target, where some of these phosphorylate 14-3-3 binding motifs in other proteins. Two specific classes of 14-3-3 targets, protein kinases and transcription factors of the bZIP and basic helix-loop-helix-like families, with important and diverse functions in the plant as a whole will be discussed. An important question to be addressed in the near future is how the interaction with 14-3-3 proteins has diverged, both structurally and functionally, between different members of the same protein family, like the kinases and transcription factors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe M, Kobayashi Y, Yamamoto S, Daimon Y, Yamaguchi A, Ikeda Y, Ichinoki H, Notaguchi M, Goto K, Araki T (2005) FD, a bZIP protein mediating signals from the floral pathway integrator FT at the shoot apex. Science 309:1052–1056
Agueci F, Rutten T, Demidov D, Houben A (2012) Arabidopsis AtNek2 kinase is essential and associates with microtubules. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30:339–348
Aitken A (2002) Functional specificity in 14-3-3 isoform interactions through dimer formation and phosphorylation. Chromosome location of mammalian isoforms and variants. Plant Mol Biol 50:993–1010
Aitken A (2006) 14-3-3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin Cancer Biol 16:162–172
Aitken A (2011) Post-translational modification of 14-3-3 isoforms and regulation of cellular function. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22:673–680
Alexander RD, Morris PC (2006) A proteomic analysis of 14-3-3 binding proteins from developing barley grains. Proteomics 6:1886–1896
Amasino RM, Michaels SD (2010) The timing of flowering. Plant Physiol 154:516–520
Anderson LE, Carol AA (2005) Enzyme co-localization in the pea leaf cytosol: 3-P-glycerate kinase, glyceraldehyde-3-P dehydrogenase, triose-P isomerase and aldolase. Plant Sci 169:620–628
Aryal UK, Krochko JE, Ross ARS (2012) Identification of phosphoproteins in Arabidopsis thaliana leaves using polyethylene glycol fractionation, immobilized metal-ion affinity chromatography, two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 11:425–437
Bai MY, Zhang LY, Gampala SS, Zhu SW, Song WY, Chong K, Wang ZY (2007) Functions of OsBZR1 and 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13839–13844
Benschop JJ, Mohammed S, O’Flaherty M, Heck AJR, Slijper M, Menke FLH (2007) Quantitative phosphoproteomics of early elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell Proteomics 6:1198–1214
Brandina I, Graham J, Lemaitre-Guillier C, Entelis N, Krasheninnkov I, Sweetlove L, Tarassov I, Martin RP (2006) Enolase takes part in a macromolecular complex associated to mitochondria in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1757:1217–1228
Bustos DM (2012) The role of protein disorder in the 14-3-3 interaction network. Mol Biosyst 8:178–184
Bustos DM, Iglesias AA (2006) Intrinsic disorder is a key characteristic in partners that bind 14-3-3 proteins. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinf 63:35–42
Caesar K, Elgass K, Chen ZH, Huppenberger P, Witthoft J, Schleifenbaum F, Blatt MR, Oecking C, Harter K (2011) A fast brassinolide-regulated response pathway in the plasma membrane of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 66:528–540
Camoni L, Harper JF, Palmgren MG (1998) 14-3-3 proteins activate a plant calcium-dependent protein kinase (CDPK). FEBS Lett 430:381–384
Chan PM, Ng YW, Manser E (2011) A robust protocol to Map binding sites of the 14-3-3 interactome: Cdc25C requires phosphorylation of both S216 and S263 to bind 14-3-3. Mol Cell Proteomics 10. doi:10.1074/mcp.M110.005157
Chang IF, Curran A, Woolsey R, Quilici D, Cushman JC, Mittler R, Harmon A, Harper JF (2009) Proteomic profiling of tandem affinity purified 14-3-3 protein complexes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proteomics 9:2967–2985
Clokie SJ, Cheung KY, Mackie S, Marquez R, Peden AH, Aitken A (2005) BCR kinase phosphorylates 14-3-3 Tau on residue 233. FEBS J 272:3767–3776
Cloutier M, Vigneault F, Lachance D, Seguin A (2005) Characterization of a poplar NIMA-related kinase PNek 1 and its potential role in meristematic activity. FEBS Lett 579:4659–4665
Comparot S, Lingiah G, Martin T (2003) Function and specificity of 14-3-3 proteins in the regulation of carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism. J Exp Bot 54:595–604
Cotelle V, Meek SEM, Provan F, Milne FC, Morrice N, MacKintosh C (2000) 14-3-3s regulate global cleavage of their diverse binding partners in sugar-starved Arabidopsis cells. EMBO J 19:2869–2876
De Schutter K et al (2007) Arabidopsis WEE1 kinase controls cell cycle arrest in response to activation of the DNA integrity checkpoint. Plant Cell 19:211–225
De Vetten NC, Ferl RJ (1994) 2 Genes encoding GF-14-(14-3-3) proteins in Zea mays—structure, expression, and potential regulation by the G-box-binding complex. Plant Physiol 106:1593–1604
Denison FC, Paul AL, Zupanska AK, Ferl RJ (2011) 14-3-3 proteins in plant physiology. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22:720–727
Di Rubbo S, Irani NG, Russinova E (2011) PP2A Phosphatases: the “on-off” regulatory switches of brassinosteroid signaling. Science Signaling 4(172):pe25. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2002046
Diaz C, Kusano M, Sulpice R, Araki M, Redestig H, Saito K, Stitt M, Shin R (2011) Determining novel functions of Arabidopsis 14-3-3 proteins in central metabolic processes. Bmc Systems Biology 5:192. doi:10.1186/1752-0509-5-192
Dubois T, Rommel C, Howell S, Steinhussen U, Soneji Y, Morrice N, Moelling R, Aitken A (1997) 14-3-3 is phosphorylated by casein kinase I on residue 233 - Phosphorylation at this site in vivo regulates Raf/14-3-3 interaction. J Biol Chem 272:28882–28888
Duby G, Poreba W, Piotrowiak D, Bobik K, Derua R, Waelkens E, Boutry M (2009) Activation of plant plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase by 14-3-3 proteins is negatively controlled by two phosphorylation sites within the H(+)-ATPase C-terminal region. J Biol Chem 284:4213–4221
Franz S, Ehlert B, Liese A, Kurth J, Cazale AC, Romeis T (2011) Calcium-dependent protein kinase CPK21 functions in abiotic stress response in arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant 4:83–96
Freeman AK, Morrison DK (2011) 14-3-3 Proteins: diverse functions in cell proliferation and cancer progression. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22:681–687
Fritz A, Brayer KJ, McCormick N, Adams DG, Wadzinski BE, Vaillancourt RR (2006) Phosphorylation of serine 526 is required for MEKK3 activity, and association with 14-3-3 blocks dephosphorylation. J Biol Chem 281:6236–6245
Fuglsang AT, Visconti S, Drumm K, Jahn T, Stensballe A, Mattei B, Jensen ON, Aducci P, Palmgren MG (1999) Binding of 14-3-3 protein to the plasma membrane H+-ATPase AHA2 involves the three C-terminal residues Tyr(946)-Thr-Val and requires phosphorylation of Thr(947). J Biol Chem 274:36774–36780
Fukazawa J, Sakai T, Ishida S, Yamaguchi I, Kamiya Y, Takahashi Y (2000) Repression ofshoot growth, a bZIP transcriptional activator, regulates cell elongation by controlling the level of gibberellins. Plant Cell 12:901–915
Fukazawa J, Nakata M, Ito T, Yamaguchi S, Takahashi Y (2010) The transcription factor RSG regulates negative feedback of NtGA20ox1 encoding GA 20-oxidase. Plant J 62:1035–1045
Gampala SS et al (2007) An essential role for 14-3-3 proteins in brassinosteroid signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 13:177–189
Ganguly S, Weller JL, Ho A, Chemineau P, Malpaux B, Klein DC (2005) Melatonin synthesis: 14-3-3-dependent activation and inhibition of arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase mediated by phosphoserine-205. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1222–1227
Gardino AK, Yaffe MB (2011) 14-3-3 Proteins as signaling integration points for cell cycle control and apoptosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22:688–695
Gardino AK, Smerdon SJ, Yaffe MB (2006) Structural determinants of 14-3-3 binding specificities and regulation of subcellular localization of 14-3-3-ligand complexes: a comparison of the X-ray crystal structures of all human 14-3-3 isoforms. Semin Cancer Biol 16:173–182
Giacometti S, Camoni L, Albumi C, Visconti S, De Michelis MI, Aducci P (2004) Tyrosine phosphorylation inhibits the interaction of 14-3-3 proteins with the plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Plant Biol 6:422–431
Giacometti S, Marrano CA, Bonza MC, Luoni L, Limonta M, De Michelis MI (2012) Phosphorylation of serine residues in the N-terminus modulates the activity of ACA8, a plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 63:1215–1224
Graham JWA, Williams TCR, Morgan M, Fernie AR, Ratcliffe RG, Sweetlove LJ (2007) Glycolytic enzymes associate dynamically with mitochondria in response to respiratory demand and support substrate channeling. Plant Cell 19:3723–3738
Grønlund AL, Dickinson JR, Kille P, Harwood JL, Herbert RJ, Francis D, Rogers HJ (2009) Plant WEE1 kinase interacts with a 14-3-3 protein, GF14 omega but a mutation of WEE1 at S485 alters their spatial interaction. Open Plant Sci J 3:40–48
Halford NG, Hey SJ (2009) Snf1-related protein kinases (SnRKs) act within an intricate network that links metabolic and stress signalling in plants. Biochem J 419:247–259
Harper JE, Breton G, Harmon A (2004) Decoding Ca2+ signals through plant protein kinases. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:263–288
He JX, Gendron JM, Sun Y, Gampala SSL, Gendron N, Sun CQ, Wang ZY (2005) BZR1 is a transcriptional repressor with dual roles in brassinosteroid homeostasis and growth responses. Science 307:1634–1638
Hermeking H, Benzinger A (2006) 14-3-3 Proteins in cell cycle regulation. Semin Cancer Biol 16:183–192
Holtgrawe D, Scholz A, Altmann B, Scheibe R (2005) Cytoskeleton-associated, carbohydrate-metabolizing enzymes in maize identified by yeast two-hybrid screening. Physiol Plant 125:141–156
Huber SC, MacKintosh C, Kaiser WM (2002) Metabolic enzymes as targets for 14-3-3 proteins. Plant Mol Biol 50:1053–1063
Hwang I, Sze H, Harper JF (2000) A calcium-dependent protein kinase can inhibit a calmodulin-stimulated Ca2+ pump (ACA2) located in the endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6224–6229
Igarashi D, Ishida S, Fukazawa J, Takahashi Y (2001) 14-3-3 Proteins regulate intracellular localization of the bZIP transcriptional activator RSG. Plant Cell 13:2483–2497
Ikeda Y, Koizumi N, Kusano T, Sano H (2000) Specific binding of a 14-3-3 protein to autophosphorylated WPK4, an SNF1-related wheat protein kinase, and to WPK4-phosphorylated nitrate reductase. J Biol Chem 275:31695–31700
Ishida S, Fukazawa J, Yuasa T, Takahashi Y (2004) Involvement of 14-3-3 signaling protein binding in the functional regulation of the transcriptional activator REPRESSION OFSHOOT GROWTH by gibberellins. Plant Cell 16:2641–2651
Ishida S, Yuasa T, Nakata M, Takahashi Y (2008) A tobacco calcium-dependent protein kinase, CDPK1, regulates the transcription factor REPRESSION OF SHOOT GROWTH in response to gibberellins. Plant Cell 20:3273–3288
Jakoby M, Weisshaar B, Droge-Laser W, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Tiedemann J, Kroj T, Parcy F, b ZIPRG (2002) bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 7:106–111
Johnson C, Crowther S, Stafford MJ, Campbell DG, Toth R, MacKintosh C (2010) Bioinformatic and experimental survey of 14-3-3-binding sites. Biochem J 427:69–78
Johnson C et al (2011) Visualization and biochemical analyses of the emerging mammalian 14-3-3-phosphoproteome. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics 10: M110.005751.
Karlova R, Boeren S, Russinova E, Aker J, Vervoort J, de Vries S (2006) The Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 protein complex includes BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE1. Plant Cell 18:626–638
Kim SY (2006) The role of ABF family bZIP class transcription factors in stress response. Physiol Plant 126:519–527
Kleppe R, Martinez A, Doskeland SO, Haavik J (2011) The 14-3-3 proteins in regulation of cellular metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22:713–719
Klychnikov OI, Li KW, Lill H, de Boer AH (2007) The V-ATPase from etiolated barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) shoots is activated by blue light and interacts with 14-3-3 proteins. J Exp Bot 58:1013–1023
Knetsch MLW, vanHeusden GPH, Ennis HL, Shaw DR, Epskamp SJP, SnaarJagalska BE (1997) Isolation of a Dictyostelium discoideum 14-3-3 homologue. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1357:243–248
Kulma A, Villadsen D, Campbell DG, Meek SEM, Harthill JE, Nielsen TH, MacKintosh C (2004) Phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding of Arabidopsis 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase. Plant J 37:654–667
Lalle M, Visconti S, Marra M, Camoni L, Velasco R, Aducci P (2005) ZmMPK6, a novel maize MAP kinase that interacts with 14-3-3 proteins. Plant Mol Biol 59:713–722
Lam BCH, Sage TL, Bianchi F, Blumwald E (2001) Role of SH3 domain-containing proteins in clathrin-mediated vesicle trafficking in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 13:2499–2512
Lee JH, Lu H (2011) 14-3-3 gamma inhibition of MDMX-mediated p21 turnover independent of p53. J Biol Chem 286:5136–5142
Lifschitz E, Eviatar T, Rozman A, Shalit A, Goldshmidt A, Amsellem Z, Alvarez JP, Eshed Y (2006) The tomato FT ortholog triggers systemic signals that regulate growth and flowering and substitute for diverse environmental stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6398–6403
Mayfield JD, Folta KM, Paul AL, Ferl RJ (2007) The 14-3-3 proteins mu and nu influence transition to flowering and early phytochrome response. Plant Physiol 145:1692–1702
Mehlmer N, Wurzinger B, Stael S, Hofmann-Rodrigues D, Csaszar E, Pfister B, Bayer R, Teige M (2010) The Ca2+-dependent protein kinase CPK3 is required for MAPK-independent salt-stress acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 63:484–498
Munnik T, Testerink C (2009) Plant phospholipid signaling: “in a nutshell”. J Lipid Res 50:S260–S265
Navarro C, Abelenda JA, Cruz-Oro E, Cuellar CA, Tamaki S, Silva J, Shimamoto K, Prat S (2011) Control of flowering and storage organ formation in potato by FLOWERING LOCUS T. Nature 478:119–U132
Nozawa A, Sawada Y, Akiyama T, Koizumi N, Sano H (2003) Variable interactions between sucrose non-fermented 1-related protein kinases and regulatory proteins in higher plants. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:2533–2540
Oakley BR, Morris NR (1983) A mutation in Aspergillus–Nidulans that blocks the transition from interphase to prophase. J Cell Biol 96:1155–1158
Obenauer JC, Cantley LC, Yaffe MB (2003) Scansite 2.0: proteome-wide prediction of cell signaling interactions using short sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3635–3641
Obsilova V, Herman P, Vecer J, Sulc M, Teisinger J, Obsil T (2004) 14-3-3 zeta C-terminal stretch changes its conformation upon ligand binding and phosphorylation at Thr(232). J Biol Chem 279:4531–4540
Obsilova S, Silhan J, Boura E, Teisinger J, Obsil T (2008) 14-3-3 proteins: a family of versatile molecular regulators. Physiol Res 57:S11–S21
O’Connell MJ, Krien MJE, Hunter T (2003) Never say never. The NIMA-related protein kinases in mitotic control. Trends Cell Biol 13:221–228
Oh CS, Martin GB (2011) Tomato 14-3-3 protein TFT7 interacts with a MAP kinase kinase to regulate immunity-associated programmed cell death mediated by diverse disease resistance proteins. J Biol Chem 286:14129–14136
Oh CS, Pedley KF, Martin GB (2010) Tomato 14-3-3 protein 7 positively regulates immunity-associated programmed cell death by enhancing protein abundance and signaling ability of MAPKKK alpha. Plant Cell 22:260–272
Okamoto M, Tanaka Y, Abrams SR, Kamiya Y, Seki M, Nambara E (2009) High humidity induces abscisic acid 8′-hydroxylase in stomata and vasculature to regulate local and systemic abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 149:825–834
Olivari C, Albumi C, Pugliarello MC, De Michelis MI (2000) Phenylarsine oxide inhibits the fusicoccin-induced activation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Plant Physiol 122:463–470
Paul AL, Liu L, McClung S, Laughner B, Chen S, Ferl RJ (2009) Comparative interactomics: analysis of Arabidopsis 14-3-3 complexes reveals highly conserved 14-3-3 interactions between humans and plants. J Proteome Res 8:1913–1924
Pitzschke A, Djamei A, Teige M, Hirt H (2009) VIP1 response elements mediate mitogen-activated protein kinase 3-induced stress gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:18414–18419
Pnueli L, Carmel-Goren L, Hareven D, Gutfinger T, Alvarez J, Ganal M, Zamir D, Lifschitz E (1998) The SELF-PRUNING gene of tomato regulates vegetative to reproductive switching of sympodial meristems and is the ortholog of CEN and TFL1. Development 125:1979–1989
Pnueli L, Gutfinger T, Hareven D, Ben-Naim O, Ron N, Adir N, Lifschitz E (2001) Tomato SP-interacting proteins define a conserved signaling system that regulates shoot architecture and flowering. Plant Cell 13:2687–2702
Purwestri YA, Ogaki Y, Tamaki S, Tsuji H, Shimamoto K (2009) The 14-3-3 protein GF14c acts as a negative regulator of flowering in rice by interacting with the florigen Hd3a. Plant Cell Physiol 50:429–438
Rienties IM, Vink J, Borst JW, Russinova E, de Vries SC (2005) The Arabidopsis SERK1 protein interacts with the AAA-ATPase AtCDC48, the 14-3-3 protein GF14 lambda and the PP2C phosphatase KAPP. Planta 221:394–405
Rodriguez MCS, Petersen M, Mundy J (2010) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants. In: Merchant S, Briggs WR, Ort D (eds) Annual review of plant biology, vol. 61. pp 621–649
Rosenquist M, Alsterfjord M, Larsson C, Sommarin M (2001) Data mining the Arabidopsis genome reveals fifteen 14-3-3 genes. Expression is demonstrated for two out of five novel genes. Plant Physiol 127:142–149
Ryu H, Kim K, Cho H, Park J, Choe S, Hwang I (2007) Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of BZR1 mediated by phosphorylation is essential in Arabidopsis brassinosteroid signaling. Plant Cell 19:2749–2762
Ryu JY, Park CM, Seo PJ (2011) The floral repressor BROTHER OF FT AND TFL1 (BFT) modulates flowering initiation under high salinity in Arabidopsis. Mol Cells 32:295–303
Schoonheim PJ, Veiga H, Pereira DD, Friso G, van Wijk KJ, de Boer AH (2007a) A comprehensive analysis of the 14-3-3 interactome in barley leaves using a complementary proteomics and two-hybrid approach. Plant Physiol 143:670–683
Schoonheim PJ, Sinnige MP, Casaretto JA, Veiga H, Bunney TD, Quatrano RS, de Boer AH (2007b) 14-3-3 Adaptor proteins are intermediates in ABA signal transduction during barley seed germination. Plant J 49:289–301
Schultz TF, Medina J, Hill A, Quatrano RS (1998) 14-3-3 Proteins are part of an abscisic acid VIVIPAROUS1 (VP1) response complex in the Em promoter and interact with VP1 and EmBP1. Plant Cell 10:837–847
Sehnke PC, Ferl RJ (1996) Plant metabolism: enzyme regulation by 14-3-3 proteins. Curr Biol 6:1403–1405
Shen W, Clark AC, Huber SC (2003) The C-terminal tail of Arabidopsis 14-3-3 omega functions as an autoinhibitor and may contain a tenth alpha-helix. Plant J 34:473–484
Shin R, Alvarez S, Burch AY, Jez JM, Schachtman DP (2007) Phosphoproteomic identification of targets of the Arabidopsis sucrose nonfermenting-like kinase SnRK2.8 reveals a connection to metabolic processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:6460–6465
Shin R, Jez JM, Basra A, Zhang B, Schachtman DP (2011) 14-3-3 Proteins fine-tune plant nutrient metabolism. FEBS Lett 585:143–147
Sinnige MP, Roobeek I, Bunney TD, Visser A, Mol JNM, de Boer AH (2005) Single amino acid variation in barley 14-3-3 proteins leads to functional isoform specificity in the regulation of nitrate reductase. Plant J 44:1001–1009
Sirichandra C, Davanture M, Turk BE, Zivy M, Valot B, Leung J, Merlot S (2010) The Arabidopsis ABA-activated kinase OST1 phosphorylates the bZIP transcription factor ABF3 and creates a 14-3-3 binding site involved in its turnover. Plos One 5
Sribar J, Sherman NE, Prijatelj P, Faure G, Gubensek F, Fox JW, Aitken A, Pungercar J, Krizaj I (2003) The neurotoxic phospholipase A(2) associates, through a non-phosphorylated binding motif, with 14-3-3 protein gamma and epsilon isoforms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302:691–696
Sun Y et al (2010) Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 19:765–777
Sunayama J, Tsuruta F, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2005) JNK antagonizes Akt-mediated survival signals by phosphorylating 14-3-3. J Cell Biol 170:295–304
Swatek KN, Graham K, Agrawal GK, Thelen JJ (2011) The 14-3-3 isoforms chi and epsilon differentially bind client proteins from developing Arabidopsis seed. J Proteome Res 10:4076–4087
Tang WQ et al (2011) PP2A activates brassinosteroid-responsive gene expression and plant growth by dephosphorylating BZR1. Nat Cell Biol 13:124–U149
Taoka K et al (2011) 14-3-3 proteins act as intracellular receptors for rice Hd3a florigen. Nature 476:332–U397
Tsugama D, Liu S, Takano T (2) A bZIP protein, VIP1, is a regulator of osmosensory signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 159:144–155
Tsuruta F, Sunayama J, Mori Y, Hattori S, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y, Yoshioka K, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2004) JNK promotes Bax translocation to mitochondria through phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins. EMBO J 23:1889–1899
Tzfira T, Vaidya M, Citovsky V (2001) VIP1, an Arabidopsis protein that interacts with Agrobacterium VirE2, is involved in VirE2 nuclear import and agrobacterium infectivity. EMBO J 20:3596–3607
van Bentem S, Hirt H (2009) Protein tyrosine phosphorylation in plants: more abundant than expected? Trends Plant Sci 14:71–76
van Heusden GPH, vander Zanden AL, Ferl RJ, Steensma HY (1996) Four Arabidopsis thaliana 14-3-3 protein isoforms can complement the lethal yeast BMH1 BMH2 double disruption. FEBS Lett 391:252–256
Vigneault F, Lachance D, Cloutier M, Pelletier G, Levasseur C, Seguin A (2007) Members of the plant NIMA-related kinases are involved in organ development and vascularization in poplar, Arabidopsis and rice. Plant J 51:575–588
Wang HJ, Yang CJ, Zhang C, Wang NY, Lu DH, Wang J, Zhang SS, Wang ZX, Ma H, Wang XL (2011) Dual role of BKI1 and 14-3-3s in brassinosteroid signaling to link receptor with transcription factors. Dev Cell 21:825–834
Wigge PA (2011) FT, a mobile developmental signal in plants. Curr Biol 21:R374–R378
Wilson JE (2003) Isozymes of mammalian hexokinase: structure, subcellular localization and metabolic function. J Exp Biol 206:2049–2057
Woodcock JM, Ma YF, Coolen C, Pham D, Jones C, Lopez AF, Pitson SM (2010) Sphingosine and FTY720 directly bind pro-survival 14-3-3 proteins to regulate their function. Cell Signal 22:1291–1299
Wu Y, Zhao Q, Gao L, Yu X-M, Fang P, Oliver DJ, Xiang C-B (2010) Isolation and characterization of low-sulphur-tolerant mutants of Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 61:3407–3422
Wu G, Wang XL, Li XB, Kamiya YJ, Otegui MS, Chory J (2011) Methylation of a phosphatase specifies dephosphorylation and degradation of activated brassinosteroid receptors. Science Signaling 4(172):ra29. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2001258
Wurtele M, Jelich-Ottmann C, Wittinghofer A, Oecking C (2003) Structural view of a fungal toxin acting on a 14-3-3 regulatory complex. EMBO J 22:987–994
Yaffe MB, Rittinger K, Volinia S, Caron PR, Aitken A, Leffers H, Gamblin SJ, Smerdon SJ, Cantley LC (1997) The structural basis for 14-3-3: phosphopeptide binding specificity. Cell 91:961–971
Yu XF et al (2011) A brassinosteroid transcriptional network revealed by genome-wide identification of BESI target genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 65:634–646
Zeevaart JAD (2008) Leaf-produced floral signals. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:541–547
Zhang H, Wang J, Goodman HM (1997) An Arabidopsis gene encoding a putative 14-3-3-interacting protein, caffeic acid/5-hydroxyferulic acid O-methyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Struct Expr 1353:199–202
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NWO grant 817.02.026 awarded to AHdeB and a scholarship awarded to JG by the China Scholarship Council. We thank Tom de Boer for the making the drawing in Fig. 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: David Robinson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Boer, A.H., van Kleeff, P.J.M. & Gao, J. Plant 14-3-3 proteins as spiders in a web of phosphorylation. Protoplasma 250, 425–440 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-012-0437-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-012-0437-z