Summary.
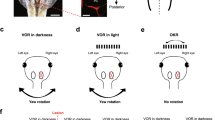
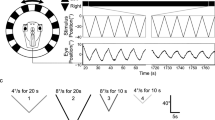
In lower vertebrates, gravity deprivation by orbital flights modifies the vestibuloocular reflex. Using the amphibian Xenopus laevis, the experiments should clarify to which extent macular structures of the labyrinth are responsible for these modifications. In particular, the shape of otoconia and number and size of sensory macular cells expressing CalBindin were considered. CalBindin is common in mature sensory cells including vestibular hair cells and is probably involved in otoconia formation. Two developmental stages were used for this study: stage 26/27 embryos, which were unable to perform the roll-induced vestibuloocular reflex (rVOR) at onset of microgravity, and stage 45 tadpoles, which had already developed the reflex. The main observations were that the developmental progress of the animals was not affected by microgravity; that in the young tadpole group with normal body shape the rVOR was not modified by microgravity, while in the older group with microgravity experience, the rVOR was augmented; and that significant effects on the shape of otoconia and on the number and size of CalBindin-expressing cells of the labyrinthine maculae cells were absent. In addition, behavioural data were never significantly correlated with morphological features of macular structures such as size and number of CalBindin-expressing cells. It is postulated that mechanisms of vestibular adaptation to microgravity during early development are probably based on mechanisms located in central structures of the vestibular system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RH Anken H Rahmann (1998) ArticleTitleInfluence of long-term hypergravity on the reactivity of succinic acid dehydrogenase and NADPH-diaphorase in the central nervous system of fish: a histochemical study Adv Space Res 22 281–285 Occurrence Handle11541407 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0273-1177(98)80021-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlsFegsL4%3D
E Balaban C Centini P Pompeiano (2002) ArticleTitleTonic gravity changes alter gene expression in the efferent vestibular nucleus Neuroreport 13 187–190 Occurrence Handle11924886 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00001756-200201210-00042
G Balsamo B Avallone F Del Genio S Trapani F Marmo (2000) ArticleTitleCalcification processes in the chick otoconia and calcium binding proteins: patterns of tetracycline incorporation and calbindin-D28K distribution Hear Res 148 1–8 Occurrence Handle10978820 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-5955(00)00094-0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXmt1SjtrY%3D
SD Black J Gerhart (1985) ArticleTitleExperimental control of the site of embryonic axis formation in Xenopus laevis eggs centrifuged before first cleavage Dev Biol 108 310–324 Occurrence Handle4076537 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0012-1606(85)90035-1 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL28%2Fot1Ojsw%3D%3D
R Boyle AF Mensinger K Yoshida S Usui A Intravaia T Tricas SM Highstein (2001) ArticleTitleNeural readaptation to Earth’s gravity following return from space J Neurophysiol 86 2118–2122 Occurrence Handle11600668 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mrltlehsg%3D%3D
F Bracchi T Gualierotti A Morabito E Rocca (1975) ArticleTitleMultiday recordings from the primary neurons of the statoreceptors of the labyrinth of the bull frog: the effect of an extended period of “weightlessness” on the rate of firing at rest and in response to stimulation by brief periods of centrifugation (OFO-A orbiting experiment) Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 334 1–27 Occurrence Handle1082707 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE287jtlegtA%3D%3D
G Clément S Moore T Raphan B Cohen (2001) ArticleTitlePerception of tilt (somatogravic illusion) in response to sustained linear acceleration during space flight Exp Brain Res 138 410–418 Occurrence Handle11465738 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002210100706
B Cohen (1974) The vestibulo-ocular reflex arc H-H Kornhuber (Eds) Vestibular system, part 1: basic mechanisms SeriesTitleHandbook of sensory physiology NumberInSeriesIV/1 Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York 477–540
NG Daunton MD Ross RA Fox ML Corcoran LK Cutler LC Wu (1991) ArticleTitleEffects of chronic hypergravity on the righting reflex and vestibular endorgan morphology in the rat Soc Neurosci Abstr 17 316
ET Degens WG Deuser RL Haedrich (1969) ArticleTitleMolecular structure and composition of fish otoliths Mar Biol 2 105–113 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00347005 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF1MXktFSksrc%3D
N Dieringer (1995) ArticleTitle“Vestibular compensation”: neural plasticity and its relations to functional recovery after labyrinthine lesions in frogs and other vertebrates Prog Neurobiol 46 97–129 Occurrence Handle7568917 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0301-0082(94)00063-N Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28%2FjtFKhtA%3D%3D
N Dieringer W Precht (1979a) ArticleTitleMechanisms of compensation for vestibular deficits in the frog. I. Modification of the excitatory commissural system Exp Brain Res 36 311–328 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL3c%2FisVGjsg%3D%3D
N Dieringer W Precht (1979b) ArticleTitleMechanisms of compensation for vestibular deficits in the frog. II. Modification of the inhibitory pathways Exp Brain Res 36 329–357 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL3c%2FisVGjsw%3D%3D
M Fejtek K Souza A Neff R Wassersug (1998) ArticleTitleSwimming kinematics and respiratory behaviour of Xenopus laevis larvae raised in altered gravity J Exp Biol 201 1917–1926 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czjtFOisw%3D%3D
C-D Fermin D Martin T Jones J Vellinger M Deuser P Hester R Hullinger (1996) ArticleTitleMicrogravity in the STV-29 space discovery affected the vestibular system of chick embryos Histol Histopathol 11 407–426 Occurrence Handle8861764 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s%2FhsV2gsw%3D%3D
R Gruener G Hoeger (1990) ArticleTitleVector-free gravity disrupts synapse formation in cell culture Am J Physiol 258 489–494
R Gruener G Hoeger (1991) ArticleTitleVector-averaged gravity alters myocyte and neuron properties in cell culture Aviat Space Environ Med 62 1159–1165 Occurrence Handle1755797 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK38%2FpsF2jsQ%3D%3D
ER Horn (2004) ArticleTitle“Critical periods” in vestibular development or adaptation of gravity sensory systems to altered gravitational conditions? Arch Ital Biol 142 155–174 Occurrence Handle15260375 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2czlslaruw%3D%3D
ER Horn (2006) ArticleTitleMicrogravity-induced modifications of the vestibuloocular reflex in Xenopus laevis tadpoles are related to development and the occurrence of tail lordosis J Exp Biol 209 2847–2858 Occurrence Handle16857868 Occurrence Handle10.1242/jeb.02298
E Horn C Sebastian (1996) ArticleTitleA hypergravity related sensitive period during the development of the roll induced vestibuloocular reflex in an amphibian (Xenopus laevis) Neurosci Lett 216 25–28 Occurrence Handle8892383 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3940(96)12993-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28Xmt1aisr4%3D
E Horn H-G Lang B Rayer (1986) ArticleTitleThe development of the static vestibulo-ocular reflex in the southern clawed toad, Xenopus laevis. I. Intact animals J Comp Physiol 159 869–878 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00603740 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s7ht1aqsg%3D%3D
M Ibsch RH Anken H Rahmann (2000) ArticleTitleWeightlessness during space-flight results in enhanced synapse formation in a fish brain vestibular nucleus Neurosci Lett 296 13–16 Occurrence Handle11099822 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01594-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotlCqurY%3D
T Kido M Takahashi (1997) ArticleTitleScanning electron microscopic study of amphibians otoconia Auris Nasus Larynx 24 125–130 Occurrence Handle9134133 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0385-8146(96)00020-X Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s3nvFOhtQ%3D%3D
DV Lychakov YA Lavrova (1985) ArticleTitleInvestigation of vestibular structure and ion composition of spur-toed frog larvae after exposure to weightlessness Kosm Biol Aviakosm Med 19 48–52 Occurrence Handle3875754 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXks1ymt78%3D
SJ Moorman R Cordova SA Davies (2002) ArticleTitleA critical period for functional vestibular development in zebrafish Dev Dyn 223 285–291 Occurrence Handle11836792 Occurrence Handle10.1002/dvdy.10052
D Necchil E Scherini L Botta C Soldani P Valli G Bernocchi (2002) ArticleTitleMorphological changes in the frog cerebellar cortex after unilateral section of the statoacustic nerve Eur J Histochem 46 317–328 Occurrence Handle12597616 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s%2FosF2itQ%3D%3D
AW Neff H Yokota HM Chung M Wakahara GM Malacinski (1993) ArticleTitleEarly amphibian anuran morphogenesis is sensitive to novel gravitational fields Dev Biol 155 270–274 Occurrence Handle8416840 Occurrence Handle10.1006/dbio.1993.1024 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3s7gs1egsA%3D%3D
J Neubert A Schatz B Bromeis W Briegleb (1994) ArticleTitleThe reaction of Xenopus laevis to linear accelerations Adv Space Res 14 299–303 Occurrence Handle11537929 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0273-1177(94)90414-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mnls1CksQ%3D%3D
PD Nieuwkoop J Faber (1967) Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin) EditionNumber2 North-Holland Amsterdam
O Pompeiano P d’Ascanio C Centini M Pompeiano E Balaban (2002) ArticleTitleGene expression in rat vestibular and reticular structures during and after space flight Neuroscience 114 135–155 Occurrence Handle12207961 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0306-4522(02)00202-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xms1Kit7c%3D
KG Pote MD Ross (1991) ArticleTitleEach otoconia polymorph has a protein unique to the polymorph Comp Biochem Physiol 98 287–295 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3MzjvFCnug%3D%3D
KG Pote MD Ross (1993) ArticleTitleUtricular otoconia of some amphibians have calcitic morphology Hear Res 67 189–197 Occurrence Handle8340270 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-5955(93)90246-W Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3szjvF2rsg%3D%3D
H Rahmann KH Slenzka KH Körtje R Hilbig (1992) ArticleTitleSynaptic plasticity and gravity: ultrastructural, biochemical and physiochemical fundamentals Adv Space Res 12 163–172 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0273-1177(92)90265-Y
B Rayer E Horn (1986) ArticleTitleThe development of the static vestibulo-ocular reflex in the southern clawed toad, Xenopus laevis. III. Chronic hemilabyrinthectomized tadpoles J Comp Physiol 159A 887–895 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00603742
B Rayer E Cagol E Horn (1983) ArticleTitleCompensation of vestibular-induced deficits in relation to the development of the southern clawed toad, Xenopus laevis Daudin J Comp Physiol 151 487–498 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00605466
J Raymond D Demêmes E Blanc C-J Dechesne (2003) Development of the vestibular system in microgravity JC Buckey SuffixJr JL Homick (Eds) The Neurolab Spacelab mission: neuroscience research in space SeriesTitleNational Aeronautics and Space Administration Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center Houston, Tex 143–149
MD Ross (1992) ArticleTitleSynaptic plasticity in utricular maculas of rats exposed to microgravity ASGSB Bull 6 100
MD Ross (1993) ArticleTitleRibbon synapse counts in utricular maculae of tadpoles raised in microgravity: Does gravity matter? ASGSB Bull 7 IssueID1 100
L Sachs (1997) Angewandte Statistik EditionNumber8 Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York
C Sebastian E Horn (1998) ArticleTitleThe minimum duration of microgravity experience during space flight which affects the development of the vestibuloocular reflex in an amphibian (Xenopus laevis) Neurosci Lett 253 171–174 Occurrence Handle9792238 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3940(98)00633-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmvVaqsL8%3D
C Sebastian E Horn (1999) ArticleTitleLight-dependent suppression of the vestibuloocular reflex during development Neuroreport 10 171–176 Occurrence Handle10094157 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00001756-199901180-00033 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7ptF2ntw%3D%3D
C Sebastian K Eßeling E Horn (1996) ArticleTitleAltered gravitational experience during early periods of life affects the static vestibulo-ocular reflex of tadpoles of the southern clawed toad, Xenopus laevis Daudin Exp Brain Res 112 213–222 Occurrence Handle8951390 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00227640 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s7gvFWisg%3D%3D
C Sebastian K Esseling E Horn (2001) ArticleTitleAltered gravitational forces affect the development of the static vestibuloocular reflex in fish (Oreochromis mossambicus) J Neurobiol 46 59–72 Occurrence Handle11108616 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1097-4695(200101)46:1<59::AID-NEU6>3.0.CO;2-X Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7gs1yhsA%3D%3D
K Slenzka R Appel R Hilbig T Kappel S Vetter B Freischutz H Rahmann (1994) ArticleTitleBehavioural and biochemical investigations of the influence of altered gravity on the CNS of aquatic vertebrates during ontogeny Adv Space Res 14 309–312 Occurrence Handle11537932 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0273-1177(94)90416-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXltVCksr0%3D
E Snetkova N Chelnaya L Serova S Saveliev E Cherdanzova S Pronych RJ Wassersug (1995) ArticleTitleThe effects of space flight on Xenopus laevis larval development J Exp Zool 273 21–32 Occurrence Handle7561721 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jez.1402730104 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK28%2FlvVCrtQ%3D%3D
KA Souza SD Black RJ Wassersug (1995) ArticleTitleAmphibian development in the virtual absence of gravity Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92 1975–1978 Occurrence Handle7892210 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.92.6.1975 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXksVCqsL8%3D
H Straka A Kunkel N Dieringer (1993) ArticleTitleSpinal compensation for postural deficits after hemilabyrinthectomy? Neuroreport 9 1071–1074
GA Ubbels M Reijnen J Meijerink J Narraway (1994) ArticleTitle Xenopus laevis embryos can establish their spatial bilateral symmetrical body pattern without gravity Adv Space Res 14 257–269 Occurrence Handle11537925 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0273-1177(94)90410-3 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mnls1Cluw%3D%3D
ML Wiederhold W Gao JL Harison KA Parker (2003) Early development of gravity-sensing organs in microgravity JC Buckey SuffixJr JL Homick (Eds) The Neurolab Spacelab mission: neuroscience research in space SeriesTitleNational Aeronautics and Space Administration Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center Houston, Tex 123–132
H Yokohata AW Neff GM Malacinski (1992) ArticleTitleAltering the position of the first horizontal cleavage furrow of the amphibian Xenopus egg reduces embryonic survival Int J Dev Biol 36 527–535
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence and reprints: Gravitationsphysiologie, Abteilung Neurobiologie, Universität Ulm, Albert-Einstein-Allee 11, 89081 Ulm, Federal Republic of Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horn, E., Böser, S., Membre, H. et al. Morphometric investigations of sensory vestibular structures in tadpoles (Xenopus laevis) after a spaceflight: implications for microgravity-induced alterations of the vestibuloocular reflex. Protoplasma 229, 193–203 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-006-0213-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-006-0213-z