Abstract
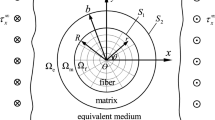
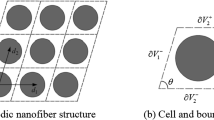
In this paper, for obtaining an overall size-dependent yield function for nanocomposites containing aligned cylindrical nanofibers, the effects of interface residual stress and interface elasticity are taken into account within a micromechanical framework. Toward this goal, the modified Hill’s condition is used, and then, in order to consider effects of the interface residual stress, strains are decomposed into two parts, a part due to the external loadings and the other due to the interface residual stress. Next, utilizing the field fluctuation method, an overall yield function containing effective elastic constants of the material is derived and then simplified for practical loading conditions. Moreover, a secant modulus scheme is adopted to examine the overall nonlinear behavior of the material in plastic deformation. Finally, by some numerical examples, it is shown that the interface stress, including the interface residual stress, makes the yield strength and plastic deformation of the metal matrix nanocomposites dependent on the nanofiber size, in contrast to the classical results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakshi S., Lahiri D., Agarwal A.: Carbon nanotube reinforced metal matrix composites—A review. Int. Mater. Rev. 55, 41–64 (2010)
Cammarata R.C.: Surface and interface stress effects in thin films. Prog. Surf. Sci. 46, 1–38 (1994)
Sharma P., Ganti S., Bhate N.: Effect of surfaces on the size-dependent elastic state of nano-inhomogeneities. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 535–537 (2003)
Duan H.L., Wang J., Karihaloo B.L., Huang Z.P.: Nanoporous materials can be made stiffer than non-porous counterparts by surface modification. Acta Mater. 54, 2983–2990 (2006)
Chen T., Dvorak G.J., Yu C.C.: Size-dependent elastic properties of unidirectional nano-composites with interface stresses. Acta Mech. 188, 39–54 (2007)
Mogilevskaya S.G., Crouch S.L., Stolarski H.K., Benusiglio A.: Equivalent inhomogeneity method for evaluating the effective elastic properties of unidirectional multi-phase composites with surface/interface effects. Int. J. Solids Struct. 47, 407–418 (2010)
Mishra S., Sonawane S.H., Singh R.P.: Studies on characterization of nano CaCO3 prepared by the in situ deposition technique and its application in PP-nano CaCO3 composites. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 43, 107–113 (2005)
Cho J., Joshi M.S., Sun C.T.: Effect of inclusion size on mechanical properties of polymeric composites with micro and nano particles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 66, 1941–1952 (2006)
Mori T., Tanaka K.: Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions. Acta Met. 21, 571–574 (1973)
Christensen R.M., Lo K.H.: Solutions for effective shear properties in three phase sphere and cylinder models. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 27, 315–330 (1979)
Hashin Z.: Analysis of composite materials—a survey. J. Appl. Mech. 50, 481–505 (1983)
Nemat-Nasser S., Hori M.: Micromechanics: Overall Properties of Heterogeneous Materials. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1999)
Qu J., Cherkaoui M.: Fundamentals of Micromechanics of Solids. Wiley, New York (2006)
Gurtin M.E., Ian Murdoch A.: A continuum theory of elastic material surfaces. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 57, 291–323 (1975)
Duan H.L., Wang J., Karihaloo B.L.: Theory of elasticity at the nanoscale. Adv. Appl. Mech. 42, 1–68 (2009)
Assadi A., Farshi B.: Size-dependent longitudinal and transverse wave propagation in embedded nanotubes with consideration of surface effects. Acta Mech. 222, 27–39 (2011)
Yang Q., Liu J.X., Fang X.Q.: Dynamic stress in a semi-infinite solid with a cylindrical nano-inhomogeneity considering nanoscale microstructure. Acta Mech. 223, 879–888 (2012)
Gao W., Yu S., Huang G.: Finite element characterization of the size-dependent mechanical behaviour in nanosystems. Nanotechnology 17(4), 1118–1122 (2006)
Assadi, A., Farshi, B.: Vibration characteristics of circular nanoplates. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 074312-1–074312-5 (2010)
Zhang, W.X., Wang, T.J.: Effect of surface energy on the yield strength of nanoporous materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 063104-1–063104-3 (2007)
Chen H., Liu X., Hu G.: Overall plasticity of micropolar composites with interface effect. Mech. Mater. 40, 721–728 (2008)
Zhang W.X., Wang T.J., Chen X.: Effect of surface/interface stress on the plastic deformation of nanoporous materials and nanocomposites. Int. J. Plast. 26, 957–975 (2010)
Goudarzi T., Avazmohammadi R., Naghdabadi R.: Surface energy effects on the yield strength of nanoporous materials containing nanoscale cylindrical voids. Mech. Mater. 42, 852–862 (2010)
Moshtaghin A.F., Naghdabadi R., Asghari M.: Effects of surface residual stress and surface elasticity on the overall yield surfaces of nanoporous materials with cylindrical nanovoids. Mech. Mater. 51, 74–87 (2012)
Chen, T., Chiu, M.S., Weng, C.N.: Derivation of the generalized Young-Laplace equation of curved interfaces in nanoscaled solids. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 074308-1–074308-5 (2006)
Qiu Y.P., Weng G.J.: A theory of plasticity for porous materials and particle-reinforced composites. J. Appl. Mech. 59, 261–268 (1992)
Hu G.: A method of plasticity for general aligned spheroidal void or fiber-reinforced composites. Int. J. Plast. 12, 439–449 (1996)
Qiu Y.P., Weng G.J.: Plastic potential and yield function of porous materials with aligned and randomly oriented spheroidal voids. Int. J. Plast. 9, 271–290 (1993)
Hashin Z., Rosen B.W.: The elastic moduli of fiber-reinforced materials. J. Appl. Mech. 31, 223–232 (1964)
Chen X.L., Liu Y.J.: Square representative volume elements for evaluating the effective material properties of carbon nanotube-based composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 29, 1–11 (2004)
Namilae S., Chandra N.: Multiscale model to study the effect of interfaces in carbon nanotube-based composites. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 127, 222–232 (2005)
Lim C.W., Li Z.R., He L.H.: Size dependent, non-uniform elastic field inside a nano-scale spherical inclusion due to interface stress. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 5055–5065 (2006)
Chen T.: Exact size-dependent connections between effective moduli of fibrous piezoelectric nanocomposites with interface effects. Acta Mech. 196, 205–217 (2008)
Pindera M.J., Aboudi J.: Micromechanical analysis of yielding of metal matrix composites. Int. J. Plast. 4(3), 195–214 (1988)
Montazeri A., Naghdabadi R.: Investigating the effect of carbon nanotube defects on the column and shell buckling of carbon nanotube-polymer composites using multiscale modeling. Int. J. Multiscale Comput. Eng. 7, 431–444 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moshtaghin, A.F., Naghdabadi, R. & Asghari, M. A study on the plastic properties of unidirectional nanocomposites with interface energy effects. Acta Mech 224, 789–809 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-012-0780-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-012-0780-3