Summary.
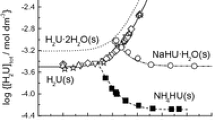
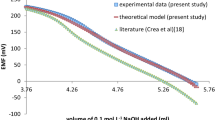
L-Cystine is the least soluble of the naturally occurring amino acids, and cystine stones, caused by a genetic disorder, account for between 1–4% of all urinary stones. Since the concentration of cystine in urine is the only factor related to the stone formation, a proper knowledge of cystine solubility in urine is necessary. Some research groups have already reported on the solubility of L-cystine, but the results are scattering. In this work, a systematic investigation of cystine solubility under conditions most pertinent to urolithiasis was carried out. The solubilities of L-cystine were measured at 25.0 and 37.0°C, from pH 1 to 9, and in different media including (i) 0.300 molċdm−3 NaCl solution and (ii) artificial urine solutions. The Joint Expert Speciation System (JESS) computer package and selected protonation constants of cystine reported in literature were used to model the solubilities of cystine. Excellent agreement was obtained between the experimentally determined solubility data and computer modelling of cystine solubility. The results of this work show that the presence of inorganic components has little influence on the solubility of cystine in urine.
Zusammenfassung.
L-Cystin ist die am geringsten lösliche natürlich vorkommende Aminosäure. Cystinsteine, die durch eine genetische Störung verursacht werden, machen etwa 1–4% aller Harnsteine aus. Da die Cystinkonzentration im Urin den einzigen für die Steinbildung verantwortlichen Faktor darstellt, ist die genaue Kenntnis der Cystinlöslichkeit in Urin eine notwendige Voraussetzung für weitere Untersuchungen. Die bisher publizierten Löslichkeitsdaten streuen jedoch sehr stark, so daß in dieser Arbeit eine systematische Studie der Cystinlöslichkeit unter Bedingungen durchgeführt wurde, die denen der Steinbildung möglichst ähnlich sind. Die Löslichkeit von L-Cystin wurde bei 25.0 und 37.0°C im pH-Bereich von 1 bis 9 in 0.300 molċdm−3 NaCl sowie in künstlichen Urinlösungen gemessen. Das Joint Expert Speciation System (JESS) sowie ausgewählte Protonierungskonstanten aus der Literatur wurden zur Modellierung der Cystinlöslichkeiten verwendet, wobei eine ausgezeichnete Übereinstimmung mit den experimentell bestimmten Werten erhalten wurde. Die Ergebnisse dieser Arbeit zeigen, daß anorganische Salze nur einen sehr geringen Einfluß auf die Cystinlöslichkeit in Urin ausüben.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received July 2, 1999./Accepted July 23, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Königsberger, E., Wang, Z. & Königsberger, LC. Solubility of L-Cystine in NaCl and Artificial Urine Solutions. Monatshefte fuer Chemie 131, 39–45 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007060050004
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007060050004