Abstract
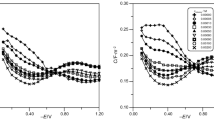
Guanine plays an important role in many biological processes since it constitutes the buildings blocks of DNA and RNA. Solutions of guanine were prepared to cover the range from 5 × 10−5 to 8 × 10−4 M. Adsorption of guanine on a mercury electrode in acetic buffers at pH 4 and pH 6 is described by means of the adsorption isotherms constants calculated from the surface pressure as a function of electrode potential and adsorbate bulk concentration. The adsorption parameters from the double layer were calculated based on the data from the differential capacity–potential curves. The entirely different change in the differential capacity in two applied acetate buffers in the absence of guanine results from different buffer composition, as in a solution with a pH 4 adsorption primarily involves acetic acid molecules, whereas in a buffer with a pH 6-acetate ions. The possibility to accurately determine E max and σ max parameters points to a physical character of guanine adsorption, which must be associated with the fact that adsorbed guanine molecules are vertically or diagonal oriented. Obtained R A (charge transfer resistance at formal potential) changes are minor and comply with changes in ΔE. Therefore, it may be concluded that in the tested range of guanine concentrations, it has no effect on kinetics of zinc cation depolarisation at a mercury electrode both in the buffer with pH 4 and pH 6.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sieńko D, Nieszporek J, Nieszporek K, Gugała D, Saba J (2006) Collect Czech Chem Commun 71:1393
Pilla AA (1974) Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 1:227
Sridharan R, De Levie R (1986) J Electroanal Chem 201:133
Wandowski T (1991) J Electroanal Chem 302:233
De Levie R, Wandlowski T (1994) J Electroanal Chem 366:265
Nikitas P, Pappa-Louisi A (1993) J Electroanal Chem 346:483
Sowerby SJ, Petersen GB (1997) J Electroanal Chem 433:85
Roelfs R, Bunge E, Schroter C, Soloimin T, Meyer H, Nichols RJ, Baumgartel H (1997) Phys Chem B 101:754
Popov A, Naneva R, Dimitrov N, Vitanov T, Bostanov V, De Levie R (1992) Electrochim Acta 37:2369
Popov A, Dimitrov N, Vitanov T (1992) Electrochim Acta 37:2373
Holzle MH, Krznaric D, Kolb DM (1995) J Electroanal Chem 386:235
Kamal MM, Ahmed ZA, Ahmed ME, Ibrahim MS, Temerk YM (1991) Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 25:137
Nikitas P (1988) J Electroanal Chem 251:235
Trasatti S (1986) In: Silva AF (ed) Interfacial electrochemistry. Reidel, Dordrecht
Lipkowski J, Buess-Herman C, Lambert JP, Gierst L (1986) J Electroanal Chem 202:169
Nieszporek J (2011) J Electroanal Chem 662:407
Solis V, Iwasita T, Pavese A, Vielstich W (1988) J Electroanal Chem 255:155
Sun SG, Clavilier J (1987) J Electroanal Chem 236:95
Nieszporek J, Dagci K (2014) Electrochim Acta 125:473
Nieszporek J (2013) J Electroanal Chem 706:108
Nosal-Wiercińska A (2010) Central Eur J Chem 8:1
Nosal-Wiercińska A (2011) J Electroanal Chem 654:66
Nosal-Wiercińska A (2014) Electroanalysis 26:1013
Gugala D, Fekner Z, Sieńko D, Nieszporek J, Saba J (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:2227
Gugała-Fekner D, Sieńko D, Nieszporek J, Klin M, Saba J (2009) J Colloid Interface Sci 332:291
Klin M, Nieszporek J, Sieńko D, Gugała-Fekner D, Saba J (2011) Acta Chim Slov 58:26
Gugała-Fekner D, Nieszporek J, Sieńko D (2015) Monatsh Chem 146:541
Lasia A (1999) In: Conway BE, Bockris J, White RE (eds) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and its applications. Modern aspects of electrochemistry. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publisher, New York
De Batisti A, Trasatti S (1974) J Electroanal Chem 54:1
Mohilner DM, Nakadomari H (1973) J Phys Chem 74:1594
Mohilner DM, Browman LW, Freeland SJ, Nakadomari H (1973) J Electrochem Soc 120:1658
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gugała-Fekner, D. Adsorption of guanine at the interface electrode-acetic buffer solution and its influence on zinc cation electroreduction. Monatsh Chem 147, 1855–1862 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-016-1825-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-016-1825-4