Abstract
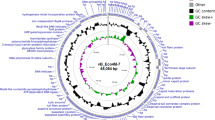
A bacteriophage infecting pathogenic Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae was isolated from a swine farm experiencing an outbreak of acute swine erysipelas; we designated this phage SE-I. SE-I has an icosahedral head, a long tail and a double-stranded DNA genome. The 34,997-bp genome has a GC content of 34 % and contains 43 open reading frames (ORFs) encoding packaging, structural, lysin-holin, and hypothetical proteins. Components of purified SE-I were separated using SDS-PAGE and analyzed using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Nine proteins were identified, encoded by ORF9, ORF15, ORF23, ORF30, ORF31, ORF33, ORF39, ORF40 and ORF 42. A phylogenetic tree constructed based on the sequence of the large terminase subunit revealed that SE-I is closely related to Staphylococcus phages P954 and phi3396. The CHAP-domain-containing protein encoded by ORF25 was expressed in E. coli and which was able to inactivate host bacteria. SE-I was able to infect 7 of 13 E. rhusiopathiae strains, but was unable to infect Salmonella, Streptococcus suis, and Staphylococcus aureus. This is the first report of the isolation, characterization, and genomic and proteomic analysis of a temperate phage infecting E. rhusiopathiae, and it might lead to the development of new anti- E. rhusiopathiae agents.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasifar R, Kropinski AM, Sabour PM, Chambers JR, MacKinnon J, Malig T, Griffiths MW (2014) Efficiency of bacteriophage therapy against Cronobacter sakazakii in Galleria mellonella (greater wax moth) larvae. Arch Virol 159:2253–2261
Alemayehu D, Ross RP, O’Sullivan O, Coffey A, Stanton C, Fitzgerald GF, McAuliffe O (2009) Genome of a virulent bacteriophage Lb338-1 that lyses the probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei cheese strain. Gene 448:29–39
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bateman A, Rawlings ND (2003) The CHAP domain: a large family of amidases including GSP amidase and peptidoglycan hydrolases. Trends Biochem Sci 28:234–237
Becker SC, Swift S, Korobova O, Schischkova N, Kopylov P, Donovan DM, Abaev I (2015) Lytic activity of the staphylolytic Twort phage endolysin CHAP domain is enhanced by the SH3b cell wall binding domain. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362:1–8
Bender JS, Shen HG, Irwin CK, Schwartz KJ, Opriessnig T (2010) Characterization of Erysipelothrix species isolates from clinically affected pigs, environmental samples, and vaccine strains from six recent swine erysipelas outbreaks in the United States. Clin Vaccine Immunol 17:1605–1611
Bender JS, Irwin CK, Shen H-G, Schwartz KJ, Opriessnig T (2011) Erysipelothrix spp. genotypes, serotypes, and surface protective antigen types associated with abattoir condemnations. J Vet Diagn Invest 23:139–142
Black LW (1989) DNA packaging in dsDNA bacteriophages. Annu Rev Microbiol 43:267–292
Boudvillain M, Nollmann M, Margeat E (2010) Keeping up to speed with the transcription termination factor Rho motor. Transcription 1:70–75
Brooke CJ, Riley TV (1999) Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: bacteriology, epidemiology and clinical manifestations of an occupational pathogen. J Med Microbiol 48:789–799
Chaturongakul S, Ounjai P (2014) Phage-host interplay: examples from tailed phages and gram-negative bacterial pathogens. Frontiers Microbiol 5:442
Clokie MR, Millard AD, Letarov AV, Heaphy S (2011) Phages in nature. Bacteriophage 1:31–45
Davis RW, Thomas M, Cameron J, St John TP, Scherer S, Padgett RA (1980) Rapid DNA isolations for enzymatic and hybridization analysis. Methods Enzymol 65:404–411
Dziewit L, Oscik K, Bartosik D, Radlinska M (2014) Molecular characterization of a novel temperate Sinorhizobium bacteriophage, capital EF, Cyrillic LM21, encoding DNA methyltransferase with CcrM-like specificity. J Virol 88:13111–13124
Eamens GJ, Forbes WA, Djordjevic SP (2006) Characterisation of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolates from pigs associated with vaccine breakdowns. Vet Microbiol 115:329–338
Feiss M, Rao VB (2012) The bacteriophage DNA packaging machine. Adv Exp Med Biol 726:489–509
Ford ME, Stenstrom C, Hendrix RW, Hatfull GF (1998) Mycobacteriophage TM4: genome structure and gene expression. Tuber Lung Dis 79:63–73
Golkar Z, Bagasra O, Pace DG (2014) Bacteriophage therapy: a potential solution for the antibiotic resistance crisis. J Infect Dev Ctries 8:129–136
Hatfull GF, Sarkis GJ (1993) DNA-sequence, structure and gene-expression of mycobacteriophage-L5—a phage system for mycobacterial genetics. Mol Microbiol 7:395–405
Hyman P, Abedon ST (2010) Bacteriophage host range and bacterial resistance. Adv Appl Microbiol 70:217–248
Imada Y, Takase A, Kikuma R, Iwamaru Y, Akachi S, Hayakawa Y (2004) Serotyping of 800 strains of Erysipelothrix isolated from pigs affected with erysipelas and discrimination of attenuated live vaccine strain by genotyping. J Clin Microbiol 42:2121–2126
Katsura I (1990) Mechanism of length determination in bacteriophage lambda tails. Adv Biophys 26:1–18
Keen EC (2015) A century of phage research: bacteriophages and the shaping of modern biology. BioEssays 37:6–9
Kenny JG, McGrath S, Fitzgerald GF, van Sinderen D (2004) Bacteriophage Tuc 2009 encodes a tail-associated cell wall-degrading activity. J Bacteriol 186:3480–3491
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Li L, Zhang Z (2014) Isolation and characterization of a virulent bacteriophage SPW specific for Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis of lactating dairy cattle. Mol Biol Rep 41:5829–5838
Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM (2003) Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem 75:3019–3030
Maurizi MR, Clark WP, Katayama Y, Rudikoff S, Pumphrey J, Bowers B, Gottesman S (1990) Sequence and structure of Clp P, the proteolytic component of the ATP-dependent Clp protease of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 265:12536–12545
Merabishvili M, Vandenheuvel D, Kropinski AM, Mast J, De Vos D, Verbeken G, Noben JP, Lavigne R, Vaneechoutte M, Pirnay JP (2014) Characterization of newly isolated lytic bacteriophages active against Acinetobacter baumannii. PloS One 9:e104853
Miller JR, Koren S, Sutton G (2010) Assembly algorithms for next-generation sequencing data. Genomics 95:315–327
Munsch-Alatossava P, Alatossava T (2013) The extracellular phage–host interactions involved in the bacteriophage LL-H infection of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. lactis ATCC 15808. Frontiers Microbiol 4:408
Nudler E, Gottesman ME (2002) Transcription termination and anti-termination in E. coli. Genes Cells 7:755–768
Opriessnig T, Hoffman LJ, Harris DL, Gaul SB, Halbur PG (2004) Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: genetic characterization of midwest US isolates and live commercial vaccines using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Vet Diagn Invest 16:101–107
Ozawa M, Yamamoto K, Kojima A, Takagi M, Takahashi T (2009) Etiological and biological characteristics of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolated between 1994 and 2001 from pigs with swine erysipelas in Japan. J Vet Med Sci 71:697–702
Pritchard DG, Dong S, Baker JR, Engler JA (2004) The bifunctional peptidoglycan lysin of Streptococcus agalactiae bacteriophage B30. Microbiology 150:2079–2087
Richardson JP (2002) Rho-dependent termination and ATPases in transcript termination. Biochim Biophys Acta 1577:251–260
Rigden DJ, Jedrzejas MJ, Galperin MY (2003) Amidase domains from bacterial and phage autolysins define a family of gamma-d, l-glutamate-specific amidohydrolases. Trends Biochem Sci 28:230–234
Santos SB, Kropinski AM, Ceyssens PJ, Ackermann HW, Villegas A, Lavigne R, Krylov VN, Carvalho CM, Ferreira EC, Azeredo J (2011) Genomic and proteomic characterization of the broad-host-range Salmonella phage PVP-SE1: creation of a new phage genus. J Virol 85:11265–11273
Schouler C, Ehrlich SD, Chopin MC (1994) Sequence and organization of the lactococcal prolate-headed bIL67 phage genome. Microbiology 140(Pt 11):3061–3069
Skurnik M, Hyytiainen HJ, Happonen LJ, Kiljunen S, Datta N, Mattinen L, Williamson K, Kristo P, Szeliga M, Kalin-Manttari L, Ahola-Iivarinen E, Kalkkinen N, Butcher SJ (2012) Characterization of the genome, proteome, and structure of yersiniophage varphiR1-37. J Virol 86:12625–12642
Sugai M, Fujiwara T, Akiyama T, Ohara M, Komatsuzawa H, Inoue S, Suginaka H (1997) Purification and molecular characterization of glycylglycine endopeptidase produced by Staphylococcus capitis EPK1. J Bacteriol 179:1193–1202
Takahashi T, Nagamine N, Kijima M, Suzuki S, Takagi M, Tamura Y, Nakamura M, Muramatsu M, Sawada T (1996) Serovars of Erysipelothrix strains isolated from pigs affected with erysipelas in Japan. J Vet Med Sci 58:587–589
Tegel H, Tourle S, Ottosson J, Persson A (2010) Increased levels of recombinant human proteins with the Escherichia coli strain Rosetta(DE3). Protein Expr purif 69:159–167
Vegge CS, Vogensen FK, McGrath S, Neve H, van Sinderen D, Brondsted L (2006) Identification of the lower baseplate protein as the antireceptor of the temperate lactococcal bacteriophages TP901-1 and Tuc 2009. J Bacteriol 188:55–63
Wang Q, Kan B, Wang R (2013) Isolation and characterization of the new mosaic filamentous phage VFJ phi of Vibrio cholerae. PLoS One 8:e70934
Wood RL, Harrington R Jr (1978) Serotypes of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolated from swine and from soil and manure of swine pens in the United States. Am J Vet Res 39:1833–1840
Wood RL (1999) Erysipelas. In: Straw BE, D’Allaire S, Mengeling ML, Taylor DJ (eds) Diseases of swine, 8th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 419–430
Zou Y, Zhu X, Muhammad HM, Jiang P, Li Y (2015) Characterization of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae strains isolated from acute swine erysipelas outbreaks in Eastern China. J Vet Med Sci 77:653–660
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by public welfare Grants from the Ministry of Agriculture, the People’s Republic of China (201203039), and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). The authors thank Dr. Tanja Opriessnig (Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, College of Veterinary Medicine, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa, USA) for offering to test serovars of the E. rhusiopathiae isolates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no competing interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, G. et al. Genomic and proteomic characterization of SE-I, a temperate bacteriophage infecting Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae . Arch Virol 161, 3137–3150 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-3018-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-3018-1