Abstract
Background
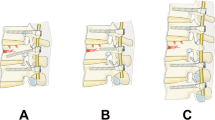
The surgical management of thoracolumbar burst fractures frequently involves posterior pedicle screw fixation. However, the application of short- or long-segment instrumentation is still controversial. The aim of this study was to compare the outcome of the short-segment fixation with inclusion of the fracture level (SSFIFL) versus the traditional long-segment fixation (LSF) for the treatment of unstable thoracolumbar junction fractures.
Methods
From December 2009 to February 2014, 60 patients with unstable thoracolumbar junction fractures (T11-L2) were divided into two groups according to the number of instrumented levels. Group 1 included 30 patients treated by SSFIFL (six-screw construct including the fracture level). Group 2 included 30 patients treated by LSF (eight-screw construct excluding the fracture level). Local kyphosis angle (LKA), anterior body height (ABH), posterior body height (PBH), ABH/PBH ratio of fractured vertebra, and Asia Scale Impairment Scale were evaluated.
Results
The two groups were similar in regard to age, sex, trauma etiology, fracture level, fracture type, neurologic status, pre-operative LKA, ABH, PBH, and ABH/PBH ratio and follow-up (p > 0.05). Reduction of post-traumatic kyphosis (assessed with LKA) and restoration of fracture-induced wedge shape of the vertebral body (assessed with ABH, PBH, and ABH/PBH ratio) at post-operative period were not significantly different between group 1 and group 2 (p = 0.234; p = 0.754). There was no significant difference between the two groups in term of correction loss at the last follow-up too (LKA was 15.97° ± 5.62° for SSFIFL and 17.76° ± 11.22° for LSF [p = 0.427]). Neurological outcome was similar in both groups.
Conclusions
Inclusion of fracture level in a short-segment fixation for a thoracolumbar junction fractures results in a kyphosis correction and in a maintenance of the sagittal alignment similar to a long-segment instrumentation. Finally, this technique allowed us to save two or more segments of vertebral motion.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altay M, Ozkurt B, Aktekin CN, Ozturk AM, Dogan O, Tabak AY (2007) Treatment of unstable thoracolumbar junction burst fractures with short- or long-segment posterior fixation in Magerl type A fractures. Eur Spine J 16(8):1145–55
Cheng LM, Wang JJ, Zeng ZL, Zhu R, Yu Y, Li C, Wu ZR (2013) Pedicle screw fixation for traumatic fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:CD009073
Farrokhi MR, Razmkon A, Maghami Z, Nikoo Z (2010) Inclusion of the fracture level in short segment fixation of thoracolumbar fractures. Eur Spine J 19(10):1651–6
Guven O, Kocaoglu B, Bezer M, Aydin N, Nalbantoglu U (2009) The use of screw at the fracture level in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech 22(6):417–421
Hu R, Mustard CA, Burns C (1996) Epidemiology of incident spinal fracture in a complete population. Spine 21:492–499
Kanna RM, Shetty AP, Rajasekaran S (2015) Posterior fixation including the fractured vertebra for severe unstable thoracolumbar fractures. Spine J 15(2):256–64
Magerl F, Aebi M, Gertzbein SD, Harms J, Nazarian S (1994) A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries. Eur Spine J 3:184–201
Ökten Aİ, Gezercan Y, Özsoy KM, Ateş T, Menekşe G, Aslan A, Çetinalp E, Güzel A (2015) Results of treatment of unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures using pedicle instrumentation with and without fracture-level screws. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 157(5):831–6
Payer M (2006) Unstable burst fractures of the thoraco-lumbar junction: treatment by posterior bisegmental correction/fixation and staged anterior corpectomy and titanium cage implantation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148(3):299–306
Reinhold M, Knop C, Beisse R, Audigé L, Kandziora F, Pizanis A, Pranzl R, Gercek E, Schultheiss M, Weckbach A, Bühren V, Blauth M (2010) Operative treatment of 733 patients with acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries: comprehensive results from the second, prospective, Internet-based multicenter study of the Spine Study Group of the German Association of Trauma Surgery. Eur Spine J 19:1657–1676
Tezeren G, Kuru I (2005) Posterior fixation of thoracolumbar burst fracture: short-segment pedicle fixation versus long-segment instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech 18(6):485–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dobran, M., Nasi, D., Brunozzi, D. et al. Treatment of unstable thoracolumbar junction fractures: short-segment pedicle fixation with inclusion of the fracture level versus long-segment instrumentation. Acta Neurochir 158, 1883–1889 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2907-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2907-0