Abstract
Background
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is increasingly used for non-invasive functional mapping in preoperative evaluation for brain surgery, and the reliability of navigated TMS (nTMS) motor representation maps has been studied in the healthy population and in brain tumor patients. The lesions behind intractable epilepsy differ from typical brain tumors, ranging from developmental cortical malformations to injuries early in development, and may influence the functional organization of the cortical areas. Moreover, the interictal cortical epileptic activity and antiepileptic medication may affect the nTMS motor threshold. The reliability of the nTMS motor representation localization in epilepsy patients has not been addressed.
Methods
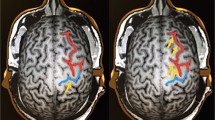
We compared the nTMS motor cortical representation maps of hand and arm muscles with the results of invasive electrical cortical stimulation (ECS) in 13 patients with focal epilepsy. The nTMS maps were projected to the cortical surface segmented from preoperative magnetic resonance images (MRI), and the positions of the subdural electrodes were extracted from the postoperative low-dose computed tomography (CT) images registered with preoperative MRI.
Results
The 3D distance between the average nTMS site and average ECS electrode location was 11 ± 4 mm for the hand and 16 ± 7 mm for arm muscle representation areas. In all patients the representation areas defined with nTMS and ECS were located on the same gyrus, also in patients with abundant interictal epileptic activity on the motor gyrus.
Conclusions
nTMS can reliably locate the hand motor cortical representation area with the accuracy needed for pre-surgical evaluation in patients with epilepsy.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APB:
-
Abductor pollicis brevis
- ADM:
-
Abductor digiti minimi
- BB:
-
Biceps brachii
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- DCS:
-
Direct cortical stimulation
- ECS:
-
Electrical cortical stimulation
- ECSCOG :
-
The weighted mean of the ECS map (arithmetic mean weighted by the inverse of the stimulating current)
- ECSE :
-
Individual ECS electrode location
- ECSG :
-
The average ECS site (arithmetic mean of the coordinates of the electrodes centers)
- ECSMIN :
-
The center of the electrode eliciting motor response with the lowest current
- EDC:
-
Extensor digitorum communis
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalography
- EMG:
-
Electromyography
- FCD:
-
Focal cortical dysplasia
- FCR:
-
Flexor carpi radialis
- MEP:
-
Motor-evoked potential
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- nTMS:
-
Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation
- nTMSG :
-
The average stimulation site (arithmetic mean of the stimulation site coordinates) projected to the brain surface of a given muscle group motor representation area in the nTMS
- RMT:
-
Resting motor threshold
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SP:
-
Silent period
- TMS:
-
Transcranial magnetic stimulation
References
Amassian VE, Cracco RQ, Maccabee PJ (1989) Focal stimulation of human cerebral cortex with the magnetic coil: a comparison with electrical stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 74:401–416
Amassian VE, Stewart M, Quirk G, Rosenthal J (1987) Physiological basis of motor effects of a transient stimulus to cerebral cortex. Neurosurgery 20:74–93
Brasil-Neto J, Cohen LG, Panizza M, Nilsson J, Roth BJ, Hallett M (1992) Optimal focal transcranial magnetic activation of the human motor cortex: effects of coil orientation, shape of the induced current pulse, and stimulus intensity. J Clin Neurophysiol 9:132–136
Classen J, Knorr U, Werhahn KJ, Schlaug G, Kunesch E, Cohen LG, Seitz RJ, Benecke R (1998) Multimodal output mapping of human central motor representation on different spatial scales. J Physiol (Lond) 512:163–179
Cohen LG (1990) Effects of coil design on delivery of focal magnetic stimulation. Technical considerations. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 75:350–357
Cruccu G, Inghilleri M, Berardelli A, Romaniello A, Manfredi M (1997) Cortical mechanisms mediating the inhibitory period after magnetic stimulation of the facial motor area. Muscle Nerve 20:418–424
Danner N, Julkunen P, Khyuppenen J, Hukkanen T, Könönen M, Säisänen L, Koskenkorva P, Vanninen R, Lehesjoki AE, Kälviäinen R, Mervaala E (2009) Altered cortical inhibition in Unverricht-Lundborg type progressive myoclonus epilepsy (EPM1). Epilepsy Res 85:81–88
Duchowny MS (2009) Clinical, functional, and neurophysiological assessment of dysplastic cortical networks: implications for cortical functioning and surgical management. Epilepsia 50:19–27
Finke M, Fadini T, Kantelhardt S, Giese A, Matthaus L, Schweikard A (2008) Brain-mapping using robotized TMS. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2008:3929–3932
Forster M, Hattingen E, Senft C, Gasser T, Seifert V, Szelényi A (2011) Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation and funcional magnetic resonance imaging—advanced adjuncts in preoperative planning for central region tumors. Neurosurgery 68:1317–1325
Hamer HM, Reis J, Mueller HH, Knake S, Overhof M, Oertel WH, Rosenow F (2005) Motor cortex excitability in focal epilepsies not including the primary motor area—a TMS study. Brain 128:811–818
Haseeb A, Asano E, Juhász C, Shah A, Sood S, Chugani HT (2007) Young patients with focal seizures may have the primary motor area for the hand in the postcentral gyrus. Epilepsy Res 76:131–139
Herwig U, Schonfeldt-Lecuona C, Wunderlich AP, von Tiesenhausen C, Thielscher A, Walter H, Spitzer M (2002) Spatial congruence of neuronavigated transcranial magnetic stimulation and functional neuroimaging. Clin Neurophysiol 113:462–468
Hill D, Maurer C, Maciunas RJ, Barwise JA, Fitzpatrick MJ, Wang MY (1998) Measurement of intraoperative brain surface deformation under a craniotomy. Neurosurgery 43:514–526
Kombos T, Süss O (2009) Neurophysiological basis of direct cortical stimulation and applied neuroanatomy of the motor cortex: a review. Neurosurg Focus 27:E3
Krieg S, Shiban E, Buchmann N, Gempt J, Foerschler A, Meyer B, Ringel F (2012) Utility of presurgical navigated transcranial magnetic brain stimulation for the resection of tumors in eloquent motor areas. J Neurosurg 116:994–1001
Krings T, Buchbinder BR, Butler WE, Chiappa KH, Jiang HJ, Rosen BR, Cosgrove GR (1997) Stereotactic transcranial magnetic stimulation: correlation with direct electrical cortical stimulation. Neurosurgery 41:1319–1325
Kumar A, Juhasz C, Asano E, Sundaram SK, Makki MI, Chugani DC, Chugani HT (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging study of the cortical origin and course of the corticospinal tract in healthy children. Am J Neuroradiol 30:1963–1970
Labyt E, Houdayer E, Cassim F, Bourriez JL, Derambure P, Devanne H (2007) Motor representation areas in epileptic patients with focal motor seizures: a TMS study. Epilepsy Res 75:197–205
Lesser RP, Lüders H, Klem G, Dinner DS, Morris HH, Hahn J (1984) Cortical afterdischarge and functional response thresholds: results of extraoperative testing. Epilepsia 25:615–621
Lesser RP, Lüders H, Klem G, Dinner DS, Morris HH, Wyllie E (1987) Extraoperative cortical functional localization in patients with epilepsy. J Clin Neurophysiol 4:27–53
Levy WJ, Amassian VE, Schmid UD, Jungreis C (1991) Mapping of motor cortex gyral sites non-invasively by transcranial magnetic stimulation in normal subjects and patients. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 43:51–75
Li X, Ricci R, Large CH, Anderson B, Nahas Z, George MS (2009) Lamotrigine and valproic acid have different effects on motorcortical neuronal excitability. J Neural Transm 116:423–429
Lotze M, Kaethner RJ, Erb M, Cohen LG, Grodd W, Topka H (2003) Comparison of representational maps using functional magnetic resonance imaging and transcranial magnetic stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol 114:306–312
Macdonell RA, Jackson GD, Curatolo JM, Abbott DF, Berkovic SF, Carey LM, Syngeniotin A, Fabinyi GC, Scheffer IE (1999) Motor cortex localization using functional MRI and transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 53:1462–1467
Mäkelä JP, Kirveskari E, Seppä M, Hämäläinen M, Forss N, Avikainen S, Salonen O, Salenius S, Kovala T, Randell T, Jääskeläinen J, Hari R (2001) Three-dimensional integration of brain anatomy and function to facilitate intraoperative navigation around the sensorimotor strip. Hum Brain Mapp 12:180–192
Mäkelä JP, Vitikainen A, Lioumis P, Paetau R, Ahtola E, Kuusela L, Valanne L, Blomstedt G, Gaily E (2012) Functional plasticity of the motor cortical structures demonstrated by navigated TMS in two patients with epilepsy. Brain Stimul. doi:10.1016/j.brs.2012.04.012
Matsumoto R, Kinoshita M, Taki J, Hitomi T, Mikuni N, Shibasaki H, Fukuyama H, Hashimoto N, Ikeda A (2005) Epileptogenicity of focal cortical dysplacia: a direct cortical paired stimulation study. Epilepsia 46:1744–1749
Nardone R, Venturi A, Ausserer H, Ladurner G, Tezzon F (2008) Cortical silent period following TMS in a patient with supplementary sensorimotor area seizures. Exp Brain Res 184:439–443
Nathan SS, Sinha SR, Gordon B, Lesser RP, Thakor NV (1993) Determination of current density distributions generated by electrical stimulation of the human cerebral cortex. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 86:183–192
Palmini A, Najm IM, Avanzini G, Babb T, Guerrini R, Foldvary-Schaefer N, Jackson GD, Lüders HO, Prayson R, Spreafico R, Vinters HV (2004) Terminology and classification of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology 62:S2–S8
Picht T, Mularski S, Kuehn B, Vajkoczy P, Kombos T, Suess O (2009) Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation for preoperative functional diagnostics in brain tumor surgery. Neurosurgery 65:93–98
Picht T, Schmidt S, Brandt S, Frey D, Hannula H, Neuvonen T, Karhu J, Vajkoczy P, Suess O (2011) Preoperative functional mapping for rolandic brain tumor surgery: comparison of navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation to direct cortical stimulation. Neurosurgery 69:581–588
Picht T, Schulz J, Hanna M, Schmidt S, Suess O, Vajkoczy P (2011) Assessment of the influence of navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation on surgical planning for tumors in or near the motor cortex. Neurosurgery 70:1248–1256
Pondal-Sordo M, Diosy D, Téllez-Zenteno JF, Girvin JP, Wiebe S (2006) Epilepsy surgery involving the sensory-motor cortex. Brain 129:3307–3314
Roberts DW, Hartov A, Kennedy FE, Miga MI, Paulsen KD (1998) Intraoperative brain shift and deformation: a quantitative analysis of cortical displacement in 28 cases. Neurosurgery 43:749–758
Rossini PM, Barker AT, Berardelli A, Caramia MD, Caruso G, Cracco RQ, Dimitrijević MR, Hallett M, Katayama Y, Lücking CH, Maertens DN, Marsden CD, Murray NMF, Rothwell JC, Swash M, Tomberg C (1994) Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord and roots: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical application. Report of an IFNC committee. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 91:79–92
Rossini PM, Rossi S (1998) Clinical applications of motor evoked potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 106:180–194
Ruohonen J, Ilmoniemi RJ (2002) Physical principles for transcranial magnetic stimulation. In: Pascual-Leone A, Davey NJ, Rothwell JC, Wassermann EM, Puri BK (eds) Handbook of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Arnold, London
Ruohonen J, Karhu J (2010) Navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurophysiol Clin 40:7–17
Säisänen L, Könönen M, Julkunen P, Määttä S, Vanninen R, Immonen A, Kälviäinen R, Jääskeläinen JE, Mervaala E (2010) Non-invasive preoperative localization of primary motor cortex in epilepsy surgery by navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation. Epilepsy Res 92:134–144
Schiffbauer H, Berger MS, Ferrari P, Freudenstein D, Rowley HA, Roberts TP (2002) Preoperative magnetic source imaging for brain tumor surgery: a quatitative comparison with intraoperative sensory and motor mapping. J Neurosurg 97:1333–1342
Schmidt S, Holst E, Irlbacher K, Oltmanns F, Merschhemke M, Brandt S (2010) A case of pathological excitability located with navigated-TMS: presurgical evaluation of focal neocortical epilepsy. Restor Neurol Neurosci 28:379–385
Solinas C, Lee YC, Reutens DC (2008) Effect of levetiracetam on cortical excitability: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Eur J Neurol 15:501–505
Sommer M, Aránzazu A, Rummel M, Speck S, Lang N, Tings T, Paulus W (2006) Half sine, monophasic and biphasic transcranial magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex. Clin Neurophysiol 117:838–844
The FIL Methods Group (2011) SPM8 Manual. Functional Imaging Laboratory, Wellcome Trust Centre for NeuroImaging, Institute of Neurology, UCL, http://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/doc/manual.pdf
Thielscher A, Kammer T (2004) Electrical field properties of two commercial figure-8 coils in TMS: calculation of focality and efficiency. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1697–1708
Van Leemput K, Hämäläinen J (2004) A cross-platform software framework for medical image processing. In: Barillot C, Haynor DR, Hellier P (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2004. Springer, Berlin, pp 1091–1092
Vitikainen A, Lioumis P, Paetau R, Salli E, Komssi S, Metsähonkala L, Paetau A, Kičić D, Blomstedt G, Valanne L, Mäkelä JP, Gaily E (2009) Combined use of non-invasive techniques for improved functional localization for a selected group of epilepsy surgery candidates. NeuroImage 45:342–348
Wassermann EM, Wang B, Zeffiru TA, Sadato N, Pascual-Leone A, Toro C, Hallett M (1996) Locating the motor cortex on the MRI with transcranial magnetic stimulation and PET. NeuroImage 3:1–9
Wilson SA, Thickbroom GW, Mastaglia FL (1993) Topography of excitatory and inhibitory muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation in the human motor cortex. Neurosci Lett 154:52–56
Yousry TA, Schmid UD, Alkadhi H, Schmidt D, Peraud A, Buettner A, Winkler P (1997) Localization of the motor hand area to a knob on the precentral gyrus. A new landmark. Brain 120:141–157
Ziemann U (2004) TMS and drugs. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1717–1729
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the staff contributing to the pre- and postoperative studies, diagnostics and data collection. Phil.Lic. Anne-Mari Vitikainen received a grant from the Finnish Cultural Foundation during the preparation of this manuscript. Ph.D. Pantelis Lioumis was supported by Helsinki University Central Hospital (EVO research funding) and the SalWe Research Program for Mind and Body (Tekes,the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation, grant 1104/10).
Conflicts of interest
Dr. Eero Salli discloses a consultation fee from Nexstim in 2009 before the initiation of this study. Ph.D. Pantelis Lioumis dicloses a consultation fee from Nexstim in 2011. Dr. Jyrki P. Mäkelä, Dr. Liisa Metsähonkala, and Phil.Lic. Anne-Mari Vitikainen report no financial interest or potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table A
Details of the electrode grids and the stimulated electrodes evoking positive motor responses for each patient. REF refers to reference electrode not evoking a response in monopolar arrangement. (XLS 52.5 KB)
Table B
Hand and arm muscle group results for maps done with monophasic stimulating pulses with motor-evoked potential (MEP) responses in navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation (nTMS) for the distance parameters dist(nTMSG,ECSCOG) and dist(nTMSG,ECSMIN). The mean, standard deviation (SD) and ranges are given. nTMSG refers to the average stimulation site in nTMS, ECSCOG to the weighted average of the corresponding electrode locations, ECSMIN to the location of the electrode evoking motor response with the minimum current and n/a to not available. (XLS 44 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vitikainen, AM., Salli, E., Lioumis, P. et al. Applicability of nTMS in locating the motor cortical representation areas in patients with epilepsy. Acta Neurochir 155, 507–518 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1609-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1609-5