Abstract
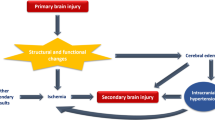
Dysfunction of neuronal signal processing and transmission occurs after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) and contributes to the high morbidity and mortality of this pathology. The underlying mechanisms include early brain injury due to elevation of the intracranial pressure, disruption of the blood–brain barrier, brain edema, reduction of cerebral blood flow, and neuronal cell death. Direct influence of subarachnoid blood metabolites on neuronal signaling should be considered. After SAH, some metabolites were shown to directly induce disruption of neuronal integrity and neuronal signaling, whereas the effects of other metabolites on neurotoxicity and neuronal signaling have not yet been investigated. Therefore, this mini-review will discuss recent evidence for a direct influence of subarachnoid blood and its metabolites on neuronal function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Khindi T, Macdonald RL, Schweizer TA (2010) Cognitive and functional outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 41(8):e519–e536
Auerbach JM, Segal M (1997) Peroxide modulation of slow-onset potentiation in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 17(22):8695–8701
Auriat AM, Silasi G, Wei Z, Paquette R, Paterson P, Nichol H, Colbourne F (2012) Ferric iron chelation lowers brain iron levels after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats but does not improve outcome. Exp Neurol 234(1):136–143
Ayer RE, Zhang JH (2008) The clinical significance of acute brain injury in subarachnoid hemorrhage and opportunity for intervention. Acta Neurochir Suppl 105:179–184
Barnham KJ, Bush AI (2008) Metals in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12(2):222–228
Bavaresco CS, Chiarani F, Matte C, Wajner M, Netto CA, Souza Wyse AT (2005) Effect of hypoxanthine on Na+, K+-ATPase activity and some parameters of oxidative stress in rat striatum. Brain Res 1041(2):198–204
Bendel O, Prunell G, Stenqvist A, Mathiesen T, Holmin S, Svendgaard NA, Euler G (2005) Experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage induces changes in the levels of hippocampal NMDA receptor subunit mRNA. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 137(1–2):119–125
Berry E, Jones RA, West CG, Brown JD (1997) Outcome of subarachnoid haemorrhage. An analysis of surgical variables, cognitive and emotional sequelae related to SPECT scanning. Br J Neurosurg 11(5):378–387
Bilgihan A, Turkozkan N, Aricioglu A, Aykol S, Cevik C, Goksel M (1994) The effect of deferoxamine on brain lipid peroxide levels and Na-K ATPase activity following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Gen Pharmacol 25(3):495–497
Bliss TV, Richter-Levin G (1993) Spatial learning and the saturation of long-term potentiation. Hippocampus 3(2):123–125
Brites D (2011) Bilirubin injury to neurons and glial cells: new players, novel targets, and newer insights. Semin Perinatol 35(3):114–120
Chang FY, Lee CC, Huang CC, Hsu KS (2009) Unconjugated bilirubin exposure impairs hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity. PLoS One 4(6):e5876
Chen-Roetling J, Liu W, Regan RF (2011) Iron accumulation and neurotoxicity in cortical cultures treated with holotransferrin. Free Radic Biol Med 51(11):1966–1974
Clark JF, Harm A, Saffire A, Biehle SJ, Lu A, Pyne-Geithman GJ (2011) Bilirubin oxidation products seen post subarachnoid hemorrhage have greater effects on aged rat brain compared to young. Acta Neurochir Suppl 110(Pt 1):157–162
Dang TN, Robinson SR, Dringen R, Bishop GM (2011) Uptake, metabolism and toxicity of hemin in cultured neurons. Neurochem Int 58:804–811
Dreier JP, Ebert N, Priller J, Megow D, Lindauer U, Klee R, Reuter U, Imai Y, Einhaupl KM, Victorov I, Dirnagl U (2000) Products of hemolysis in the subarachnoid space inducing spreading ischemia in the cortex and focal necrosis in rats: a model for delayed ischemic neurological deficits after subarachnoid hemorrhage? J Neurosurg 93(4):658–666
Dreier JP, Windmuller O, Petzold G, Lindauer U, Einhaupl KM, Dirnagl U (2002) Ischemia triggered by red blood cell products in the subarachnoid space is inhibited by nimodipine administration or moderate volume expansion/hemodilution in rats. Neurosurgery 51(6):1457–1465
Egge A, Waterloo K, Sjoholm H, Ingebrigtsen T, Forsdahl S, Jacobsen EA, Romner B (2005) Outcome 1 year after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: relation between cognitive performance and neuroimaging. Acta Neurol Scand 112(2):76–80
Falcao AS, Silva RF, Pancadas S, Fernandes A, Brito MA, Brites D (2007) Apoptosis and impairment of neurite network by short exposure of immature rat cortical neurons to unconjugated bilirubin increase with cell differentiation and are additionally enhanced by an inflammatory stimulus. J Neurosci Res 85(6):1229–1239
Gasparova Z, Jariabka P, Stolc S (2008) Effect of transient ischemia on long-term potentiation of synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal slices. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 29(5):702–705
Giniatullin AR, Darios F, Shakirzyanova A, Davletov B, Giniatullin R (2006) SNAP25 is a pre-synaptic target for the depressant action of reactive oxygen species on transmitter release. J Neurochem 98(6):1789–1797
Giniatullin AR, Giniatullin RA (2003) Dual action of hydrogen peroxide on synaptic transmission at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol 552(Pt 1):283–293
Giniatullin AR, Grishin SN, Sharifullina ER, Petrov AM, Zefirov AL, Giniatullin RA (2005) Reactive oxygen species contribute to the presynaptic action of extracellular ATP at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol 565(Pt 1):229–242
Goldstein L, Teng ZP, Zeserson E, Patel M, Regan RF (2003) Hemin induces an iron-dependent, oxidative injury to human neuron-like cells. J Neurosci Res 73(1):113–121
Grojean S, Koziel V, Vert P, Daval JL (2000) Bilirubin induces apoptosis via activation of NMDA receptors in developing rat brain neurons. Exp Neurol 166(2):334–341
Gu Y, Hua Y, He Y, Wang L, Hu H, Keep RF, Xi G (2011) Iron accumulation and DNA damage in a pig model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 111:123–128
Hadjivassiliou M, Tooth CL, Romanowski CA, Byrne J, Battersby RD, Oxbury S, Crewswell CS, Burkitt E, Stokes NA, Paul C, Mayes AR, Sagar HJ (2001) Aneurysmal SAH: cognitive outcome and structural damage after clipping or coiling. Neurology 56(12):1672–1677
Hahm ET, Seo JW, Hur J, Cho YW (2010) Modulation of presynaptic GABA release by oxidative stress in mechanically-isolated rat cerebral cortical neurons. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 14(3):127–132
Hasegawa Y, Suzuki H, Sozen T, Altay O, Zhang JH (2011) Apoptotic mechanisms for neuronal cells in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 110(Pt 1):43–48
Hirata K, Kawano T, Mori K (1993) Changes in monoaminergic neuronal function in the lower brain stem following subarachnoid hemorrhage induced in rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 13(6):639–648
Joseph JA, Erat S, Denisova N, Villalobos-Molina R (1998) Receptor- and age-selective effects of dopamine oxidation on receptor-G protein interactions in the striatum. Free Radic Biol Med 24(5):827–834
Kamsler A, Segal M (2004) Hydrogen peroxide as a diffusible signal molecule in synaptic plasticity. Mol Neurobiol 29(2):167–178
Katsuki H, Nakanishi C, Saito H, Matsuki N (1997) Biphasic effect of hydrogen peroxide on field potentials in rat hippocampal slices. Eur J Pharmacol 337(2–3):213–218
Klann E, Roberson ED, Knapp LT, Sweatt JD (1998) A role for superoxide in protein kinase C activation and induction of long-term potentiation. J Biol Chem 273(8):4516–4522
Kranc KR, Pyne GJ, Tao L, Claridge TD, Harris DA, Cadoux-Hudson TA, Turnbull JJ, Schofield CJ, Clark JF (2000) Oxidative degradation of bilirubin produces vasoactive compounds. Eur J Biochem 267(24):7094–7101
Kreiter KT, Copeland D, Bernardini GL, Bates JE, Peery S, Claassen J, Du YE, Stern Y, Connolly ES, Mayer SA (2002) Predictors of cognitive dysfunction after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 33(1):200–208
Kvaltinova Z, Lukovic L, Stolc S (1993) Effect of incomplete ischemia and reperfusion of the rat brain on the density and affinity of alpha-adrenergic binding sites in the cerebral cortex. Prevention of changes by stobadine and vitamin E. Neuropharmacology 32(8):785–791
Laird MD, Wakade C, Alleyne CH Jr, Dhandapani KM (2008) Hemin-induced necroptosis involves glutathione depletion in mouse astrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med 45(8):1103–1114
Lee JY, Keep RF, He Y, Sagher O, Hua Y, Xi G (2010) Hemoglobin and iron handling in brain after subarachnoid hemorrhage and the effect of deferoxamine on early brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(11):1793–1803
Lee JY, Keep RF, Hua Y, Ernestus RI, Xi G (2011) Deferoxamine reduces early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 112:101–106
Levy YS, Streifler JY, Panet H, Melamed E, Offen D (2002) Hemin-induced apoptosis in PC12 and neuroblastoma cells: implications for local neuronal death associated with intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurotox Res 4(7–8):609–616
Li B, Luo C, Tang W, Chen Z, Li Q, Hu B, Lin J, Zhu G, Zhang JH, Feng H (2012) Role of HCN channels in neuronal hyperexcitability after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Neurosci 32(9):3164–3175
Li CY, Shi HB, Song NY, Yin SK (2011) Bilirubin enhances neuronal excitability by increasing glutamatergic transmission in the rat lateral superior olive. Toxicology 284(1–3):19–25
Li CY, Shi HB, Wang J, Ye HB, Song NY, Yin SK (2011) Bilirubin facilitates depolarizing GABA/glycinergic synaptic transmission in the ventral cochlear nucleus of rats. Eur J Pharmacol 660(2–3):310–317
Matz PG, Fujimura M, Lewen A, Morita-Fujimura Y, Chan PH (2001) Increased cytochrome c-mediated DNA fragmentation and cell death in manganese-superoxide dismutase-deficient mice after exposure to subarachnoid hemolysate. Stroke 32(2):506–515
McDonald JW, Shapiro SM, Silverstein FS, Johnston MV (1998) Role of glutamate receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in bilirubin-induced brain injury in the Gunn rat model. Exp Neurol 150(1):21–29
Paramo B, Hernandez-Fonseca K, Estrada-Sanchez AM, Jimenez N, Hernandez-Cruz A, Massieu L (2010) Pathways involved in the generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species during glucose deprivation and its role on the death of cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 167(4):1057–1069
Regan RF, Chen J, Benvenisti-Zarom L (2004) Heme oxygenase-2 gene deletion attenuates oxidative stress in neurons exposed to extracellular hemin. BMC Neurosci 5:34
Regan RF, Panter SS (1993) Neurotoxicity of hemoglobin in cortical cell culture. Neurosci Lett 153(2):219–222
Regan RF, Rogers B (2003) Delayed treatment of hemoglobin neurotoxicity. J Neurotrauma 20(1):111–120
Rocchitta G, Migheli R, Mura MP, Grella G, Esposito G, Marchetti B, Miele E, Desole MS, Miele M, Serra PA (2005) Signaling pathways in the nitric oxide and iron-induced dopamine release in the striatum of freely moving rats: role of extracellular Ca2+ and L-type Ca2+ channels. Brain Res 1047(1):18–29
Rodrigues CM, Sola S, Brites D (2002) Bilirubin induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in developing rat brain neurons. Hepatology 35(5):1186–1195
Rodrigues CM, Sola S, Brito MA, Brites D, Moura JJ (2002) Bilirubin directly disrupts membrane lipid polarity and fluidity, protein order, and redox status in rat mitochondria. J Hepatol 36(3):335–341
Rogers B, Yakopson V, Teng ZP, Guo Y, Regan RF (2003) Heme oxygenase-2 knockout neurons are less vulnerable to hemoglobin toxicity. Free Radic Biol Med 35(8):872–881
Romner B, Sonesson B, Ljunggren B, Brandt L, Saveland H, Holtas S (1989) Late magnetic resonance imaging related to neurobehavioral functioning after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 25(3):390–396
Sah R, Galeffi F, Ahrens R, Jordan G, Schwartz-Bloom RD (2002) Modulation of the GABA(A)-gated chloride channel by reactive oxygen species. J Neurochem 80(3):383–391
Saida A, Ito H, Shibuya T, Watanabe Y (1997) Time-course alterations of monoamine levels and cerebral blood flow in brain regions after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Brain Res Bull 43(1):69–80
Saveland H, Nilsson OG, Boris-Moller F, Wieloch T, Brandt L (1996) Intracerebral microdialysis of glutamate and aspartate in two vascular territories after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 38(1):12–19
Selim M (2009) Deferoxamine mesylate: a new hope for intracerebral hemorrhage: from bench to clinical trials. Stroke 40(3 Suppl):S90–S91
Shi HB, Kakazu Y, Shibata S, Matsumoto N, Nakagawa T, Komune S (2006) Bilirubin potentiates inhibitory synaptic transmission in lateral superior olive neurons of the rat. Neurosci Res 55(2):161–170
Tariq A, Ai J, Chen G, Sabri M, Jeon H, Shang X, Macdonald RL (2010) Loss of long-term potentiation in the hippocampus after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Neuroscience 165(2):418–426
van Gijn J, Kerr RS, Rinkel GJ (2007) Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet 369(9558):306–318
Vaz AR, Silva SL, Barateiro A, Falcao AS, Fernandes A, Brito MA, Brites D (2011) Selective vulnerability of rat brain regions to unconjugated bilirubin. Mol Cell Neurosci 48(1):82–93
Wang X, Mori T, Sumii T, Lo EH (2002) Hemoglobin-induced cytotoxicity in rat cerebral cortical neurons: caspase activation and oxidative stress. Stroke 33(7):1882–1888
Yip S, Ip JK, Sastry BR (1996) Electrophysiological actions of hemoglobin on rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Brain Res 713(1–2):134–142
Yip S, Sastry BR (2000) Effects of hemoglobin and its breakdown products on synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal CA1 neurons. Brain Res 864(1):1–12
Zecca L, Youdim MB, Riederer P, Connor JR, Crichton RR (2004) Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(11):863–873
Zhang L, Liu W, Tanswell AK, Luo X (2003) The effects of bilirubin on evoked potentials and long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus in vivo. Pediatr Res 53(6):939–944
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kamp and Dibué contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamp, M.A., Dibué, M., Etminan, N. et al. Evidence for direct impairment of neuronal function by subarachnoid metabolites following SAH. Acta Neurochir 155, 255–260 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1559-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1559-y