Abstract
Background
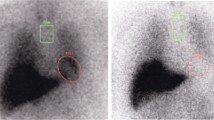
123I-meta-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) myocardial scintigraphy is a useful tool for differentiating idiopathic Parkinson's disease (PD) from other parkinsonian syndromes, but its prognostic value in PD has not been established. The objective of this study was to clarify the correlation between cardiac MIBG uptake parameters and the outcome in PD patients subjected to the subthalamic nucleus stimulation.
Method
We enrolled 31 consecutive PD patients and calculated the heart-to-mediastinum ratio (H/M) and washout rate (WR) based on the activity measured at 15 min (early phase) and 3 h (delayed phase) after the intravenous injection of MIBG (111 MBq). Cardinal motor symptoms and activity of daily living (ADL) were assessed on the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) and Schwab and England (S–E) ADL scale, before and 3 months after surgery.
Findings
Neither early nor delayed H/M correlated with any of the preoperative subscores on the UPDRS or S–E, nor with postoperative outcome. On the other hand, increased WR was a positive predictor for postoperative improvement rate on S–E in medication-off state (p = 0.00003). Also, WR showed a more faint but significant correlation with preoperative levodopa responsiveness on S–E (p = 0.008).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that 123I-MIBG scintigraphy in combination with levodopa-responsiveness evaluation may represent a useful tool for prediction of outcomes in patients subjected to STN stimulation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando Y, Obayashi K, Tanaka Y, Tsuji T, Uchino M, Takahashi M, Ando M (1994) Radiolabelled metaiodobenzylguanidine in assessment of autonomic dysfunction. Lancet 343:984–985
Braak H, Tredici KD, Rüb U, de Vos RAI, Ernst NH, Steur ENHJ, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Charles PD, Van Blercom N, Krack P, Lee SL, Xie J, Besson G, Benabid AL, Pollak P (2002) Predictors of effective bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation for PD. Neurology 59:932–934
Chung EJ, Lee WY, Yoon WT, Kim BJ, Lee GH (2009) MIBG scintigraphy for differentiating Parkinson's disease with autonomic dysfunction from Parkinsonism- predominant multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 24:1650–1655
Erola T, Heikkinen ER, Haapaniemi T, Tuominen J, Juolasmaa A, Myllylä VV (2006) Efficacy of bilateral subthalamic nucleus (STN) stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:389–394
Hakusui S, Yasuda T, Yanagi T, Tohyama J, Hasegawa Y, Koike Y, Hirayama M, Takahashi A (1994) A radiological analysis of heart sympathetic functions with meta-[123I] iodobenzylguanidine in neurological patients with autonomic failure. J Auton Nerv Syst 49:81–84
Hallett M, Litvan I (1999) The task force on surgery for Parkinson's disease. Evaluation of surgery for Parkinson's disease. A report of the therapeutic and technology assessment subcommittee of the American academy of neurology. Neurology 53:1910–1921
Iwanaga K, Wakabayashi K, Yoshimoto M, Tomita I, Satoh H, Takashima H, Satoh A, Seto M, Tsujihata M, Takahashi H (1999) Lewy body-type degeneration in cardiac plexus in Parkinson's and incidental Lewy body disease. Neurology 52:1269–1271
Kasama S, Toyama T, Sumino H, Nakazawa M, Matsumoto N, Sato Y, Kumakura H, Takayama Y, Ichikawa S, Suzuki T, Kurabayashi M (2008) Prognostic value of serial cardiac 123I-MIBG imaging in patients with stabilized chronic heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. J Nucl Med 49:907–914
Katayama Y, Kasai M, Oshima H, Fukaya C, Yamamato T, Ogawa K, Mizutani T (2001) Subthalamic nucleus stimulation for Parkinson disease: benefits observed in levodopa-intolerant patients. J Neurosurg 95:213–221
Kleiner-Fisman G, Herzog J, Fisman DN, Tamma F, Lyons KE, Pahwa R, Lang AE, Deuschl G (2006) Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation: summary and meta-analysis of outcomes. Mov Disord 21(Suppl 14):S290–S304
Krack P, Batir A, van Blercom N, Chabardes S, Fraix V, Ardouin C, Koudsie A, Limousin P, Benazzouz A, LeBas JF, Benabid A-L, Pollak P (2003) A five-year follow-up of bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson's disease. N Eng J Med 349:1925–1934
Langston JW (2006) The Parkinson's complex: Parkinsonism is just the tip of the iceberg. Ann Neurol 59:591–596
Lyons KE, Davis JT, Pahwa R (2007) Subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson's disease patients intolerant to levodopa. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85:169–174
Merlet P, Valette H, Dubois-Randé JL, Moyse D, Duboc D, Dove P (1992) Bourguignon MH, Benvenuti C, Duval AM, Agostini D, Loisance D, Castaigne A, Syrota A. Prognostic value of cardiac metaiodobenzylguanidine imaging in patients with heart failure. J Nucl Med 33:471–477
Moro E, Scerrati M, Romito LMA, Roselli R, Tonali P, Albanese A (1999) Chronic subthalamic nucleus stimulation reduces medication requirements in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 53:85–90
Nagamachi S, Wakamatsu H, Kiyohara S, Fujita S, Futami S, Tamura S, Nakazato M, Yamashita S, Arita H, Nishii R, Kawai K (2008) Usefulness of rCBF analysis in diagnosing Parkinson's disease: supplemental role with MIBG myocardial scintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med 22:557–564
Nagayama H, Hamamoto M, Ueda M, Nagashima J, Katayama Y (2005) Reliability of MIBG myocardial scintigraphy in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:249–251
Orimo S, Ozawa E, Oka T, Nakade S, Tsuchiya K, Yoshimoto M, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H (2001) Differentional histopathology accounting for a decrease in myocardial MIBG uptake in PD and MSA. Neurology 57:1140–1141
Østergaard K, Sunde N, Dupont E (2002) Effects of bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with severe Parkinson's disease and motor fluctuations. Mov Disord 17:693–700
Post KK, Singer C, Papapetropoulos S (2008) Cardiac denervation and dysautonomia in Parkinson's disease: a review of screening techniques. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 14:524–531
Romito LM, Scerrati M, Contarino MF, Bentivoglio AR, Tonali P, Albanese A (2002) Long-term follow up of subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Neurology 58:1546–1550
Taki J, Nakajima K, Hwang EH, Matsunari I, Komai K, Yoshita M, Sakajiri K (2000) Tonami N (2000) Peripheral sympathetic dysfunction in patients with Parkinson's disease without autonomic failure is heart selective and disease specific. Eur J Nucl Med 27:566–573
Taki J, Yoshita M, Yamada M, Tonami N (2004) Significance of 123I-MIBG scintigraphy as a pathophysiological indicator in the assessment of Parkinson's disease and related disorders: it can be a specific marker for Lewy body disease. Ann Nucl Med 18:453–461
Verberne HJ, Brewster LM, Somsen GA, van Eck-Smit BL (2008) Prognostic value of myocardinal 123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) parameters in patients with heart failure: a systemic review. Eur Heart J 29:1147–1159
Vingerhoets FJ, Villemure JG, Temperli P, Pollo C, Pralong E, Ghika J (2002) Subthalamic DBS replaces levodopa in Parkinson's disease: two-year follow-up. Neurology 58:396–401
Welter ML, Houeto JL, Tezenas du Montcel S, Mesnage V, Bonnet AM, Pillon B, Agid Y et al (2002) Clinical predictive factors of subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Brain 125:575–583
Yamada K, Goto S, Hamasaki T, Kuratsu J-I (2008) Effect of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation on levodopa-unresponsive axial symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150:15–22
Yamada K, Goto S, Kuratsu J, Matsuzaki K, Nagahiro S, Shimazu H, Kaji R (2007) General anesthesia for stereotactic implantation of stimulating electrodes within the subthalamic nucleus. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 13:101–107
Yoshita M, Taki J, Yokoyama K, Noguchi-Shinohara M, Matsumoto Y, Nakajima K, Yamada M (2006) 123I-MIBG radioactivity in the differential diagnosis of DLB from AD. Neurology 66:1850–1854
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and a foundation subscribed by Hokuto Hospital, Obihiro, Hokkaido, Japan.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and a foundation subscribed by Hokuto Hospital, Obihiro, Hokkaido, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, K., Shiraishi, Sy., Hamasaki, T. et al. Cardiac 123I-MIBG scintigraphy as an outcome-predicting tool for subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurochir 152, 2063–2068 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0825-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0825-0