Abstract
Background
Vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which involves injecting polymethylmethacrylate into the compressed vertebral body. At present the indications include the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures, vertebral myeloma, and metastases. The value of vertebroplasty in osteoporotic compression fracture has been discussed comprehensively. The surgical operation for burst fractures without neurological deficit remains controversial. Some authors have asserted that vertebroplasty is contraindicated in patients with burst fracture. However, we performed the procedure, after considering the patents general condition, to reduce surgical risks and the duration of immobilisation. The purpose of this study is to investigate clinical outcomes, kyphosis correction, wedge angle, and height restoration of thoraco-lumbar osteoporotic burst fractures treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty.
Materials and methods
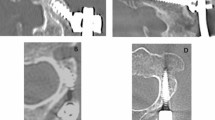
Twenty-five patients with osteoporotic burst fracture were treated with postural reduction followed by vertebroplasty. We measured the kyphosis, wedge angle, spinal canal compromise and the height of the fractured vertebral body initially, after postural reduction, and after vertebroplasty.
Findings
The average height of the collapsed vertebral bodies was 24.8% of the original height. Average kyphosis angle was 19.4° and average wedge angle was 19.8° at first. Mean canal encroachment was initially 25.1%. Kyphosis angle, wedge angle, and anterior, middle, and posterior height improved significantly after the procedure. The mean amelioration of the spinal canal encroachment after vertebroplasty was 23.3%. The average increase in anterior vertebral body height was 7.5 mm, central was 5.8 mm, and posterior was 0.9 mm. The mean reduction in kyphosis angle was 6.8° and the mean reduction in wedge angle was 9.7°.
Conclusion
Although vertebroplasty has been considered as contraindicated in thoraco-lumbar burst fractures, we successfully used the procedure as a safe treatment in patients with osteoporotic burst fracture without neurologic deficit. This method could eliminate the need for and risks of major spinal surgery. We would like to offer it as a relatively safe and effective methods of management in thoraco-lumbar burst fractures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ, McCann RM (2000) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal stabilization. Spine 25:923–928
Been HD, Bouma GJ (1999) Comparison of two types of surgery for thoraco-lumbar burst fractures: combined anterior and posterior stabilisation vs. posterior instrumentation only. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 141:349–357
Benson DR, Burkus JK, Montesano PX, Sutherland TB, McLain RF (1992) Unstable thoraco-lumbar and lumbar burst fractures treated with the AO fixateur interne. J Spinal Disord 5:335–343
Bradford DS, McBride GG (1987) Surgical management of thoraco-lumbar spine fractures with incomplete neurologic deficits. Clin Orthop Relat Res(218):201–216
Cantor JB, Lebwohl NH, Garvey T, Eismont FJ (1993) Nonoperative management of stable thoraco-lumbar burst fractures with early ambulation and bracing. Spine 18:971–976
Chen YJ, Tan TS, Chen WH, Chen CC, Lee TS (2006) Intradural cement leakage: a devastatingly rare complication of vertebroplasty. Spine 31:E379–E382
Chin DK, Kim YS, Cho YE, Shin JJ (2006) Efficacy of postural reduction in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures followed by percutaneous vertebroplasty. Neurosurgery 58:695–700 (discussion 695–700)
Cotten A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, Assaker R, Leblond D, Duquesnoy B, Chastanet P, Clarisse J (1996) Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up. Radiology 200:525–530
Danisa OA, Shaffrey CI, Jane JA, Whitehill R, Wang GJ, Szabo TA, Hansen CA, Shaffrey ME, Chan DP (1995) Surgical approaches for the correction of unstable thoraco-lumbar burst fractures: a retrospective analysis of treatment outcomes. J Neurosurg 83:977–983
Denis F (1983) The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoraco-lumbar spinal injuries. Spine 8:817–831
Denis F, Armstrong GW, Searls K, Matta L (1984) Acute thoraco-lumbar burst fractures in the absence of neurologic deficit. A comparison between operative and nonoperative treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res(189):142–149
Deramond H, Depriester C, Galibert P, Le Gars D (1998) Percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate. Technique, indications, and results. Radiol Clin North Am 36:533–546
Devlin VJ (2003) Spine secrets. Hanley & Belfus, Philadelphia, PA
Dickson JH, Harrington PR, Erwin WD (1978) Results of reduction and stabilization of the severely fractured thoracic and lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am 60:799–805
Dimar JR 2nd, Wilde PH, Glassman SD, Puno RM, Johnson JR (1996) Thoraco-lumbar burst fractures treated with combined anterior and posterior surgery. Am J Orthop 25:159–165
Farcy JP, Weidenbaum M, Glassman SD (1990) Sagittal index in management of thoraco-lumbar burst fractures. Spine 15:958–965
Frymoyer JW, Wiesel SW (2004) The adult and pediatric spine. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D (1987) [Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty]. Neurochirurgie 33:166–168
Gertzbein SD, Court-Brown CM, Marks P, Martin C, Fazl M, Schwartz M, Jacobs RR (1988) The neurological outcome following surgery for spinal fractures. Spine 13:641–644
Grados F, Depriester C, Cayrolle G, Hardy N, Deramond H, Fardellone P (2000) Long-term observations of vertebral osteoporotic fractures treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty. Rheumatology (Oxford) 39:1410–1414
Harrington KD (2001) Major neurological complications following percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83-A:1070–1073
Heini PF, Walchli B, Berlemann U (2000) Percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty with PMMA: operative technique and early results. A prospective study for the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures. Eur Spine J 9:445–450
Hiwatashi A, Moritani T, Numaguchi Y, Westesson PL (2003) Increase in vertebral body height after vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:185–189
Jacobs RR, Asher MA, Snider RK (1980) Thoraco-lumbar spinal injuries. A comparative study of recumbent and operative treatment in 100 patients. Spine 5:463–477
Jacobs RR, Casey MP (1984) Surgical management of thoraco-lumbar spinal injuries. General principles and controversial considerations. Clin Orthop Relat Res(189):22–35
Jensen ME, Evans AJ, Mathis JM, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Dion JE (1997) Percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body compression fractures: technical aspects. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:1897–1904
Kramer DL, Rodgers WB, Mansfield FL (1995) Transpedicular instrumentation and short-segment fusion of thoraco-lumbar fractures: a prospective study using a single instrumentation system. J Orthop Trauma 9:499–506
Kuklo TR, Polly DW, Owens BD, Zeidman SM, Chang AS, Klemme WR (2001) Measurement of thoracic and lumbar fracture kyphosis: evaluation of intraobserver, interobserver, and technique variability. Spine 26:61–65 (discussion 66)
Louis R (1985) Spinal stability as defined by the three-column spine concept. Anat Clin 7:33–42
Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM, Barr MS, Jensen ME, Deramond H (2001) Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:373–381
Mathis JM, Petri M, Naff N (1998) Percutaneous vertebroplasty treatment of steroid-induced osteoporotic compression fractures. Arthritis Rheum 41:171–175
McAfee PC, Yuan HA, Fredrickson BE, Lubicky JP (1983) The value of computed tomography in thoraco-lumbar fractures. An analysis of one hundred consecutive cases and a new classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am 65:461–473
McKiernan F, Jensen R, Faciszewski T (2003) The dynamic mobility of vertebral compression fractures. J Bone Miner Res 18:24–29
McLain RF, Sparling E, Benson DR (1993) Early failure of short-segment pedicle instrumentation for thoraco-lumbar fractures. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75:162–167
Mumford J, Weinstein JN, Spratt KF, Goel VK (1993) Thoraco-lumbar burst fractures. The clinical efficacy and outcome of nonoperative management. Spine 18:955–970
Oner FC, Verlaan JJ, Verbout AJ, Dhert WJ (2006) Cement augmentation techniques in traumatic thoraco-lumbar spine fractures. Spine 31:S89–S95 (discussion S104)
Payer M (2006) Unstable burst fractures of the thoraco-lumbar junction: treatment by posterior bisegmental correction/fixation and staged anterior corpectomy and titanium cage implantation. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:299–306 (discussion 306)
Schnee CL, Ansell LV (1997) Selection criteria and outcome of operative approaches for thoraco-lumbar burst fractures with and without neurological deficit. J Neurosurg 86:48–55
Seybold EA, Sweeney CA, Fredrickson BE, Warhold LG, Bernini PM (1999) Functional outcome of low lumbar burst fractures. A multicenter review of operative and nonoperative treatment of L3–L5. Spine 24:2154–2161
Shen WJ, Liu TJ, Shen YS (2001) Nonoperative treatment versus posterior fixation for thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures without neurologic deficit. Spine 26:1038–1045
Shen WJ, Shen YS (1999) Nonsurgical treatment of three-column thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures without neurologic deficit. Spine 24:412–415
Teng MM, Cheng H, Ho DM, Chang CY (2006) Intraspinal leakage of bone cement after vertebroplasty: a report of 3 cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:224–229
Teng MM, Wei CJ, Wei LC, Luo CB, Lirng JF, Chang FC, Liu CL, Chang CY (2003) Kyphosis correction and height restoration effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1893–1900
Tropiano P, Huang RC, Louis CA, Poitout DG, Louis RP (2003) Functional and radiographic outcome of thoraco-lumbar and lumbar burst fractures managed by closed orthopaedic reduction and casting. Spine 28:2459–2465
Trumm CG, Jakobs TF, Zech CJ, Weber C, Reiser MF, Hoffmann RT (2006) [Vertebroplasty in the treatment of back pain]. Radiologe 46:495–505
Truumees E, Hilibrand A, Vaccaro AR (2004) Percutaneous vertebral augmentation. Spine J 4:218–229
Tsai TT, Chen WJ, Lai PL, Chen LH, Niu CC, Fu TS, Wong CB (2003) Polymethylmethacrylate cement dislodgment following percutaneous vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine 28:E457–E460
Weill A, Chiras J, Simon JM, Rose M, Sola-Martinez T, Enkaoua E (1996) Spinal metastases: indications for and results of percutaneous injection of acrylic surgical cement. Radiology 199:241–247
Wilcox RK, Allen DJ, Hall RM, Limb D, Barton DC, Dickson RA (2004) A dynamic investigation of the burst fracture process using a combined experimental and finite element approach. Eur Spine J 13:481–488
Winking M, Stahl JP, Oertel M, Schnettler R, Boker DK (2004) Treatment of pain from osteoporotic vertebral collapse by percutaneous PMMA vertebroplasty. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:469–476
Winn HR, Youmans JR (2004) Youmans neurological surgery. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, J.J., Chin, D.K. & Yoon, Y.S. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic burst fractures. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 151, 141–148 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0189-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0189-5