Abstract
A new species belonging to Aspergillus section Cremei is described, A. europaeus sp. nov. This species is most closely related to A. wentii, A. dimorphicus, and A. chrysellus and can be distinguished by an unique phenotype (colour of sporulation, production of yellow soluble pigment on MEA, shape of vesicle, ornamentation of conidia), specific spectrum of produced exometabolites and internal transcribed spacers (ITS), β-tubulin and calmodulin gene sequence data. In total, 18 isolates were identified which originated from soil (n = 14), cork (n = 2), indoor air (n = 1) and clinical material (n = 1) in the Czech Republic, Romania, Spain, Portugal, France and Tunisia. All strains were first identified by morphological characters as A. wentii or A. tamarii suggesting that A. europaeus is a common species but it has been overlooked and frequently misidentified. The ex-type strain is CCF 4409T = CBS 134393T = IBT 32228T = NRRL 66252T.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berka RM, Dunn-Coleman N, Ward M (1992) Industrial enzymes from Aspergillus species. In: Bennett JW, Klich MA (eds) Aspergillus: biology and industrial applications, vol 23. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, pp 155–202
Busi S, Peddikotla P, Upadyayula SM, Yenamandra V (2009) Isolation and biological evaluation of two bioactive metabolites from Aspergillus gorakhpurensis. Rec Nat Prod 3:161–164
Crous PW, Wingfield MJ, Le Roux JJ, Richardson DM, Strasberg D, Shivas RG, Alvarado P, Edwards J, Moreno G, Sharma R, Sonawane MS, Tan YP, Altés A, Barasubiye T, Barnes CW, Blanchette RA, Boertmann D, Bogo A, Carlavilla JR, Cheewangkoon R, Daniel R, de Beer ZW, de Jesús Yáñez-Morales M, Duong TA, Fernández-Vicente J, Geering ADW, Guest DI, Held BW, Heykoop M, Hubka V, Ismail AM, Kajale SC, Khemmuk W, Kolařík M, Kurli R, Lebeuf R, Lévesque CA, Lombard L, Magista D, Manjón JL, Marincowitz S, Mohedano JM, Nováková A, Oberlies NH, Otto EC, Paguigan ND, Pascoe IG, Pérez-Butrón JL, Perrone G, Rahi P, Raja HA, Rintoul T, Sanhueza RMV, Scarlett K, Shouche YS, Shuttleworth LA, Taylor PWJ, Thorn RG, Vawdrey LL, Solano-Vidal R, Voitk A, Wong PTW, Wood AR, Zamora JC, Groenewald JZ (2015) Fungal planet description sheets: 371–399. Persoonia 35:264–327. doi:10.3767/003158515X690269
Domsch KH, Gams W, Anderson TH (2007) Compendium of soil fungi, 2nd edn. IHW-Verlag, Eching
Dorner JW, Cole RJ, Springer JP, Cox RH, Cutler H, Wicklow DT (1980) Isolation and identification of two new biologically active norditerpene dilactones from Aspergillus wentii. Phytochemistry 19:1157–1161. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(80)83075-5
Flannigan B (1986) Mycotoxins and the fermentation industries. In: Flannigan B (ed) Spoilage and mycotoxins of cereals and other stored products. CAB International, London, pp 109–114
Frisvad JC, Larsen TO (2015) Chemodiversity in the genus Aspergillus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:7859–7877. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6839-z
Frisvad JC, Samson RA (1991) Mycotoxins produced by species of Penicillium and Aspergillus occurring in cereals. In: Chełkowski J (ed) Cereal grain: mycotoxins, fungi and quality in drying and storage. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 441–476
Frisvad JC, Thrane U (1987) Standardized high-performance liquid chromatography of 182 mycotoxins and other fungal metabolites based on alkylphenone retention indices and UV-VIS spectra (diode array detection). J Chromatogr 404:195–214. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)86850-3
Frisvad JC, Nielsen KF, Samson RA (2005) Recommendations concerning the chronic problem of misidentification of mycotoxigenic fungi associated with foods and feeds. In: Hocking AD, Pitt JI, Samson RA, Thrane U (eds) Advances in experimental medicine and biology, vol 571. Springer, New York, pp 33–46
González-Andrade M, Del Valle P, Macías-Rubalcava M, Sosa-Peinado A, Del Carmen González M, Mata R (2013) Calmodulin inhibitors from Aspergillus stromatoides. Chem Biodivers 10:328–337. doi:10.1002/cbdv.201200321
Halsey C, Lumley H, Luckit J (2011) Necrotising external otitis caused by Aspergillus wentii: a case report. Mycoses 54:e211–e213. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2009.01815.x
Hamasaki T, Kimura Y (1983) Isolation and structures of four new metabolites from Aspergillus wentii. Agric Biol Chem 47:163–165
Houbraken J, Samson RA (2011) Phylogeny of Penicillium and the segregation of Trichocomaceae into three families. Stud Mycol 70:1–51. doi:10.3114/sim.2011.70.01
Houbraken J, Spierenburg H, Frisvad JC (2012) Rasamsonia, a new genus comprising thermotolerant and thermophilic Talaromyces and Geosmithia species. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 101:403–421. doi:10.1007/s10482-011-9647-1
Houbraken J, de Vries RP, Samson RA (2014) Modern taxonomy of biotechnologically important Aspergillus and Penicillium species. Advances Appl Microbiol 86:199–249
Hubka V, Kubátová A, Mallátová N, Sedláček P, Melichar J, Skořepová M, Mencl K, Lysková P, Šrámková B, Chudíčková M, Hamal P, Kolařík M (2012) Rare and new aetiological agents revealed among 178 clinical Aspergillus strains obtained from Czech patients and characterised by molecular sequencing. Med Mycol 50:601–610. doi:10.3109/13693786.2012.667578
Hubka V, Lysková P, Frisvad JC, Peterson SW, Skořepová M, Kolařík M (2014) Aspergillus pragensis sp. nov. discovered during molecular re-identification of clinical isolates belonging to Aspergillus section Candidi. Med Mycol 52:565–576. doi:10.1093/mmy/myu022
Hubka V, Nissen C, Jensen R, Arendrup M, Čmoková A, Kubátová A, Skořepová M (2015a) Discovery of a sexual stage in Trichophyton onychocola, a presumed geophilic dermatophyte isolated from toenails of patients with a history of T. rubrum onychomycosis. Med Mycol 53:798–809. doi:10.1093/mmy/myv044
Hubka V, Nováková A, Kolařík M, Jurjević Ž, Peterson SW (2015b) Revision of Aspergillus section Flavipedes: seven new species and proposal of section Jani sect. nov. Mycologia 107:169–208. doi:10.3852/14-059
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Johnson D, Nelson G, Ciegler A (1968) Starch hydrolysis by conidia of Aspergillus wentii. Appl Microbiol 16:1678–1683
Jurjević Ž, Kubátová A, Kolařík M, Hubka V (2015) Taxonomy of Aspergillus section Petersonii sect. nov. encompassing indoor and soil-borne species with predominant tropical distribution. Pl Syst Evol 301:2441–2462. doi:10.1007/s00606-015-1248-4
Kelly KL (1964) Inter-society color council—National bureau of standards color name charts illustrated with centroid colors. US Government Printing Office, Washington
LeMense EH, Corman J, Van Lanen JM, Langlykke AF (1947) Production of mold amylases in submerged culture. J Bacteriol 54:149–159
Lowe DA (1992) Fungal enzymes. In: Arora DK, Elander RP, Murekji KG (eds) Handbook of applied mycology, Fungal biotechnology, vol 4. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 681–706
Mehrotra B, Prasad R (1969) Aspergillus dimorphicus and Emericella cleisto-minuta spp. nov. from Indian soils. Trans Brit Mycol Soc 52:331–336. doi:10.1016/S0007-1536(69)80047-1
Nováková A, Hubka V, Saiz-Jimenez C, Kolařík M (2012) Aspergillus baeticus sp. nov. and Aspergillus thesauricus sp. nov., two species in section Usti from Spanish caves. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2778–2785. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.041004-0
Nováková A, Hubka V, Dudová Z, Matsuzawa T, Kubátová A, Yaguchi T, Kolařík M (2014a) New species in Aspergillus section Fumigati from reclamation sites in Wyoming (USA) and revision of A. viridinutans complex. Fung Diversity 64:253–274. doi:10.1007/s13225-013-0262-5
Nováková A, Hubka V, Sáiz-Jiménez C (2014b) Microscopic fungi isolated from cave air and sediments in the Nerja Cave—preliminary results. In: Sáiz-Jiménez C (ed) The conservation of subterranean cultural heritage. CRC Press, Leiden, pp 239–245
Peterson SW (1995) Phylogenetic analysis of Aspergillus sections Cremei and Wentii, based on ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol Res 99:1349–1355. doi:10.1016/S0953-7562(09)81220-3
Peterson SW (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of Aspergillus species using DNA sequences from four loci. Mycologia 100:205–226. doi:10.3852/mycologia.100.2.205
Peterson SW, Varga J, Frisvad JC, Samson RA (2008) Phylogeny and subgeneric taxonomy of Aspergillus. In: Varga J, Samson RA (eds) Aspergillus in the genomic era. Wageningen Academic Publishers, Wageningen, pp 33–56
Pitt JI, Hocking AD (2009) Aspergillus and related teleomorphs. In: Pitt J, Hocking A (eds) Fungi and Food Spoilage, 3rd edn. Springer, London, pp 275–337
Pitt JI, Taylor JW (2014) Aspergillus, its sexual states, and the new International Code of Nomenclature. Mycologia 105:1051–1062. doi:10.3852/14-060
Qureshi I, Begum T, Noorani R (1976) Isolation and identification of the metabolic products of Aspergillus pulvinus Kwon and Fennel. Comparative studies of production of terrein and ergosterol in different media. Pakistan J Sci Industr Res 19:120–122
Rabie C, Terblanche M (1967) Influence of temperature on the toxicity of different isolates of Aspergillus wentii Wehm. S African J Agric Sci 10:263–266
Rabie C, Terblanche M, Smit J, de Klerk W (1965) Toxicity of Aspergillus wentii Wehmer. S African J Agric Sci 8:875–879
Rabie C, Steyn P, van Heerden F (1986) The isolation and identification of some toxic constituents of Aspergillus wentii Wehmer. Mycotoxin Res 2:19–24. doi:10.1007/BF03191958
Rainer J, Peintner U, Pöder R (2001) Biodiversity and concentration of airborne fungi in a hospital environment. Mycopathologia 149:87–97. doi:10.1023/A:1007273131130
Rank C, Nielsen KF, Larsen TO, Varga J, Samson RA, Frisvad JC (2011) Distribution of sterigmatocystin in filamentous fungi. Fungal Biol 115:406–420. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2011.02.013
Raper KB, Fennell DI (1965) The genus Aspergillus. Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore
Reid RDL (1975) Some metabolites of Aspergillus flaschentraegeri. PhD Thesis, Glasgow University, Glasgow
Roehr M, Kubicek CP, Kominek J (1992) Industrial acids and other small molecules. In: Bennett JW, Klich MA (eds) Aspergillus: Biology and industrial applications, vol 23. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston, pp 91–131
Samson RA, Houbraken J, Thrane U, Frisvad JC, Andersen B (2010) Food and indoor fungi. CBS KNAW Biodiversity Center, Utrecht
Samson RA, Visagie CM, Houbraken J, Hong SB, Hubka V, Klaassen CHV, Perrone G, Seifert KA, Tanney JB, Varga J, Yaguchi T, Frisvad JC (2014) Phylogeny, identification and nomenclature of the genus Aspergillus. Stud Mycol 78:141–173. doi:10.1016/j.simyco.2014.07.004
Selva A, Traldi P, Camarda L, Nasini G (1980) New secondary metabolites of Aspergillus wentii Wehmer. The positive and negative ion mass spectra produced by electron impact. Biol Mass Spectrom 7:148–152. doi:10.1002/bms.1200070403
Shurtleff W, Aoyagi A (2012) History of soy sauce (160 CE to 2012): Extensively annotated bibliography and sourcebook. Soyinfo Center, Lafayette
Siddhardha B (2010) Studies on the isolation characterization and bioevaluation of secondary metabolites from Aspergillus funiculosus, Aspergillus gorakhpurensis and Curvularia oryzae. PhD Thesis, Indian Institute of Chemical Technology, Hyderabad
Sun H-F, Li X-M, Meng L, Cui C-M, Gao S-S, Li C-S, Huang C-G, Wang B-G (2012) Asperolides A–C, tetranorlabdane diterpenoids from the marine alga-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus wentii EN-48. J Nat Prod 75:148–152. doi:10.1021/np2006742
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molec Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197
Vanderwolf KJ, Malloch D, McAlpine DF, Forbes GJ (2013) A world review of fungi, yeasts, and slime molds in caves. Int J Speleol 42:77–96. doi:10.5038/1827-806X.42.1.9
Wells JM, Cole RJ, Kirksey JW (1975) Emodin, a toxic metabolite of Aspergillus wentii isolated from weevil damaged chestnuts. J Appl Microbiol 30:26–28
Wicklow DT, McAlpin CE, Yeoh QL (2007) Diversity of Aspergillus oryzae genotypes (RFLP) isolated from traditional soy sauce production within Malaysia and Southeast Asia. Mycoscience 48:373–380. doi:10.1007/s10267-007-0383-3
Wood BJB (1977) Oriental food uses of Aspergillus. In: Smith JE, Pateman JA (eds) The British mycological symposium series no 1. Genetics and physiology of Aspergillus. Academic Press, London, pp 481–498
Xu R, Xu G-M, Li X-M, Li C-S, Wang B-G (2015) Characterization of a newly isolated marine fungus Aspergillus dimorphicus for optimized production of the anti-tumor agent wentilactones. Mar Drugs 13:7040–7054. doi:10.3390/md13117040
Yildirim K, Kupcu I, Gulsan F (2010) Biotransformation of some steroids by Aspergillus wentii. Z Naturf C 65:688–692. doi:10.1515/znc-2010-11-1209
Zhang Z, Miao L, Sun W, Jiao B, Wang B, Yao L, Huang C (2012) Wentilactone B from Aspergillus wentii induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation and migration of human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 35:1964–1971
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic (SVV project) and by the project “BIOCEV—Biotechnology and Biomedicine Centre of the Academy of Sciences and Charles University” (CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0109) from the European Regional Development Fund. Molecular genetic analyses were supported by the projects of Charles University Grant Agency (GAUK 1130214). The survey in European caves was supported through a grant from the Czech Science Foundation (Grant No. P506-12-1064). We thank M. Chudíčková for her invaluable assistance in laboratory, C. S. Pereira, C. Barreto and P. Lysková for supplying isolates of A. europaeus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling editor: Stephen W. Peterson.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Information on electronic supplementary material
Information on electronic supplementary material
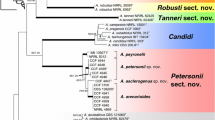
Online Resource 1. Alignment of partial calmodulin gene sequences used for reconstruction of tree on Figure 1.
Online Resource 2. Alignment of partial β-tubulin gene sequences used for reconstruction of tree on Figure 1.
Online Resource 3. Alignment of ITS rDNA region sequences used for reconstruction of tree on Figure 1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hubka, V., Nováková, A., Samson, R.A. et al. Aspergillus europaeus sp. nov., a widely distributed soil-borne species related to A. wentii (section Cremei). Plant Syst Evol 302, 641–650 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-016-1293-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-016-1293-7