Abstract
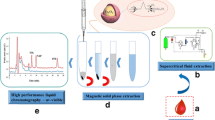
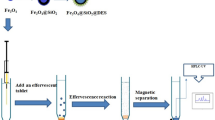
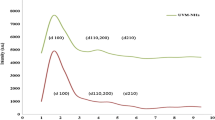
Nanoparticles (NPs) consisting of a magnetic Fe3O4 core and a nickel(II)-doped silica shell were prepared and are shown to be viable materials for selective magnetic extraction of trace quantities of the tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) imatinib, nilotinib, erlotinib and sunitinib. The NPs were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, DLS and XRD analysis, and the results revealed a uniform in size (with a typical diameter of 40 nm) and a core-shell structure. The magnetic nanoadsorbent displays good affinity of the TKIs, probably because of the affinity between the Ni(II) ions of the NPs with the nitrogen atoms in the TKIs. The magnetism of the NPs enables them to be quickly separated from serum and cerebrospinal fluid samples. Imidazole, with its higher affinity for Ni(II) than that of the TKIs, was used for desorption of the TKIs from the NPs prior to their quantification by HPLC with UV detection. The detection limits are as low as 200, 480, 130, and 250 ng·L‾1 for imatinib, sunitinib, erlotinib, and nilotinib, respectively. The intra-day precisions (RSDs) were lower than 4.0 %. The method displays a wide linear range. It was applied to the determination of TKIs in (spiked) human serum and cerebrospinal fluid and gave recoveries in the range from 94.6 to 98.6 %.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steeghs N, Nortier JW, Gelderblom H (2007) Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of solid tumors: an update of recent developments. Ann Surg Oncol 14(2):942–953
Motzer RJ, Michaelson MD, Redman BG, Hudes GR, Wilding G, Figlin RA, Ginsberg MS, Kim ST, Baum CM, DePrimo SE (2006) Activity of SU11248, a multitargeted inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and platelet-derived growth factor receptor, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24(1):16–24
Padmalatha M, Kulsum S, Rahul C, Thimma Reddy D, Vidyasagar G (2011) Spectrophotometric methods for the determination of erlotinib in pure and pharmaceutical dosage forms. Int J Pharm Res Dev 3(6):103–109
Larson RA, Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O'Brien SG, Riviere GJ, Krahnke T, Gathmann I, Wang Y (2008) Imatinib pharmacokinetics and its correlation with response and safety in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: a subanalysis of the IRIS study. Blood 111(8):4022–4028
Rudin CM, Liu W, Desai A, Karrison T, Jiang X, Janisch L, Das S, Ramirez J, Poonkuzhali B, Schuetz E (2008) Pharmacogenomic and pharmacokinetic determinants of erlotinib toxicity. J Clin Oncol 26(7):1119–1127
Blay J-Y (2009) Pharmacological management of gastrointestinal stromal tumours: an update on the role of sunitinib. Ann Oncol. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp291
Neville K, Parise RA, Thompson P, Aleksic A, Egorin MJ, Balis FM, McGuffey L, McCully C, Berg SL, Blaney SM (2004) Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of imatinib after administration to nonhuman primates. Clin Cancer Res 10(7):2525–2529
Baccarani M, Saglio G, Goldman J, Hochhaus A, Simonsson B, Appelbaum F, Apperley J, Cervantes F, Cortes J, Deininger M (2006) Evolving concepts in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 108(6):1809–1820
Lankheet N, Hillebrand M, Rosing H, Schellens J, Beijnen J, Huitema A (2013) Method development and validation for the quantification of dasatinib, erlotinib, gefitinib, imatinib, lapatinib, nilotinib, sorafenib and sunitinib in human plasma by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr 27(4):466–476
Roth O, Spreux-Varoquaux O, Bouchet S, Rousselot P, Castaigne S, Rigaudeau S, Raggueneau V, Therond P, Devillier P, Molimard M (2010) Imatinib assay by HPLC with photodiode-array UV detection in plasma from patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: comparison with LC-MS/MS. Clin Chim Acta 411(3):140–146
Cavaliere B, Monteleone M, Naccarato A, Sindona G, Tagarelli A (2012) A solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatographic approach combined with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry for the assay of carbamate pesticides in water samples. J Chromatogr A 1257:149–157
Payán MR, López MÁB, Fernández-Torres R, Navarro MV, Mochón MC (2011) Hollow fiber-based liquid phase microextraction (HF-LPME) for a highly sensitive HPLC determination of sulfonamides and their main metabolites. J Chromatogr B 879(2):197–204
Fritz JS (1999) Analytical solid-phase extraction. Wiley-Vch
Basheer C, Narasimhan K, Yin M, Zhao C, Choolani M, Lee HK (2008) Application of micro-solid-phase extraction for the determination of persistent organic pollutants in tissue samples. J Chromatogr A 1186(1):358–364
Ramandi NF, Shemirani F, Farahani MD (2014) Dispersive solid phase extraction of lead (II) using a silica nanoparticle-based ionic liquid ferrofluid. Microchim Acta 181(15–16):1833–1841
Ríos A, Zougagh M, Bouri M (2013) Magnetic (nano) materials as an useful tool for sample preparation in analytical methods. A review Anal Method 5(18):4558–4573
Cui Y, Liu S, Wei K, Liu Y, Hu Z (2015) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of trace-level mercury (II) ions using magnetic core-shell nanoparticles modified with thiourea-derived chelating agents. Microchim Acta 182(7–8):1337–1344
Kamran S, Asadi M, Absalan G (2013) Adsorption of acidic, basic, and neutral proteins from aqueous samples using Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles modified with an ionic liquid. Microchim Acta 180(1–2):41–48
Martín M, González Orive A, Lorenzo-Luis P, Hernández Creus A, González-Mora JL, Salazar P (2014) Quinone-rich poly (dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles for biosensor applications. Chem Phys Chem 15(17):3742–3752
Safari M, Yamini Y, Tahmasebi E, Ebrahimpour B (2016) Magnetic nanoparticle assisted supramolecular solvent extraction of triazine herbicides prior to their determination by HPLC with UV detection. Microchim Acta 183(1):203–210
Giokas DL, Zhu Q, Pan Q, Chisvert A (2012) Cloud point–dispersive μ-solid phase extraction of hydrophobic organic compounds onto highly hydrophobic core–shell Fe 2 O 3@ C magnetic nanoparticles. J Chromatogr A 1251:33–39
Eskandari H, Naderi-Darehshori A (2012) Preparation of magnetite/poly (styrene-divinylbenzene) nanoparticles for selective enrichment-determination of fenitrothion in environmental and biological samples. Anal Chim Acta 743:137–144
Wang Y, Tian T, Wang L, Hu X (2013) Solid-phase preconcentration of cadmium (II) using amino-functionalized magnetic-core silica-shell nanoparticles, and its determination by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Microchim Acta 180(3–4):235–242
Zhai Y, He Q, Han Q (2012) Solid-phase extraction of trace metal ions with magnetic nanoparticles modified with 2, 6-diaminopyridine. Microchim Acta 178(3–4):405–412
Bolandnazar S, Divsalar A, Valizadeh H, Khodaei A, Zakeri-Milani P (2013) Development and application of an HPLC method for erlotinib protein binding studies. Analysis 19(21):22
Yan A, Liu X, Qiu G, Wu H, Yi R, Zhang N, Xu J (2008) Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of size-controlled Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 458(1):487–491
Deng Y, Qi D, Deng C, Zhang X, Zhao D (2008) Superparamagnetic high-magnetization microspheres with an Fe3O4@ SiO2 core and perpendicularly aligned mesoporous SiO2 shell for removal of microcystins. J Am Chem Soc 130(1):28–29
Qu J, Li W, Cao C-Y, Yin X-J, Zhao L, Bai J, Qin Z, Song W-G (2012) Metal silicate nanotubes with nanostructured walls as superb adsorbents for uranyl ions and lead ions in water. J Mater Chem 22(33):17222–17226
Fang Q, Xuan S, Jiang W, Gong X (2011) Yolk-like micro/nanoparticles with Superparamagnetic iron oxide cores and hierarchical nickel silicate shells. Adv Funct Mater 21(10):1902–1909
Wegner SV, Spatz JP (2013) Cobalt (III) as a stable and inert mediator ion between NTA and His6-tagged proteins. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(29):7593–7596
Xie H-Y, Zhen R, Wang B, Feng Y-J, Chen P, Hao J (2010) Fe3O4/Au Core/Shell nanoparticles modified with Ni2 + − Nitrilotriacetic acid specific to histidine-tagged proteins. J Phys Chem C 114(11):4825–4830
Sundberg RJ, Martin RB (1974) Interactions of histidine and other imidazole derivatives with transition metal ions in chemical and biological systems. Chem Rev 74(4):471–517
Felicio R, Cavalheiro E, Dockal E (2001) Preparation, characterization and thermogravimetric studies of [N, N′-cis-1, 2-cyclohexylene bis (salicylideneaminato)] cobalt (II) and [N, N′-(±)-trans-1, 2-cyclo-hexylene bis (salicylideneaminato)] cobalt (II. Polyhedron 20(3):261–268
Salehi M, Amirnasr M, Meghdadi S, Mereiter K, Bijanzadeh HR, Khaleghian A (2014) Synthesis, characterization, and X-ray crystal structure of cobalt (III) complexes with a N 2 O 2-donor Schiff base and ancillary ligands. Spectral, antibacterial activity, and electrochemical studies. Polyhedron 81:90–97
Bouchet S, Chauzit E, Ducint D, Castaing N, Canal-Raffin M, Moore N, Titier K, Molimard M (2011) Simultaneous determination of nine tyrosine kinase inhibitors by 96-well solid-phase extraction and ultra performance LC/MS-MS. Clin Chim Acta 412(11):1060–1067
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their appreciation to the Semnan University Research Council for financial support of this study. The authors also thank Dr. Moazeni (Tehran, Iran, parsian-pharma.co) for providing studied drugs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.77 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghazaghi, M., Mousavi, H.Z., Shirkhanloo, H. et al. Ultrasound assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction of four tyrosine kinase inhibitors from serum and cerebrospinal fluid by using magnetic nanoparticles coated with nickel-doped silica as an adsorbent. Microchim Acta 183, 2779–2789 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1927-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1927-z