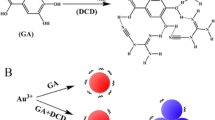
Abstract
The colorimetric assay for neomycin presented here is based on melamine-modified gold nanoparticles (mel-AuNPs) and the finding that hydrogen bonding between melamine and neomycin results in the aggregation of mel-AuNPs. This results in a change in the color of the solution from wine red to blue and in a red-shift of the absorption maximum of the mel-AuNPs. The concentration of neomycin can be determined by spectrophotometry. The ratio of absorptions at 680 nm and 520 nm is linearly related to the logarithm of the concentration of neomycin in the 0.1 to 5.0 nM range and in the 5 to 100 nM range, with regression coefficients of 0.997 and 0.999, respectively. The detection limit (at an S/N ratio of 3) is 30 pM. This is far below the usual safety limit. The method was applied to the detection of trace levels of neomycin in milk samples and gave recoveries between 98 and 105 %.

The presence of neomycin induces the aggregation of melamine-modified gold nanoparticles, this resulting in a color change from red to blue. The concentration of neomycin substrates can be quantified by bare eyes or a UV–Vis spectrometer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waksman SA, Lechevalier HA (1949) Neomycin, a new antibiotic active against streptomycin-resistant bacteria, including tuberculosis organisms. Science 109:305–307
Clark CH (1977) Toxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Mod Vet Pract 58:594–598
Xu NF, Qu CL, Ma W, Xu LG, Liu LQ, Kuang H, Xu CL (2011) Development and application of one-step ELISA for the detection of neomycin in milk. Food Agr Immunol 22:259–269
Zhou GD, Wang F, Wang HL, Kambam S, Chen XQ (2013) Colorimetric and fluorometric detection of neomycin based on conjugated polydiacetylene supramolecules. Macromol Rapid Commun 34:944–948
Peng JD, Tang JX, He RX, He YT, Xiao Y (2013) Validation of the high performance liquid chromatography method for the analysis of neomycin sulfate with resonance rayleigh scattering detection. Anal Methods 5:5572–5578
Stypulkowska K, Blazewicz A, Fijalek Z, Warowna-Grzeskiewicz M, Srebrzynska K (2013) Determination of neomycin and related substances in pharmaceutical preparations by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry and charged aerosol detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 76:207–214
Ding YS, Yu H, Mou SF (2004) Optimizing the quadruple-potential waveform for the pulsed amperometric detection of neomycin. J Chromatogr A 1039:39–43
Huidobro AL, Garcia A, Barbas C (2009) Rapid analytical procedure for neomycin determination in ointments by CE with direct UV detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 49:1303–1307
De-Los-Santos-Alvarez N, Lobo-Castanon MJ, Miranda-Ordieres AJ, Tunon-Blanco P (2009) SPR sensing of small molecules with modified RNA aptamers: detection of neomycin B. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2547–2553
Chen YQ, Hu XH, Xiao XL (2010) Sample preparation for determination of neomycin in swine tissues by liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. Anal Lett 43:2496–2504
Pimsen R, Khumsri A, Wacharasindhu S, Tumcharern G, Sukwattanasinitt M (2014) Colorimetric detection of dichlorvos using polydiacetylene vesicles with acetylcholinesterase and cationic surfactants. Biosens Bioelectron 62:8–12
Nidya M, Umadevi M, Rajkumar BJM (2014) Structural, morphological and optical studies of L-cysteine modified silver nanoparticles and its application as a probe for the selective colorimetric detection of Hg2+. Spectrochim Acta A 133:265–271
Wang ZX, Ma LN (2009) Gold nanoparticle probes. Coordin Chem Rev 253:1607–1618
Liu JF, Zhang XF, Xiao C, Yang AK, Zhao H, He YJ, Li XJ, Yuan ZB (2015) Colorimetric and visual determination of dicyandiamide using gallic acid-capped gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:435–441
Chen ZB, Zhang CM, Zhou TH, Ma H (2015) Gold nanoparticle based colorimetric probe for dopamine detection based on the interaction between dopamine and melamine. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1417-0
Liu DB, Qu WS, Chen WW, Zhang W, Wang Z, Jiang XY (2010) Highly sensitive, colorimetric detection of mercury (II) in aqueous media by quaternary ammonium group-capped gold nanoparticles at room temperature. Anal Chem 82:9606–9610
Guo YM, Wang Z, Qu WS, Shao HW, Jiang XY (2011) Colorimetric detection of mercury, lead and copper ions simultaneously using protein-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4064–4069
Apyari VV, Dmitrienko SG, Arkhipova VV, Atnagulov AG, Gorbunova MV, Zolotov YA (2013) Label-free gold nanoparticles for the determination of neomycin. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 115:416–420
Chi H, Liu BH, Guan GJ, Zhang ZP, Han MY (2010) A simple, reliable and sensitive colorimetric visualization of melamine in milk by unmodified gold nanoparticles. Analyst 135:1070–1075
Asami H, Saigusa H (2014) Multiple hydrogen-bonding interactions of uric acid/9-methyluric acid with melamine identified by infrared spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 118:4851–4857
Cowan JA, Ohyama T, Wang DQ, Natarajan K (2000) Recognition of a cognate RNA aptamer by neomycin B: quantitative evaluation of hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 28:2935–2942
Ji XH, Song XN, Li J, Bai YB, Yang WS, Peng XG (2007) Size control of gold nanocrystals in citrate reduction: the third role of citrate. J Am Chem Soc 129:13939–13948
Huang KW, Yu CJ, Tseng WL (2010) Sensitivity enhancement in the colorimetric detection of lead (II) ion using gallic acid-capped gold nanoparticles: improving size distribution and minimizing interparticle repulsion. Biosens Bioelectron 25:984–989
Frens G (1973) Controlled nucleation for regulation of particle-size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nature-Phys Sci 241:20–22
Haiss W, Thanh TKN, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV–vis spectra. Anal Chem 79:4215–4221
Zhang XF, Wu ZJ, Xue Y, Zhang Y, Zhao H, He YJ, Li XJ, Yuan ZB (2013) Colorimetric detection of melamine based on the interruption of the synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Anal Methods 5:1930–1934
Li L, Li BX, Cheng D, Mao LH (2010) Visual detection of melamine in raw milk using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probe. Food Chem 122:895–900
Kundu J, Neumann O, Janesko BG, Zhang D, Lal S, Barhoumi A, Scuseria GE, Halas NJ (2009) Adenine- and adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-gold binding interactions studied by surface-enhanced raman and infrared spectroscopies. J Phys Chem C 113:14390–14397
Chen W, Deng HH, Hong L, Wu ZQ, Wang S, Liu AL, Lin XH, Xia XH (2012) Bare gold nanoparticles as facile and sensitive colorimetric probe for melamine detection. Analyst 137:5382–5386
Zhang XF, Zhang Y, Zhao H, He YJ, Li XJ, Yuan ZB (2013) Highly sensitive and selective colorimetric sensing of antibiotics in milk. Anal Chim Acta 778:63–69
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Major National Scientific Research Plan of China (973 Program) (Grant No. 2011CB933202) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21205132).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, C., Liu, J., Yang, A. et al. Colorimetric determination of neomycin using melamine modified gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182, 1501–1507 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1480-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1480-1