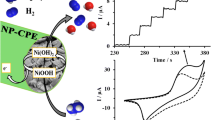
Abstract
The direct electrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide in alkaline medium at a carbon ionic liquid electrode modified with copper oxide nanoparticles was investigated. The electrode was prepared by mixing graphite particles, ionic liquid (n-octylpyridium hexafluorophosphate) and copper oxide nanoparticles. Unlike the film-modified electrode, the fabrication of this electrode is simple and highly reproducible. The combination of the good conductivity of the ionic liquid and the high catalytic activity of the nanoparticles resulted in an electrode with attractive properties for the determination of hydrogen peroxide. The concentration of NaOH and the loading of copper oxide nanoparticles were optimized. The linear range for the determination of hydrogen peroxide is from 1.0 μM to 2.5 mM, the detection limit is 0.5 μM. High stability, sensitivity, selectivity and reproducibility, fast response, the ease of preparation, and surface renewal made the electrode well suitable for the determination of hydrogen peroxide in real samples.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ping JF, Mao XL, Fan K, Li DY, Ru SP, Wu J, Ying YB (2010) A Prussian blue-based amperometric sensor for the determination of hydrogen peroxide residues in milk. Ionics 16:523
Karyakin AA, Karyakina EE, Gorton L (2000) Amperometric Biosensor for Glutamate Using Prussian Blue-Based “Artificial Peroxidase” as a Transducer for Hydrogen Peroxide. Anal Chem 72:1720
Ricci F, Palleschi G (2005) Sensors and biosensors preparation, optimisation and applications of Prussian Blue modified electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 21:389
Šljukić B, Banks CE, Crossley A, Compton RG (2007) Copper Oxide—Graphite Composite Electrodes: Application to Nitrite Sensing. Electroanalysis 19:79
Zang J, Chang ML, Cui X, Wang J, Sun X, Dong H, Sun CQ (2007) Tailoring Zinc Oxide Nanowires for High Performance Amperometric Glucose Sensor. Electroanalysis 19:1008
Sun W, Li XQ, Qin P, Jiao K (2009) Electrodeposition of Co Nanoparticles on the Carbon Ionic Liquid Electrode as a Platform for Myoglobin Electrochemical Biosensor. J Phys Chem C 113:11294
Wang X, Li Y (2002) Selected-Control Hydrothermal Synthesis of α- and β-MnO2 Single Crystal Nanowires. J Am Chem Soc 124:2880
Salimi A, Sharifi E, Noorbakhsh A, Soltanian S (2007) Immobilization of glucose oxidase on electrodeposited nickel oxide nanoparticles: Direct electron transfer and electrocatalytic activity. Biosens Bioelectron 22:3146
Selvaraju T, Ramaraj R (2009) Electrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide at nanostructured copper modified electrode. J Appl Electrochem 39:321
Batchelor-McAuley C, Du Y, Wildgoose GG, Compton RG (2008) The use of copper(II) oxide nanorod bundles for the non-enzymatic voltammetric sensing of carbohydrates and hydrogen peroxide. Sens Actuators B Chem 135:230
Pitcher MW (2006) MATERIALS SCIENCE: There's Still Plenty of Room at the Bottom. Science 313:300
Boukai AI, Bunimovich Y, Tahir-Kheli J, Yu JK, Goddard WA, Heath JR (2008) Silicon nanowires as efficient thermoelectric materials. Nature 451:168
Wang X, Hu CG, Liu H, Du GJ, He XS, Xi Y (2010) Synthesis of CuO nanostructures and their application for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Sens Actuators B Chem 144:220
Paixao RLC, Bertotti M (2004) Development of a breath alcohol sensor using a copper electrode in an alkaline medium. J Electroanal Chem 571:101
Li M, Feng CP, Zhang ZY, Shen ZL, Sugiura N (2009) Electrochemical reduction of nitrate using various anodes and a Cu/Zn cathode. Electrochem Commun 11:1853
Miao XM, Yuan R, Chai YQ, Shi YT, Yuan YY (2008) Direct electrocatalytic reduction of hydrogen peroxide based on Nafion and copper oxide nanoparticles modified Pt electrode. J Electroanal Chem 612:157
Le WZ, Liu YQ (2009) Preparation of nano-copper oxide modified glassy carbon electrode by a novel film plating potential cycling method and its characterization. Sens Actuators B Chem 141:147
Zhang XJ, Wang GF, Liu XW, Wu JJ, Li M, Gu J, Liu H, Fang B (2008) Different CuO Nanostructures: Synthesis, Characterization. Applications for Glucose. J Phys Chem C 112:16845
Jia WZ, Guo M, Zheng Z, Yu T, Wang Y, Rodriguez EG, Lei Y (2008) Vertically Aligned CuO Nanowires Based Electrode for Amperometric Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide. Electroanalysis 20:2153
Zhuang RR, Jian FF (2010) Electrocatalysis for the hydrogen peroxide and nitrite at carbon paste electrode modified with a new zinc complex of 1-pentyl-1H-benzo[d][1, 2, 3]triazole. J Solid State Electrochem 14:747
Šljukić B, Banks CE, Crossley A, Compton RG (2006) Iron(III) Oxide Graphite Composite Electrodes: Application to the Electroanalytical Detection of Hydrazine and Hydrogen Peroxide. Electroanalysis 18:1757
Šljukić B, Banks CE, Crossley A, Compton RG (2007) Lead(IV) oxide–graphite composite electrodes: Application to sensing of ammonia, nitrite and phenols. Anal Chim Acta 587:240
Huddleston JG, Visser AE, Reichert WM, Willauer HD, Broker GA, Rogers RD (2001) Characterization and comparison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquids incorporating the imidazolium cation. Green Chem 3:156
Wei D, Ivaska A (2008) Applications of ionic liquids in electrochemical sensors. Anal Chim Acta 607:126
Maleki H, Safavi A, Tajabadi F (2006) High-Performance Carbon Composite Electrode Based on an Ionic Liquid as a Binder. Anal Chem 78:3820
Liu HT, He P, Li ZY, Sun CY, Shi LH, Liu Y, Zhu GY, Li JH (2005) An ionic liquid-type carbon paste electrode and its polyoxometalate-modified properties. Electrochem Commun 7:1357
Sun W, Gao RF, Jiao K (2007) Electrochemistry and Electrocatalysis of Hemoglobin in Nafion/nano-CaCO3 Film on a New Ionic Liquid BPPF6 Modified Carbon Paste Electrode. J Phys Chem B 111:4560
Wang Q, Yun YB, Zheng JB (2009) Nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on a polyaniline-single walled carbon nanotubes composite in a room temperature ionic liquid. Microchim Acta 167:153
Du P, Liu SN, Wu P, Cai CX (2007) Preparation and characterization of room temperature ionic liquid/single-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposites and their application to the direct electrochemistry of heme-containing proteins/enzymes. Electrochim Acta 52:6534
Zhu WL, Zhou Y, Zhang JR (2009) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of myoglobin based on silica-coated gold nanorods/room temperature ionic liquid/silica sol-gel composite film. Talanta 80:224
Lin YH, Lu F, Tu Y, Ren ZF (2004) Glucose Biosensors Based on Carbon Nanotube Nanoelectrode Ensembles. Nano Lett 4:191
Safavi A, Maleki N, Moradlou O, Tajabadi F (2006) Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid, and uric acid using carbon ionic liquid electrode. Anal Biochem 359:224
Hrbac J, Halouzka V, Zboril R, Papadopoulos K, Triantis T (2007) Carbon Electrodes Modified by Nanoscopic Iron(III) Oxides to Assemble Chemical Sensors for the Hydrogen Peroxide Amperometric Detection. Electroanalysis 19:1850
Garjonyte R, Malinauskas A (1998) Amperometric sensor for hydrogen peroxide, based on Cu2O or CuO modified carbon paste electrodes. Fresenius J Anal Chem 360:122
Lin MS, Leu HJ (2005) A Fe3O4-Based Chemical Sensor for Cathodic Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide. Electroanalysis 17:2068
Nien P, Tung T, Ho K (2006) Amperometric Glucose Biosensor Based on Entrapment of Glucose Oxidase in a Poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Film. Electroanalysis 18:1408
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of China (No. NCET-07-0725), the Key Scientific Project of China (No. 2009ZX08012-004B) and the Key Scientific Project of Zhejiang Province of China (No. 2008C14077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ping, J., Ru, S., Fan, K. et al. Copper oxide nanoparticles and ionic liquid modified carbon electrode for the non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 171, 117–123 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0420-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0420-3