Abstract
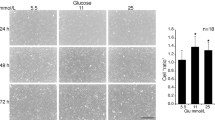
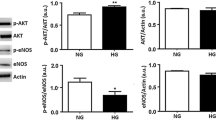
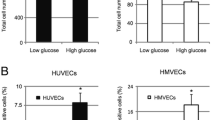
TNF-α and hyperglycemia are important factors contributing to vascular complications in obese and diabetic patients. The present studies aimed to examine, in endothelial cells, downstream signaling mechanisms that may ultimately link TNF-α and hyperglycemia to vascular pathology. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells were cultured and incubated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α and/or 25 mmol/l glucose. The expression of early growth response gene-1 (Egr-1) and ERK1/2 protein was quantified by Western blotting, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) levels were measured by ELISA. Both glucose and TNF-α increased Egr-1 expression, while simultaneous exposure to the two factors exerted an additive effect. Furthermore, PAI-1 was also upregulated in the presence of TNF-α and glucose. The MEK inhibitor, PD98059, downregulated TNF-α-induced Egr-1 expression. TNF-α (10 ng/ml) increased ERK1/2 levels 1.76 ± 0.23-fold (P < 0.01) after 25 mmol/l glucose pretreatment, but added glucose did not enhance ERK1/2 activation when given subsequent to TNF-α treatment. TNF-α induced Egr-1 protein expression and PAI-1 levels through the ERK1/2 pathway. Differential regulation of Egr-1 expression by glucose and TNF-α in endothelial cells may be an important consideration in the mechanisms linking these factors to the development of vascular dysfunction in metabolic disorders such as diabetes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaudry M, Delisle H (2005) Public(‘s) nutrition. Public Health Nutr 8:743–748
Persson J, Lindberg K, Gustafsson TP, Eriksson P, Paulsson-Berne G, Lundman P (2010) Low plasma adiponectin concentration is associated with myocardial infarction in young individuals. J Intern Med 268:194–205. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2010.02247.x
Chen C, Jiang J, Lü JM, Chai H, Wang X, Lin PH, Yao Q (2010) Resistin decreases expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase through oxidative stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 299:H193–H201. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00431.2009
Nieto-Vazquez I, Fernández-Veledo S, Krämer DK, Vila-Bedmar R, Garcia-Guerra L, Lorenzo M (2008) Insulin resistance associated to obesity: the link TNF-alpha. Arch Physiol Biochem 114:183–194. doi:10.1080/13813450802181047
Martens FMAC, Rabelink TJ, op ‘t Roodt J, de Koning EJP, Visseren FLJ (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces endothelial dysfunction in diabetic adults, an effect reversible by the PPAR-gamma agonist pioglitazone. Eur Heart J 27:1605–1609. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl079
Paquot N, Tappy L (2005) Adipocytokines: link between obesity, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis. Rev Med Liege 60:369–373
Gururajan M, Simmons A, Dasu T, Spear BT, Calulot C, Robertson DA, Wiest DL, Monroe JG, Bondada S (2008) Early growth response genes regulate B cell development, proliferation, and immune response. J Immunol 181:4590–4602
Blessing E, Preusch M, Kranzhöfer R, Kinscherf R, Marx N, Rosenfeld ME, Isermann B, Weber CM, Kreuzer J, Gräfe J, Katus HA, Bea F (2008) Anti-atherosclerotic properties of telmisartan in advanced atherosclerotic lesions in apolipoprotein E deficient mice. Atherosclerosis 199:295–303. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2007.10.037
McCaffrey TA, Fu C, Du B, Eksinar S, Kent KC, Bush H Jr, Kreiger K, Rosengart T, Cybulsky MI, Silverman ES, Collins T (2000) High-level expression of Egr-1 and Egr-1-inducible genes in mouse and human atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest 105:653–662. doi:10.1172/JCI8592
Demyanets S, Kaun C, Rychli K, Rega G, Pfaffenberger S, Afonyushkin T, Bochkov VN, Maurer G, Huber K, Wojta J (2007) The inflammatory cytokine oncostatin M induces PAI-1 in human vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro via PI 3-kinase and ERK1/2-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H1962–H1968. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01366.2006
Shi L, Kishore R, McMullen MR, Nagy LE (2002) Lipopolysaccharide stimulation of ERK1/2 increases TNF-alpha production via Egr-1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C1205–C1211. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00511.2001
Sobel BE (1999) Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and vasculopathy. A reconcilable paradox. Circulation 99:2496–2498
Thogersen AM, Jansson JH, Boman K (1998) High plasminogen activator inhibitor and tissue plasminogen activator levels in plasma precede a first acute myocardial infarction in both men and women: evidence for the fibrinolytic system as an independent primary risk factor. Circulation 98:2241–2247
Cao YL, Wang YX, Wang DF, Meng X, Zhang J (2008) Correlation between omental TNF-alpha protein and plasma PAI-1 in obesity subjects. Int J Cardiol 128:399–405. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.05.033
Rukhsana N, Hasan Andrew I, Hemin Schafer (2008) Upregulates egr-1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells via reactive oxygen species ERK-1/2–Elk-1 and NF-B. Circul Res 102:42–50. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.155143
Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG (2001) Finnish diabetes prevention study group. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 344:1343–1350. doi:10.1056/NEJM200105033441801
Tchernof A, Nolan A, Sites CK (2002) Weight loss reduces C-reactive protein levels in obese postmenopausal women. Circulation 105:564–569
Sobel BE (1999) Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and vasculopathy. A reconcilable paradox. Circulation 99:2496–2498
Birgel M, Gottschling-Zeller H, Rohrig K, Hauner H (2000) Role of cytokines in the regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression and secretion in newly differentiated subcutaneous human adipocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1682–1687
Thogersen AM, Jansson JH, Boman K (1998) High plasminogen activator inhibitor and tissue plasminogen activator levels in plasma precede a first acute myocardial infarction in both men and women: evidence for the fibrinolytic system as an independent primary risk factor. Circulation 98:2241–2247
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81000327/H0712).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Y., Zhang, J., Meng, X. et al. TNF-α induces early growth response gene-1 expression via ERK1/2 activation in endothelial cells. Acta Diabetol 50, 27–31 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-010-0248-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-010-0248-7