Abstract
Purpose
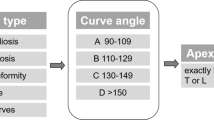
Coronal malalignment (CM) causes pain, impairment of function and cosmetic problems for adult spinal deformity (ASD) patients in addition to sagittal malalignment. Certain types of CM are at risk of insufficient re-alignment after correction. However, CM has received minimal attention in the literature compared to sagittal malalignment. The purpose was to establish reliability for our recently published classification system of CM in ASD among spine surgeons.
Methods
Fifteen readers were assigned 28 cases for classification, who represented CM with reference to their full-length standing anteroposterior and lateral radiographs. The assignment was repeated 2 weeks later, then a third assignment was done with reference to additional side bending radiographs (SBRs). Intra-, inter-rater reliability and contribution of SBRs were determined.
Results
Intra-rater reliability was calculated as 0.95, 0.86 and 0.73 for main curve types, subtypes with first modifier, and subtypes with two modifiers respectively. Inter-rater reliability averaged 0.91, 0.75 and 0.52. No differences in intra-rater reliability were shown between the four expert elaborators of the classification and other readers. SBRs helped to increase the concordance rate of second modifiers or changed to appropriate grading in cases graded type A in first modifier.
Conclusions
Adequate intra- and inter-rater reliability was shown in the Obeid-CM classification with reference to full spine anteroposterior and lateral radiographs. While side bending radiographs did not improve the classification reliability, they contributed to a better understanding in certain cases. Surgeons should consider both the sagittal and coronal planes, and this system may allow better surgical decision making for CM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pellise F, Vila-Casademunt A, Ferrer M, Domingo-Sabat M, Bago J, Perez-Grueso FJ, Alanay A, Mannion AF, Acaroglu E (2015) Impact on health related quality of life of adult spinal deformity (ASD) compared with other chronic conditions. Eur Spine J 24:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3542-1
Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F (2005) The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:2024–2029
Schwab F, Lafage V, Boyce R, Skalli W, Farcy JP (2006) Gravity line analysis in adult volunteers: age-related correlation with spinal parameters, pelvic parameters, and foot position. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:E959–967. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000248126.96737.0f
Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S, Hostin R, Shaffrey CI, Smith JS, Boachie-Adjei O, Burton DC, Akbarnia BA, Mundis GM, Ames CP, Kebaish K, Hart RA, Farcy JP, Lafage V, International Spine Study G (2013) Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting of adult spinal deformity: a prospective multicenter analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:E803–812. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e318292b7b9
Takemoto M, Boissiere L, Novoa F, Vital JM, Pellise F, Perez-Grueso FJ, Kleinstuck F, Acaroglu ER, Alanay A, Obeid I, Obeid I (2016) Sagittal malalignment has a significant association with postoperative leg pain in adult spinal deformity patients. Eur Spine J 25:2442–2451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4616-z
Schwab F, Ungar B, Blondel B, Buchowski J, Coe J, Deinlein D, DeWald C, Mehdian H, Shaffrey C, Tribus C, Lafage V (2012) Scoliosis Research Society-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification: a validation study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 37:1077–1082. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31823e15e2
Bess S, Schwab F, Lafage V, Shaffrey CI, Ames CP (2013) Classifications for adult spinal deformity and use of the scoliosis research society-schwab adult spinal deformity classification. Neurosurg Clin N Am 24:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2012.12.008
Glassman SD, Berven S, Bridwell K, Horton W, Dimar JR (2005) Correlation of radiographic parameters and clinical symptoms in adult scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 30:682–688
Cho W, Mason JR, Smith JS, Shimer AL, Wilson AS, Shaffrey CI, Shen FH, Novicoff WM, Fu KM, Heller JE, Arlet V (2013) Failure of lumbopelvic fixation after long construct fusions in patients with adult spinal deformity: clinical and radiographic risk factors: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine 19:445–453. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.6.spine121129
Bao H, Yan P, Qiu Y, Liu Z, Zhu F (2016) Coronal imbalance in degenerative lumbar scoliosis: Prevalence and influence on surgical decision-making for spinal osteotomy. Bone Joint J 98:1227–1233. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.98B9.37273
Zhang Z, Song K, Wu B, Chi P, Wang Z, Wang Z (2019) Coronal imbalance in adult spinal deformity following posterior spinal fusion with instrument: a related parameters analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 44:550–557. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000002897
Ploumis A, Simpson AK, Cha TD, Herzog JP, Wood KB (2015) Coronal spinal balance in adult spine deformity patients with long spinal fusions: a minimum 2- to 5-year follow-up study. J Spinal Disord Technol 28:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0b013e3182aab2ff
Bourghli A, Guerin P, Vital JM, Aurouer N, Luc S, Gille O, Pointillart V, Obeid I (2012) Posterior spinal fusion from T2 to the sacrum for the management of major deformities in patients with Parkinson disease: a retrospective review with analysis of complications. J Spinal Disord Technol 25:E53–60. https://doi.org/10.1097/BSD.0b013e3182496670
Choi HJ, Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Lafage VC, Schwab FJ, Ames CP, Matsumoto M, Baik JS, Ha Y (2015) Coronal plane spinal malalignment and Parkinson's disease: prevalence and associations with disease severity. Spine J 15:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2014.07.004
Obeid I, Berjano P, Lamartina C, Chopin D, Boissiere L, Bourghli A (2018) Classification of coronal imbalance in adult scoliosis and spine deformity: a treatment-oriented guideline. Eur Spine J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-018-5826-3
Margulies JY, Floman Y, Robin GC, Neuwirth MG, Kuflik P, Weidenbaum M, Farcy JP (1998) An algorithm for selection of instrumentation levels in scoliosis. Eur Spine J 7:88–94
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Lowe T, Berven SH, Schwab FJ, Bridwell KH (2006) The SRS classification for adult spinal deformity: building on the King/Moe and Lenke classification systems. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31:S119–125. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.brs.0000232709.48446.be
Ha KY, Jang WH, Kim YH, Park DC (2016) Clinical relevance of the SRS-schwab classification for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 41:E282–288. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000001229
Koller H, Pfanz C, Meier O, Hitzl W, Mayer M, Bullmann V, Schulte TL (2016) Factors influencing radiographic and clinical outcomes in adult scoliosis surgery: a study of 448 European patients. Eur Spine J 25:532–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3898-x
Alzakri A, Boissiere L, Cawley DT, Bourghli A, Pointillart V, Gille O, Vital JM, Obeid I (2018) L5 pedicle subtraction osteotomy: indication, surgical technique and specificities. Eur Spine J 27:644–651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-017-5403-1
Ames CP, Smith JS, Eastlack R, Blaskiewicz DJ, Shaffrey CI, Schwab F, Bess S, Kim HJ, Mundis GM Jr, Klineberg E, Gupta M, O'Brien M, Hostin R, Scheer JK, Protopsaltis TS, Fu KM, Hart R, Albert TJ, Riew KD, Fehlings MG, Deviren V, Lafage V, International Spine Study G (2015) Reliability assessment of a novel cervical spine deformity classification system. J Neurosurg Spine 23:673–683. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.12.SPINE14780
Thaler M, Lechner R, Gstottner M, Luegmair M, Liebensteiner M, Nogler M, Bach C (2012) Interrater and intrarater reliability of the Kuntz et al new deformity classification system. Neurosurgery 71:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31824f4e58
Obeid I, Boissiere L, Vital JM, Bourghli A (2015) Osteotomy of the spine for multifocal deformities. Eur Spine J 24(Suppl 1):S83–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3660-9
Bourghli A, Cawley D, Novoa F, Rey M, Alzakri A, Larrieu D, Vital JM, Gille O, Boissiere L, Obeid I (2018) 102 lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomies: one surgeon's learning curve. Eur Spine J 27:652–660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-018-5481-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, K., Boissière, L., Cawley, D.T. et al. A new classification for coronal malalignment in adult spinal deformity: a validation and the role of lateral bending radiographs. Eur Spine J 29, 2287–2294 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-020-06513-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-020-06513-5