Abstract
Introduction
Disc degeneration and re-herniation after nucleotomy procedures are common problems. Simultaneous application of hyaluronic acid (HA)-based matrix has been proposed to limit disc degeneration. This, however, is hampered by loss of the substituted matrix out of the disc. Hence, in situ polymerization of the injected matrix with ultraviolet light (UVL) directly used after injection may be useful. Therefore, this study evaluates a new HA/collagen hydrogel matrix with in situ polymerization after implantation in an established porcine nucleotomy model.
Materials and methods
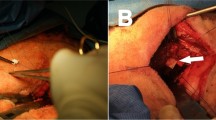
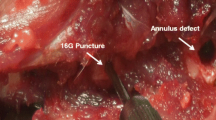
12 mature minipigs were used. A total of 60 lumbar discs were analyzed. 36 discs underwent partial nucleotomy with a 16G biopsy needle. Of those, 24 discs received matrix (porcine nucleus pulposus collagenous scaffold component and chemically modified HA) which was in situ polymerized using UVL immediately after transplantation. 12 nucleotomized discs and 24 non-nucleotomized discs served as controls. After 24 weeks, animals were killed. X-rays, MRIs, histology, and gene expression analysis were done.
Results
Disc height was reduced equally after sole nucleotomy and nucleotomy with HA treatment and in MRIs signal intensity decreased. For both nucleotomy groups, the nucleus histo-degeneration score showed a significant increase compared to controls. In histology, HA treatment resulted in more scarring and inflammation in the annulus. Gene expression of catabolic MMPs was up-regulated, whereas IFN-gamma, IL-6, and IL-1b were unchanged.
Conclusion
Although nucleotomy and administration of the implant material did not cause generalized inflammation of the disc, localized annular damage with annulus inflammation and scarring resulted in detrimental degenerative disc changes. As a result, therapeutic strategies should strongly focus on the prevention of annular damage or techniques for annular repair to remain disc integrity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paesold G, Nerlich AG, Boos N (2007) Biological treatment strategies for disc degeneration: potentials and shortcomings. Eur Spine J 16:447–468
Meisel HJ, Ganey T, Hutton WC, Libera J, Minkus Y, Alasevic O (2006) Clinical experience in cell-based therapeutics: intervention and outcome. Eur Spine J 15(3):397–405
Wilke HJ, Heuer F, Neidlinger-Wilke C, Claes L (2006) Is a collagen scaffold for a tissue engineered nucleus replacement capable of restoring disc height and stability in an animal model? Eur Spine J 15(3):433–438
Heuer F, Ulrich S, Claes L, Wilke HJ (2008) Biomechanical evaluation of conventional anulus fibrosus closure methods required for nucleus replacement. Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine 9:307–313
Moore RJ (2006) The vertebral endplate: disc degeneration, disc regeneration. Eur Spine J 15(3):333–337
Bron JL, Helder MN, Meisel HJ, Van Royen BJ, Smit TH (2009) Repair, regenerative and supportive therapies of the annulus fibrosus: achievements and challenges. Eur Spine J 18:301–313
Omlor GW, Bertram H, Kleinschmidt K, Fischer J, Brohm K, Guehring T, Anton M, Richter W (2010) Methods to monitor distribution and metabolic activity of mesenchymal stem cells following in vivo injection into nucleotomized porcine intervertebral discs. Eur Spine J 19(4):601–612
Pfeiffer M, Griss P, Franke P, Bornscheuer C, Orth J, Wilke A, Clausen JD (1994) Degeneration model of the porcine lumbar motion segment: effects of various intradiscal procedures. Eur Spine J 3:8–16
Pfeiffer M, Boudriot U, Pfeiffer D, Ishaque N, Goetz W, Wilke A (2003) Intradiscal application of hyaluronic acid in the non-human primate lumbar spine: radiological results. Eur Spine J 12:76–83
Revell PA, Damien E, Di Silvio L, Gurav N, Longinotti C, Ambrosio L (2007) Tissue engineered intervertebral disc repair in the pig using injectable polymers. J Mater Sci Mater Med 18(2):303–308
Nesti LJ, Li WJ, Shanti RM, Jiang YJ, Jackson W, Freedman BA, Kuklo TR, Giuliani JR, Tuan RS (2008) Intervertebral disc tissue engineering using a novel hyaluronic acid-nanofibrous scaffold (HANFS) amalgam. Tissue Eng Part A 14(9):1527–1537
Erggelet C, Neumann K, Endres M, Haberstroh K, Sittinger M, Kaps C (2007) Regeneration of ovine articular cartilage defects by cellfree polymer-based implants. Biomaterials 28:5570–5580
Abbushi A, Endres M, Cabraja M, Kroppenstedt SN, Thomale UW, Sittinger M, Hegewald AA, Morawietz L, Lemke AJ, Bansemer VG, Kaps C, Woiciechowsky C (2008) Regeneration of intervertebral disc tissue by resorbable cell-free polyglycolic acid-based implants in a rabbit model of disc degeneration. Spine 33:1527–1532
Endres M, Abbushi A, Thomale UW, Cabraja M, Kroppenstedt SN, Morawietz L, Casalis PA, Zenclussen ML, Lemke AJ, Horn P, Kaps C, Woiciechowsky C (2010) Intervertebral disc regeneration after implantation of a cell-free bioresorbable implant in a rabbit disc degeneration model. Biomaterials 31:5836–5841
Nakashima S, Matsuyama Y, Takahashi K, Satoh T, Koie H, Kanayama K, Tsuji T, Maruyama K, Imagama S, Sakai Y, Ishiguro N (2009) Regeneration of intervertebral disc by the intradiscal application of cross-linked hyaluronate hydrogel and cross-linked chondroitin sulfate hydrogel in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc injury. Biomed Mater Eng 19:421–429
Hegewald AA, Knecht S, Baumgartner D, Gerber H, Endres M, Kaps C, Stüssi E, Thomé C (2009) Biomechanical testing of a polymer-based biomaterial for the restoration of spinal stability after nucleotomy. J Orthop Surg Res. 4:25
Chou AI, Nicoll SB (2008) Characterization of photocrosslinked alginate hydrogels for nucleus pulposus cell encapsulation. J Biomed Mater Res A 91(1):187–194
Smeds KA, Pfister-Serres A, Miki D, Dastgheib K, Inoue M, Hatchell DL, Grinstaff MW (2001) Photocrosslinkable polysaccharides for in situ hydrogel formation. J Biomed Mater Res 51:115–121
Nettles DL, Vail TP, Morgan MT, Grinstaff MW, Setton LA (2004) Photocrosslinkable hyaluron as a scaffold for articular cartilage repair. Ann Biomed Eng 32:391–397
Omlor GW, Nerlich AG, Wilke HJ, Pfeiffer M, Lorenz H, Schaaf-Keim M, Bertram H, Richter W, Carstens C, Guehring T (2009) A new porcine in vivo animal model of disc degeneration—response of annulus fibrosus cells, chondrocyte-like nucleus pulposus cells and notochordal nucleus pulposus cells to partial nucleotomy. Spine 34(25):2730–2739
Boos N, Weissbach S, Rohrbach H, Weiler C, Spratt KF, Nerlich AG (2002) Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo award in basic science. Spine 27:2631–2644
Weiler C, Lopez-Ramos M, Mayer HM, Korge A, Siepe CJ, Wuertz K, Weiler V, Boos N, Nerlich AG (2011) Histological analysis of surgical lumbar intervertebral disc tissue provides evidence for an association between disc degeneration and increased body mass index. BMC Res Notes 4:497
Marcus R, Peritz E, Gabriel KR (1976) On closed testing procedures with special reference to ordered analysis of variance. Biometrika 63:655–660
Atlas SJ, Keller RB, Wu YA, Deyo RA, Singer DE (2005) Long-term outcomes of surgical and nonsurgical management of sciatica secondary to a lumbar disc herniation: 10 year results from the maine lumbar spine study. Spine 30:927–935
Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA (2007) Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human intervertebral discs: IL-1b and TNFalpha expression profile. Arthritis Res Ther 9:77
Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ, Hoyland JA (2005) The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther 7:732–745
Burke JG, Watson RW, McCormack D, Dowling FE, Walsh MG, Fitzpatrick JM (2002) Intervertebral discs which cause low back pain secrete high levels of proinflammatory mediators. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:196–201
Shamji MF, Setton LA, Jarvis W, So S, Chen J, Jing L, Bullock R, Isaacs RE, Brown C, Richardson WJ (2010) Proinflammatory cytokine expression profile in degenerated and herniated human intervertebral disc tissues. Arthritis Rheum 62:1974–1982
Holm S, Mackiewicz Z, Holm AK, Konttinen YT, Kouri VP, Indahl A, Salo J (2009) Pro-inflammatory, pleiotropic, and anti-inflammatory TNF-a, IL-6, and IL-10 in experimental porcine intervertebral disk degeneration. Vet Pathol 46:1292–1300
Berlemann U, Schwarzenbach O (2009) An injectable nucleus replacement as an adjunct to microdiscectomy: 2 year follow-up in a pilot clinical study. Eur Spine J 18:1706–1712
Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J, Menage J (2006) Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88:10–14
Key JA, Ford LT (1948) Experimental intervertebral-disc lesions. J Bone Joint Surg Am 30:621–630
Korecki CL, Costi JJ, Iatridis JC (2008) Needle puncture injury affects intervertebral disc mechanics and biology in an organ culture model. Spine 33:235–241
Acknowledgments
We thank Bernhard Pieta for helping with animal acquisition and surgical assistance.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omlor, G.W., Nerlich, A.G., Lorenz, H. et al. Injection of a polymerized hyaluronic acid/collagen hydrogel matrix in an in vivo porcine disc degeneration model. Eur Spine J 21, 1700–1708 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2291-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2291-2