Abstract
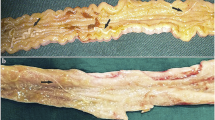
Aelurostrongylus abstrusus (Raillet), the cat lungworm, is a parasitic round worm which lives in the terminal bronchioles and the alveolar ducts inside the lungs of cats as final hosts. Snails or slugs can be intermediate hosts while rodents, frogs, toads, lizards, birds, and snakes can play the role of transporter from the intermediate host into the final host. The ingested third-stage larvae migrate towards the lungs through the blood vessels. In this research, first, the observation of A. abstrusus infection in a stray cat in Iran is described. Later, the larval detection of this worm in infected cat’s blood throughout the world will be discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RC (2000) Nematode parasites of vertebrates their development and transmission, 2nd edn. CABI publishing, Wallingford, pp 163–164
Ash LR (1970) Diagnostic morphology of the third-stage larvae of Angiostrongylus cantonensis, Angiostrongylus vasorum, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Anafilaroides rostratus (Nematoda: Metastrongyloidea). J Parasitol 56(2):249–253
Barutzki D, Schaper R (2013) Occurrence and regional distribution of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus in cats in Germany. Parasitol Res 112:855–861. doi:10.1007/s00436-012-3207-0
Ellis AE, Brown CA, Yabsley MJ (2010) Aelurostrongylus abstrusus larvae in the colon of two cats. J Vet Diagn Investig 22:652–655
Hobmaier M, Hobmaier A (1935) Mammalian phase of the lungworm Aelurostrongylus abstrusus in the cat. J Am Vet Med Assoc 87:191–198
Losonsky JM, Thrall DE, Prestwood AK (1983) Radiographic evaluation of pulmonary abnormalities after Aelurostrongylus abstrusus inoculation in cats. Am J Vet Res 44(3):478–482
Mackerras MJ (1957) Observations on the life history of the cat lungworm, Aelurostrongylus abstrusus (Railliet, 1898) (Nematoda: Metastrongylidae). Aust J Zool 5:188–195
Payo-Puente P, Diez A, Gonzalo-Orden JM, Marcia KikuyoNotomi MK, Rodriguez-Altonaga JA, Francisco A, Rojo-Vazquez FA, Orden MA (2005) Computed tomography in cats infected by Aelurostrongylus abstrusus: 2 Clinic Cases. Int J Appl Res Vet Med 3(4):339–343
Payo-Puente P, Botelho-Dinis M, CarvajaUruena AM, Payo-Puente M, Gonzalo-Orden JM, Rojo-Vazquez FA (2007) Prevalence study of the lungworm Aelurostrongylus abstrususin stray cats of Portugal. J Feline Med Surg 10:242–246. doi:10.1016/j.jfms.2007.12.002
Stockdale PHG (1970) The pathogenesis of the lesions elicited by Aelurostrongylus abstrusus durings its Prepatent Period. Vet Pathol 7(2):102–115. doi:10.1177/030098587000700202
Traversa D, Guglielmini C (2008) Feline aelurostrongylosis and canine angiostrongylosis a challenging diagnosis for two emerging verminous pneumonia infections. Vet Parasitol 157:163–174
Traversa D, Di Cesare A, Milillo P, Iorio R, Otranto D (2008a) Aelurostrongylus abstrususin a feline colony from central Italy: Clinical features, diagnostic procedures and molecular characterization. Parasitol Res 103:1191–1196
Traversa D, Lia RP, Iorio R, Boari A, Paradies P, Capelli G, Avolio S, Otranto D (2008b) Diagnosis and risk factors of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus (Nematoda, Strongylida) infection in cats from Italy. Vet Parasitol 153:182–186
Traversa D, Di Cesare A, Conboy G (2010) Canine and feline cardiopulmonary parasitic nematodes in Europe: Emerging and underestimated. Parasites Vectors 3:62. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-3-62
Tuzer E, Toparlak M, Gargili A, Kelefi V, Esatgil MU (2002) A Case of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus Infection in a Cat in Istanbul, Turkey and its Treatment with Moxidectin and Levamisole. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 26:411–414
Willard MD, Roberts RE, Allison N, Grieve RB, Escher K (1988) Diagnosis of Aelurostrongylus abstrusus and Dirofilaria immitis infections in cats from a human shelter. J Am Vet Med Assoc 192:913–916
Conflict of interest
No competing financial interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rassouli, M., Ghaderi, J., Goudarzi, A. et al. Aelurostrongylus abstrusus in a stray cat’s blood stream. Comp Clin Pathol 24, 773–775 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-014-1979-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-014-1979-6