Abstract
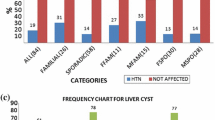
The aim of this study was to investigate whether certain DR alleles might contribute to the genetic susceptibility among adult polycystic kidney disease patients in Egypt. This case–control study involved human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR typing for 40 non-related Egyptian patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Patients were compared with a group of 50 healthy subjects. Human leukocyte antigen DRB1 typing was carried out on allele level (DRB1*01 — DRB1*16) using polymerase chain reaction-sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes (PCR-SSOP). No statistically significant association of the disease with HLA-DRB1 was observed. So, HLA-DRB1 does not contribute to polycystic kidney disease in Egyptian patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aajil A (2011) The association between HLA-class I antigens and polycystic ovary syndrome in a sample of Iraqi patients. Iraqi Journal of Cancer and Medical Genetics 4(1):52–56
Amaout MA (2011) Cystic kidney diseases. In: Goldman L, Ausiello D (eds) Cecil medicine 24th ed. Elsevier, Philadelphia, Chap128
Dausset J, Hors J (1975) Some contributions of the HLA complex to the genetics of human diseases. Transplantation Review 22:44–74
Devuyst O, Persu A, Vo-Cong M-T (2003) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: modifier genes and endothelial dysfunction. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18(11):2211–2215
Dyer P, Watters E, Klouda P, Harris R, Mallick N (1982) Absence of linkage between adult polycystic kidney disease and the major histocompatibility system. Tissue Antigens 20:108–111
Fauchet R, Le Pogamp P, Genetet B, Chevet D, Gueguen M, Simon P, Ramee MP, Cartier F (1980) HLA-DR4 antigen and IgA nephropathy. Tissue Antigens 16:405–410
Harris PC, Torres VE (2009) Polycystic kidney disease. Annu Rev Med 60:321–337
Karahan GE, Seyhun Y, Oguz F, Kekik C, Onal E (2009) Impact of HLA on the underlying primary diseases in Turkish patients with end-stage renal disease. Renal failure 31:44–49
Klouda PT, Manos J, Acheson ES, Dyer PA, Goldby FS, Harris R, Lawler W, Mallick NP, Williams G (1979) Strong association between idiopathic membranous nephropathy and HLA-DRW3. Lancet ii:770–771
Pei Y (2005) Nature and nurture on phenotypic variability of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 67:1630–1631
Rees AJ, Peters DK, Compston DAS, Batchelor JR (1978) Strong association between HLA-DRw2 and antibody mediated Goodpastures Syndrome. Lancet i:966–5268
Rossetti S, Consugar MB, Chapman AB, Torres VE, Guay-Woodford LM, Grantham JJ, Bennett WM, Meyers CM, Walker DL, Bae K, Zhang QJ, Thompson PA, Miller JP, Harris PC, CRISP Consortium (2007) Comprehensive molecular diagnostics in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2143–2160
Spengler J, Wegener S, Schüler H, Kraatz G (1989) HLA antigen frequencies in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney degeneration. Z Urol Nephrol 82(12):691–694
Torres VE, Grantham JJ, Chapman AB, Mrug M, Bae KT, King BF Jr, Wetzel LH, Martin D, Lockhart ME, Bennett WM, Moxey-Mims M, Abebe KZ, Lin Y, Bost JE, Consortium for radiologic imaging studies of polycystic kidney disease (CRISP) (2011) Potentially Modifiable Factors Affecting the Progression of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6(3):640–647
Wilson PD (2004) Polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 350(2):151–164
Xu L (1990) Association of polycystic kidney disease and an HLA haplotype within a family clan. Urol Res 18:239–240
Yoon SH, Oh HB, Kim HK, Hong SC, Oh YM, Lee DS, Lee SD (2007) Association of HLA class II genes with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension in Koreans. Lung 185(3):145–149
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no financial or proprietary interest in any product mentioned in this paper.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
The authors have no financial or proprietary interest in any product mentioned in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahin, R.M.H., Shouman, A.M.A. Contribution of HLA-DR to polycystic kidney disease in a sample of Egyptian patients. Comp Clin Pathol 24, 423–426 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-014-1919-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-014-1919-5