Abstract
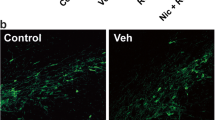
We investigated the effect of cannabis treatment on the development of oxidative stress and nigrostriatal cell injury induced by intrastriatal rotenone injection in rats. Rotenone was injected into the right striatum at a concentration of 5 mM (3 μl/rat). The control rats received the vehicle (DMSO). Subsequently, the effect of Cannabis sativa extract treatment on rotenone toxicity was evaluated. Starting on the second day of rotenone injection, rats were treated with C. sativa extract (5, 10, or 15 mg/kg) (expressed as Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol) subcutaneously (s.c.) once daily for 30 days. Biochemical markers of oxidative stress, malondialdehyde (MDA), reduced glutathione (GSH), nitric oxide, paraoxonase 1 (PON1) activity, catalase activity, as well as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), were determined in different brain areas after 30 days of rotenone treatment. Histopathology and immunohistochemical expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), capase 3, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) were also performed. Results showed that intrastriatal injection of rotenone resulted in increased brain oxidative stress in the cerebral cortex, striatum, hippocampus, midbrain, and cerebellum. MDA increased by 41.4–70 %, nitric oxide increased by 48.3–77.5 %, while GSH decreased by 25.0–34.2 %. PON1 and catalase activities decreased by 43.0–60.8 % and by 14.2–36 %, respectively, in these areas. Striatal TNF-α increased by 638.9 % of control value after rotenone injection. Rotenone induced motor deficits (decreased rearing activity). Rotenone caused marked nigrostriatal neurodegeneration, decreased TH immunoreactivity, and increased both iNOS and caspase 3 immunoreactivities in the striatum. Cannabis decreased brain oxidative stress and nitric oxide release induced by intrastriatal rotenone in several brain areas. Cannabis also decreased the elevated TNF-α in the striatum. Cannabis did not protect against the immunohistochemical changes in the striatum and substantia nigra or against neuronal degeneration induced by rotenone treatment. Collectively, these results indicated that the administration of cannabis did not protect against nigrostriatal damage caused by intrastriatal rotenone.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Salam OME, El-Shamarka ME-S, Salem NA, Gaafar AE-DM (2012) Effects of Cannabis sativa extract on haloperidol-induced catalepsy and oxidative stress in the mice. EXCLI J 11:45–58
Abdel-Salam OME, Omara EA, El-Shamarka ME-S, Hussein JS (2013) Nigrostriatal damage after systemic rotenone and/or lipopolysaccharide and the effect of cannabis. Comp Clin Pathol 1–16
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Alam M, Schmidt WJ (2002) Rotenone destroys dopaminergic neurons and induces parkinsonian symptoms in rats. Behav Brain Res 136:317–324
Ashton CH (2001) Pharmacology and effects of cannabis: a brief review. Br J Psychiat 178:101–106
Bashkatova V, Alam M, Vanin A, Schmidt WJ (2004) Chronic administration of rotenone increases levels of nitric oxide and lipid peroxidation products in rat brain. Exp Neurol 186:235–241
Belin AC, Ran C, Anvret A, Paddock S, Westerlund M, Håkansson A, Nissbrandt H, Söderkvist P, Dizdar N, Ahmadi A, Anvret M, Willows T, Sydow O, Galter D (2012) Association of a protective paraoxonase 1 (PON1) polymorphism in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 26(522):30–35
Benninger DH, Thees S, Kollias SS, Bassetti CL, Waldvogel D (2009) Morphological differences in Parkinson’s disease with and without rest tremor. J Neurol 256:256–263
Bernheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O, Jellinger K, Seitelberger F (1973) Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J NeurolSci 20:415–455
Berardelli A, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD, Hallett M (2001) Pathophysiology of bradykinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 124:2131–2146
Betarbet R, Sherer TB, MacKenzie G, Garcia-Osuna M, Panov AV, Greenamyre JT (2000) Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Neurosci 3:1301–1306
Borrelli F, Fasolino I, Romano B, Capasso R, Maiello F, Coppola D, Orlando P, Battista G, Pagano E, Di Marzo V, Izzo AA (2013) Beneficial effect of the non-psychotropic plant cannabinoid cannabigerol on experimental inflammatory bowel disease. Biochem Pharmacol 85:1306–1316
Cabral GA, Harmon KN, Carlisle SJ (2001) Cannabinoid-mediated inhibition of inducible nitric oxide production by rat microglial cells: evidence for CB1 receptor participation. Adv Exp Med Biol 493:207–214
Carmine A, Buervenich S, Sydow O, Anvret M, Olson L (2002) Further evidence for an association of the paraoxonase 1 (PON1) Met-54 allele with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 17:764–766
Carroll CB, Zeissler ML, Hanemann CO, Zajicek JP (2012) Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) exerts a direct neuroprotective effect in a human cell culture model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 38:535–547
Casarejos MJ, Perucho J, Gomez A, Muñoz MP, Fernandez-Estevez M, Sagredo O, Fernandez Ruiz J, Guzman M, de Yebenes JG, Mena MA (2013) Natural cannabinoids improve dopamine neurotransmission and tau and amyloid pathology in a mouse model of tauopathy. J Alzheimers Dis 35:525–539
Chen Y, Buck J (2000) Cannabinoids protect cells from oxidative cell death: a receptor-independent mechanism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:807–812
Costa LG, Vitalone A, Cole TB, Furlong CE (2005) Modulation of paraoxonase (PON1) activity. Biochem Pharmacol 69:541–550
Croxford JL (2003) Therapeutic potential of cannabinoids in CNS disease. CNS Drugs 17:179–202
Dexter DT, Carayon A, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y, Wells FR, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1991) Alterations in the levels of iron, ferritin and other trace metals in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases affecting the basal ganglia. Brain 114:1953–1975
Dickinson DA, Forman HJ (2002) Cellular glutathione and thiols metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol 64:1019–1026
Draganov DI, La Du BN (2004) Pharmacogenetics of paraoxonases: a brief review. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 369:78–88
Dringen R (2000) Metabolism and functions of glutathione in brain. Prog Neurobiol 62:649–671
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem 82:70–77
ElSohly MA, Slade D (2005) Chemical constituents of marijuana: the complex mixture of natural cannabinoids. Life Sci 78:539–548
Facchinetti F, Del Giudice E, Furegato S, Passarotto M, Leon A (2003) Cannabinoids ablate release of TNFalpha in rat microglial cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Glia 41:161–168
Feng Y, Liang ZH, Wang T, Qiao X, Liu HJ, Sun SG (2006) alpha-Synuclein redistributed and aggregated in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease rats. Neurosci Bull 22:288–293
Fischer Stenger K, Dove Pettit DA, Cabral GA (1993) Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: suppression of post-translational events. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:1558–1565
Fitzmaurice PS, Ang L, Guttman M, Rajput AH, Furukawa Y, Kish SJ (2003) Nigral glutathione deficiency is not specific for idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 18:969–976
Floyd RA (1990) Role of oxygen free radicals in carcinogenesis and brain ischemia. FASEB J 4:2587–2597
Floyd RA (1999) Antioxidants, oxidative stress, and degenerative neurological disorders. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 222:236–245
Frankola KA, Greig NH, Luo W, Tweedie D (2011) Targeting TNF-α to elucidate and ameliorate neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10:391–403
Freire C, Koifman S (2012) Pesticide exposure and Parkinson’s disease: epidemiological evidence of association. Neurotoxicology 33:947–971
Gorell JM, Johnson CC, Rybicki BA, Peterson EL, Richardson RJ (1998) The risk of Parkinson’s disease with exposure to pesticides, farming, well water, and rural living. Neurology 50:1346–1350
Graybiel AM (2000) The basal ganglia. Curr Biol 10:R509–R511
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 3rd edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Hampson AJ, Grimaldi M, Lolic M, Wink D, Rosenthal R, Axelrod J (2000) Neuroprotective antioxidants from marijuana. Ann N Y Acad Sci 899:274–282
Hancock DB, Martin ER, Mayhew GM, Stajich JM, Jewett R, Stacy MA, Scott BL, Vance JM, Scott WK (2008) Pesticide exposure and risk of Parkinson’s disease: a family-based case–control study. BMC Neurol 8:6
Hansson EL, Rönnbäck L (2003) Glial neuronal signaling in the central nervous system. FASEB J 17:341–348
Hantraye P, Brouillet E, Ferrante R, Palfi S, Dolan R, Matthews RT, Beal MF (1996) Inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase prevents MPTP-induced parkinsonism in baboons. Nat Med 2:1017–1021
Harvey BS, Ohlsson KS, Mååg JL, Musgrave IF, Smid SD (2012) Contrasting protective effects of cannabinoids against oxidative stress and amyloid-β evoked neurotoxicity in vitro. Neurotoxicology 33:138–146
He Y, Imam SZ, Dong Z, Jankovic J, Ali SF, Appel SH, Le W (2003) Role of nitric oxide in rotenone-induced nigro-striatal injury. J Neurochem 86:1338–1345
Hermida-Ameijeiras A, Méndez-Alvarez E, Sánchez-Iglesias S, Sanmartín-Suárez C, Soto-Otero R (2004) Autoxidation and MAO-mediated metabolism of dopamine as a potential cause of oxidative stress: role of ferrous and ferric ions. Neurochem Int 45:103–116
Hien PP, Gortnizka H, Kraemer R (2003) Rotenone-potential and prospect for sustainable agriculture. Omonrice 11:83–92
Higashino K, Takahashi Y, Yamamura Y (1972) Release of phenyl acetate esterase from liver microsomes by carbon tetrachloride. Clin Chim Acta 41:313–320
Hsu M, Srinivas B, Kumar J, Subramanian R, Andersen J (2005) Glutathione depletion resulting in selective mitochondrial complex I inhibition in dopaminergic cells is via an NO-mediated pathway not involving peroxynitrite: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 92:1091–1103
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J NeurolNeurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184
Jamroz-Wisniewska A, Beltowski J, Stelmasiak Z, Bartosik-Psujek H (2009) Paraoxonase 1 activity in different types of multiple sclerosis. MultScler 15:399–402
Jeon YJ, Yang KH, Pulaski JT, Kaminski NE (1996) Attenuation of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression by delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol is mediated through the inhibition of nuclear factor- kappa B/Rel activation. Mol Pharmacol 50:334–341
Jha N, Jurma O, Lalli G, Liu Y, Pettus EH, Greenamyre JT, Liu RM, Forman HJ, Andersen JK (2000) Glutathione depletion in PC12 results in selective inhibition of mitochondrial complex I activity. Implications for Parkinson's disease. J Biol Chem 275:26096–26101
Kim SH, Won SJ, Mao XO, Jin K, Greenberg DA (2005) Involvement of protein kinase A in cannabinoid receptor-mediated protection from oxidative neuronal injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:88–94
Kim SH, Won SJ, Mao XO, Jin K, Greenberg DA (2006) Molecular mechanisms of cannabinoid protection from neuronal excitotoxicity. Mol Pharmacol 69:691–696
Kondo I, Yamamoto M (1998) Genetic polymorphism of paraoxonase 1 (PON1) and susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 806:271–273
La Du BN (1992) Human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase. In: Kalow W (ed) Pharmacogenetics of drug metabolism. Pergamon, New York, pp 51–91
Lakhan SE, Rowland M (2009) Whole plant cannabis extracts in the treatment of spasticity in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. BMC Neurol 9:59
Lee PC, Rhodes SL, Sinsheimer JS, Bronstein J, Ritz B (2013) Functional paraoxonase 1 variants modify the risk of Parkinson’s disease due to organophosphate exposure. Environ Int 56:42–47
Madathil KS, Karuppagounder SS, Haobam R, Varghese M, Rajamma U, Mohanakumar KP (2013) Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors protect against rotenone-induced, oxidative stress mediated parkinsonism in rats. Neurochem Int 62:674–683
Molina-Holgado F, Molina-Holgado E, Guaza C, Rothwell NJ (2002) Role of CB1 and CB2 receptors in the inhibitory effects of cannabinoids on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide release in astrocyte cultures. J Neurosci Res 67:829–836
Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA (1989) Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol 38:1709–1715
Moncada S, Palmer RMJ, Higgs EA (1991) Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 43:109–142
Moshage H, Kok B, Huizenga JR (1995) Nitrite and nitrate determination in plasma: a critical evaluation. ClinChem 41:892–896
Müller-Vahl KR, Kolbe H, Schneider U, Emrich HM (1999) Cannabis in movement disorders. Forsch Komplementar med 6(Suppl 3):23–27
Muramatsu Y, Kurosaki R, Mikami T, Michimata M, Matsubara M, Imai Y, Kato H, Itoyama Y, Araki T (2002) Therapeutic effect of neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (7-nitroindazole) against MPTP neurotoxicity in mice. Metab Brain Dis 17:169–182
Nagatsu T, Mogi M, Ichinose H, Togari A (2000) Changes in cytokines and neurotrophins in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 60:277–290
Olanow CW, Tatton WG (1999) Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:123–144
Pankratz N, Foroud T (2007) Genetics of Parkinson disease. Genet Med 9:801–811
Panov A, Dikalov S, Shalbuyeva N, Taylor G, Sherer T, Greenamyre JT (2005) Rotenone model of Parkinson disease: multiple brain mitochondria dysfunctions after short term systemic rotenone intoxication. J Biol Chem 280:42026–42035
Park KM, Bowers WJ (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediated signaling in neuronal homeostasis and dysfunction. Cell Signal 22:977–983
Pearce RK, Owen A, Daniel S, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1997) Alterations in the distribution of glutathione in the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 104:661–677
Pertwee RG, Ross RA (2002) Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 66:101–121
Primo-Parmo SL, Sorenson RC, Teiber J, La Du BN (1996) The human serum paraoxonase/arylesterase gene (PON1) is one member of a multigene family. Genomics 33:498–507
Priyadarshi A, Khuder SA, Schaub EA, Shrivastava S (2000) A meta analysis of Parkinson’s disease and exposure to pesticides. Neurotoxicology 21:435–440
Ren Y, Feng J (2007) Rotenone selectively kills serotonergic neurons through a microtubule-dependent mechanism. J Neurochem 103:303–311
Romano B, Borrelli F, Fasolino I, Capasso R, Piscitelli F, Cascio M, Pertwee R, Coppola D, Vassallo L, Orlando P, Di Marzo V, Izzo A (2013) The cannabinoid TRPA1 agonist cannabichromene inhibits nitric oxide production in macrophages and ameliorates murine colitis. Br J Pharmacol 169:213–329
Ruiz-Larrea MB, Leal AM, Liza M, Lacort M, de Groot H (1994) Antioxidant effects of estradiol and 2-hydroxyestradiol on iron-induced lipid peroxidation of rat liver microsomes. Steroids 59:383–388
Sastre-Garriga J, Vila C, Clissold S, Montalban X (2011) THC and CBD oromucosal spray (Sativex A®) in the management of spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis. Expert Rev Neurother 11:627–637
Sayre LM, Perry G, Smith MA (2008) Oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Chem Res Toxicol 21:172–188
Schmidt WJ, Alam M (2006) Controversies on new animal models of Parkinson’s disease pro and con: the rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease (PD). J Neural Transm Suppl 70:273–276
Seres I, Paragh G, Deschene E, Fulop T Jr, Khalil A (2004) Study of factors influencing the decreased HDL associated PON1 activity with aging. Exp Gerontol 39:59–66
Sheng WS, Hu S, Min X, Cabral GA, Lokensgard JR, Peterson PK (2005) Synthetic cannabinoid WIN55,212-2 inhibits generation of inflammatory mediators by IL-1beta-stimulated human astrocytes. Glia 49:211–219
Sherer TB, Kim JH, Betarbet R, Greenamyre JT (2003a) Subcutaneous rotenone exposure causes highly selective dopaminergic degeneration and alpha-synuclein aggregation. Exp Neurol 179:9–16
Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Testa CM, Seo BB, Richardson JR, Kim JH, Miller GW, Yagi T, Matsuno-Yagi A, Greenamyre JT (2003b) Mechanism of toxicity in rotenone models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 23:10756–10764
Sian J, Dexter DT, Lees AJ, Daniel S, Agid Y, Javoy-Agid F, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1994) Alterations in glutathione levels in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders affecting basal ganglia. Ann Neurol 36:348–355
Sies H (1991a) Oxidative stress: introduction. In: Sies H (ed) Oxidative stress, oxidants and antioxidants. London Academic, London, pp xv–xxii
Sies H (1991b) Role of reactive oxygen species in biological processes. KlinWochenschr 69:965–968
Sies H (1997) Oxidative stress: oxidants and antioxidants. Exp Physiol 82:291–295
Sofic E, Lange KW, Jellinger K, Riederer P (1992) Reduced and oxidized glutathione in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 142:128–130
Townsend DM, Tew KD, Tapiero H (2003) The importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed Pharmacother 57:145–155
Turner JC, Mahlberg PG (1984) Separation of acid and neutral cannabinoids in Cannabis sativa L. using HPLC. In: Agurell S, Dewey WL, Willete RE (eds) The cannabinoids: chemical, pharmacologic, and therapeutic aspects. Academic Press, USA, pp 79–88
Van Den Eeden SK, Tanner CM, Bernstein AL, Fross RD, Leimpeter A, Bloch DA, Nelson LM (2003) Incidence of Parkinson’s disease: variation by age, gender, and race/ethnicity. Am J Epidemiol 157:1015–1022
van der Stelt M, Veldhuis WB, Bär PR, Veldink GA, Vliegenthart JF, Nicolay K (2001) Neuroprotection by Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, the main active compound in marijuana, against ouabain-induced in vivo excitotoxicity. J Neurosci 21:6475–6479
Venderová K, Růzicka E, Vorísek V, Visnovský P (2004) Survey on cannabis use in Parkinson’s disease: subjective improvement of motor symptoms. Mov Disord 19:1102–1106
Verhoeckx KC, Korthout HA, van Meeteren-Kreikamp AP, Ehlert KA, Wang M, van der Greef J, Rodenburg RJ, Witkamp RF (2006) Unheated Cannabis sativa extracts and its major compound THC-acid have potential immuno-modulating properties not mediated by CB1 and CB2 receptor coupled pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 6:656–665
Watanabe H, Muramatsu Y, Kurosaki R, Michimata M, Matsubara M, Imai Y, Araki T (2004) Protective effects of neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in mouse brain against MPTP neurotoxicity: an immunohistological study. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 14:93–104
Watson AD, Berliner JA, Hama SY, La Du BN, Faull KF, Fogelman AM, Navab M (1995) Protective effect of high density lipoprotein associated paraoxonase. Inhibition of the biological activity of minimally oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest 96:2882–2891
Wehr H, Bednarska-Makaruk M, Graban A, Lipczyńska-Łojkowska W, Rodo M, Bochyńska A, Ryglewicz D (2009) Paraoxonase activity and dementia. J Neurol Sci 283:107–108
Wirdefeldt K, Adami HO, Cole P, Trichopoulos D, Mandel J (2011) Epidemiology and etiology of Parkinson’s disease: a review of the evidence. Eur J Epidemiol 26(Suppl 1):S1–S58
Wu YN, Johnson SW (2007) Rotenone potentiates NMDA currents in substantianigra dopamine neurons. Neurosci Lett 421:96–100
Zajicek JP, Apostu VI (2011) Role of cannabinoids in multiple sclerosis. CNS Drugs 25:187–201
Zheng ZM, Specter SC (1996) Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol suppresses tumor necrosis factor alpha maturation and secretion but not its transcription in mouse macrophages. Int J Immunopharmacol 18:53–68
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Salam, O.M.E., Youness, E.R., Khadrawy, Y.A. et al. The effect of cannabis on oxidative stress and neurodegeneration induced by intrastriatal rotenone injection in rats. Comp Clin Pathol 24, 359–378 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-014-1907-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-014-1907-9