Pisum sativum
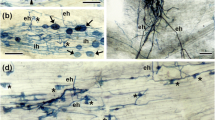
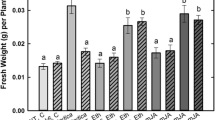
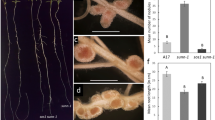
(pea) mutants of the wild type cv. Frisson and six supernodulating Medicago truncatula mutants of the wild-type cv. Jemalong line J5 for their ability to form endomycorrhizas. The six mutants of M. truncatula were shown to be allelic mutants of the same gene Mtsym12, whereas distinct genes (sym28 and sym29) are known to determine the supernodulation character of the P64 and P88 pea mutants, respectively. Mutant P88 of pea and the majority of the M. truncatula mutants were significantly more colonized by the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae than their corresponding wild types, 4 weeks and 30 days after inoculation, respectively. These differences were expressed essentially in transversal intensity rather than in length intensity of root colonization and appeared to correspond to an increase in arbuscule formation. Results are discussed in relation to the mutated genes and, in particular, whether the observed effects are due indirectly to plant physiological modifications or are a direct result of possible common factors of regulation of nodulation and mycorrhizal development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 9 February 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morandi, D., Sagan, M., Prado-Vivant, E. et al. Influence of genes determining supernodulation on root colonization by the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae in Pisum sativum and Medicago truncatula mutants. Mycorrhiza 10, 37–42 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720050285
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720050285