Abstract
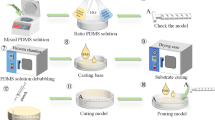
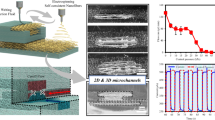
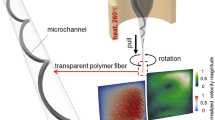
A rapid and simple fabrication approach to achieve helical microfluidic channels with circular cross section using template-assisted method is proposed in this article based on rope coiling effect in the extrusion process of a desktop 3D printer. Rope coil effect is a common phenomenon in the falling process of a slender string of viscous fluid and is used to fabricate helical microstructures served as the templates in the sacrificial template-assisted method, which holds great promise to fabricate micro-channels with desired vascular architectures. The helical microstructures are fabricated with the high viscous PVA (Polyvinyl alcohol) paste extruded out of the nozzle orifice from a certain falling height. After the PDMS block embedded with PVA helical template has been fabricated, the template would then be removed by melting in hot water easily to obtain the microfluidic channels. Two major processing parameters, falling height and flow rate are studied in relation to two main geometric features of helical structures: coil diameter and wire diameter. Besides, the dimension and the shape of helical microstructures are further studied for fabrication of microfluidic channels with varying geometric parameters. The presented method facilitates the rapid and convenient construction of three-dimensional (3D) helical microfluidic channels for a wide variety of lab-on-chip applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asthana A, Kim KO, Perumal J, Kim DM, Kim DP (2009) Facile single step fabrication of microchannels with varying size. Lab Chip 9(8):1138
Becker H, Locascio LE (2002) Polymer microfluidic devices. Talanta 56(2):267
Bellini A (2002) Fused deposition of ceramics: a comprehensive experimental, analytical and computational study of material behavior, fabrication process and equipment design
Bloomstein T, Ehrlich D (1992) Laser-chemical three-dimensional writing for microelectromechanics and application to standard-cell microfluidics. J Vac Sci Technol B 10(6):2671
Brun PT, Audoly B, Ribe NM, Eaves TS, Lister JR (2015) Liquid ropes: a geometrical model for thin viscous jet instabilities. Phys Rev Lett 114(17):174501
Choi CH, Yi H, Hwang S, Weitz DA, Lee CS (2011) Microfluidic fabrication of complex-shaped microfibers by liquid template-aided multiphase microflow. Lab Chip 11(8):1477
Dean RN, Nordine PC, Christodoulou CG (2000) 3-D helical THz antennas. Microw Opt Technol Lett 24(2):106
Delendik K, Emeliantchik I, Litomin A, Rumyantsev V, Voitik O (2003) Aluminium oxide microchannel plates. Nucl Phys B Proc Suppl 125:394
Duffy DC, McDonald JC, Schueller OJ, Whitesides GM (1998) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly (dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem 70(23):4974
Esser-Kahn AP, Thakre PR, Dong H, Patrick JF, Vlasko-Vlasov VK, Sottos NR, Moore JS, White SR (2011) Three-dimensional microvascular fiber-reinforced composites. Adv Mater 23(32):3654. doi:10.1002/adma.201100933
Farahani RD, Chizari K, Therriault D (2014) Three-dimensional printing of freeform helical microstructures: a review. Nanoscale 6(18):10470
Guerin L, Bossel M, Demierre M, Calmes S, Renaud P (1997) Simple and low cost fabrication of embedded microchannels by using a new thick-film photoplastic. In: Transducers, vol 97, pp 1419–1422
Habibi M, Ribe N, Bonn D (2007) Coiling of elastic ropes. Phys Rev Lett 99(15):154302
He S, Chen F, Yang Q, Liu K, Shan C, Bian H, Liu H, Meng X, Si J, Zhao Y (2012) Facile fabrication of true three-dimensional microcoils inside fused silica by a femtosecond laser. J Micromech Microeng 22(22):105017
Jo BH, Van Lerberghe LM, Motsegood KM, Beebe DJ (2000) Three-dimensional micro-channel fabrication in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer. J Microelectromechanical Syst 9(1):76
Kirchhoff MR, Güttler J, Waldschik A, Feldmann M, Büttgenbach S (2008) Revised fabrication process for micro-fluxgate-magnetometers: Usage of electrodepositable photoresist. Microelectron Eng 85(5):1047
Ladd C, So JH, Muth J, Dickey MD (2013) 3D printing of free standing liquid metal microstructures. Adv Mater 25(36):5081
Lebel LL, Aissa B, Khakani MAE, Therriault D (2010) Ultraviolet-assisted direct-write fabrication of carbon nanotube/polymer nanocomposite microcoils. Adv Mater 22(5):592
Liao Y, Song J, Li E, Luo Y, Shen Y, Chen D, Cheng Y, Xu Z, Sugioka K, Midorikawa K (2012) Rapid prototyping of three-dimensional microfluidic mixers in glass by femtosecond laser direct writing. Lab Chip 12(4):746
Luelf T, Bremer C, Wessling M (2016) Rope coiling spinning of curled and meandering hollow fiber membranes. J Membr Sci 12:1246
Mahadevan L, Ryu WS, Samuel AD (1998) Fluid ‘rope trick’ investigated. Nature 392(6672):140
Maleki M, Habibi M, Golestanian R, Ribe N, Bonn D (2004) Liquid rope coiling on a solid surface. Phys Rev Lett 93(21):214502
Monzón MD, Gibson I, Benítez AN, Lorenzo L, Hernández PM, Marrero MD (2013) Process and material behavior modeling for a new design of micro-additive fused deposition. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67(9–12):2717
Nguyen DT, Leho YT, Esser-Kahn AP (2012) A three-dimensional microvascular gas exchange unit for carbon dioxide capture. Lab Chip 12:1246. doi:10.1039/C2LC00033D
Parekh DP, Ladd C, Panich L, Moussa K, Dickey MD (2016) Simple 3D Printed Scaffold-Removal Method for the Fabrication of Intricate Microfluidic Devices. Lab Chip 16(10):1812
Passieux R, Guthrie L, Rad SH, Lvesque M, Therriault D (2015) Instability-assisted direct writing of microstructured fibers featuring sacrificial bonds. Adv Mater 27(24):3676
Ribe NM (2004) Coiling of viscous jets. Proc R Soc Lond Ser A 460(2051):3223
Ribe NM, Habibi M, Bonn D (2012) Liquid Rope Coiling. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 44(8):249
Ribe NM, Huppert HE, Hallworth MA, Habibi M, Bonn D (2006) Multiple coexisting states of liquid rope coiling. J Fluid Mech 555:275
Roberts MA, Rossier JS, Bercier P, Girault H (1997) UV laser machined polymer substrates for the development of microdiagnostic systems. Anal Chem 69(11):2035
Saggiomo V, Velders AH (2015) Simple 3D printed scaffold-removal method for the fabrication of intricate microfluidic devices. Adv Sci. doi:10.1002/advs.201500125
Shariatpanahi SP, Bonn D, Ejtehadi MR, Zad AI (2016) Electrical bending instability in electrospinning visco-elastic solutions. J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 54(11):1036
Shengguan H, Feng C, Keyin L, Qing Y, Hewei L, Hao B, Xiangwei M, Chao S, Jinhai S, Yulong Z (2012) Fabrication of three-dimensional helical microchannels with arbitrary length and uniform diameter inside fused silica. Opt Lett 37(18):3825
Song SH, Lee CK, Kim TJ, Shin IC, Jun SC, Jung HI (2010) A rapid and simple fabrication method for 3-dimensional circular microfluidic channel using metal wire. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(2–3):533
Therriault D, White SR, Lewis JA (2003) Chaotic mixing in three-dimensional microvascular networks fabricated by direct-write assembly. Nature Mater 2(4):265
Tottori S (2015) Formation of liquid rope coils in a coaxial microfluidic device. Rsc Adv 5:33691
Yamada A, Niikura F, Ikuta K (2008) A three-dimensional microfabrication system for biodegradable polymers with high resolution and biocompatibility. J Micromech Microeng 18(2):025035
Acknowledgments
We thank the support from Project (No. 51221004) supported by the Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of National Natural Science Foundation of China,Project (No.145) supported by 2015 Visiting Scholars Professional Development Program of Zhejiang Provincial Education Office.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Wm., Zhu, Tk., Jin, Ya. et al. Facile fabrication of helical microfluidic channel based on rope coiling effect. Microsyst Technol 23, 2957–2964 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3010-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-3010-4