Abstract
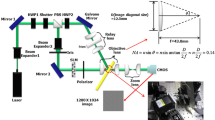
In a holographic data storage system (HDSS), misalignment of the optical components causes data distortion, including barrel, pincushion, and rotation distortion. Because holographic data storage systems are very sensitive, misalignment inevitably results in data distortion. It is important to acquire accurate distortion-free data from a HDSS system. This paper proposes an intelligent distortion-detection algorithm for restoring data in HDSSs. We used a fuzzy system and subtractive clustering algorithm to generate fuzzy rules for the detection algorithm. The proposed algorithm determines a value indicating how distorted the data image is. Using this algorithm, it is possible to compensate for data distortion. A simulation performed well using barrel, pincushion and rotation images.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernal MP, Coufal H, Grygier RK, Hoffnagle JA, Jefferson CM, Macfarlane RM et al (1996) A precision tester for studies of holographic optical storage materials and recording physics. Appl Opt 35(14):2360–2374
Cannon RL, Dave JV, Bezdek JC (1986) Efficient implementation of the fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms. Pattern Anal Mach Intell IEEE Trans 2:248–255
Curtis K, Dhar L, Hill A, Wilson W, Ayres M (2011) Holographic data storage: from theory to practical systems. Wiley, West Sussex
Demirli K, Muthukumaran P (2000) Higher order fuzzy system identification using subtractive clustering. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 9(3):129–158
Gribbon KT, Bailey DG (2004) A novel approach to real-time bilinear interpolation. Electron Des Test Appl, IEEE International Workshop on IEEE, pp 126–131
Hecht E, Zajac A (2002) Optics. Addison-Wesley, USA
Kim JH, Yang H, Kim N, Jeong W, Park JB (2012) Pattern analysis for tilt servo control in holographic data storage system. Microsyst Technol 18(9–10):1677–1692
Kim JH, Jeong W, Yang H (2013) Tilt servo control by intelligent algorithm in holographic data storage system. Jpn J Appl Phys 52(9):09LD12
Lim SY, Lee J, Lee JS, Jeong W, Yang H, Park NC et al (2013) Disturbances analysis considering an effective servo system for holographic disc drive. Jpn J Appl Phys 52(9):09LF03
Liu WY, Xiao CJ, Wang BW, Shi Y, Fang SF (2003) Study on combining subtractive clustering with fuzzy c-means clustering. Mach Learn Cybern Int Conf IEEE 5:2659–2662
Priyono A, Ridwan M, Alias AJ, OK Rahmat RA, Hassan A, Mohd Ali MA (2012) Generation of fuzzy rules with subtractive clustering. J Teknol 43(1):143–153
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2013R1A1A2012658).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, W., Kim, J.H., Lim, SY. et al. An intelligent distortion-detection algorithm for restoring data in a holographic data storage system. Microsyst Technol 20, 1571–1578 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2177-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2177-9