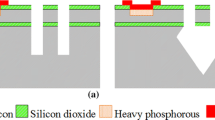
Abstract
This paper presents a new method for electrically isolating released single crystal silicon MEMS structures. The technology employees double-side processing deep reactive ion etching to obtain functional high aspect ratio micromechanical structures and deep silicon oxidizing to isolate them from bulk silicon. Applicability of the technology to MEMS design was demonstrated with fabrication of the monolithic integrated bulk micromachined comb drive.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold JC, Sawin HH (1991) Charging of pattern features during plasma etching. J Appl Phys 70(10):5314–5317 doi:10.1063/1.350241
Bayiati P, Tserepi A, Gogolides E, Misiakos K (2004) Selective plasma-induced deposition of fluorocarbon films on metal surfaces for actuation in microfluidics. J Vac Sci Technol A 22(4):1546–1551. doi:10.1116/1.1764815
Blauw MA, Zijlstra T, van der Drift E (2001) Balancing the etching and passivation in time-multiplexed dry etching of silicon. J Vac Sci Technol B 19:2930–2934
Brosnihan T, Bustillo J, Pisano A, Howe R (1997) Embedded interconnect and electrical isolation for high-aspect ratio, soi inertial instruments. In: Proceeding of international conference on solid state sensors and actuators, TRANSDUCERS 97, Chicago, pp 637–640
Cowen A, Hames G, Monk D, Wilcenski S, Hardy B (2011) Soimumps design handbook. http://www.memscap.com, revision 8.0
Craigie C, Sheehan T, Johnson V, Burkett S, Moll A, Knowlton W (2002) Polymer thickness effects on bosch etch profiles. J Vac Sci Technol B 20(6):2229–2232. doi:10.1116/1.1515910
Docker PT, Kinnell PK, Ward MCL (2004) Development of the one-step drie dry process for unconstrained fabrication of released mems devices. J Micromech Microeng 14:941–944
Harness T, Syms RRA (2000) Characteristic modes of electrostatic comb-drive x–y microactuators. J Micromech Microeng 10(1):7. http://stacks.iop.org/0960-1317/10/i=1/a=302
Hsieh J, Fang W (2002) A boron etch-stop assisted lateral silicon etching process for improved high-aspect-ratio silicon micromachining and its applications. J Micromech Microeng 12(3):574–581
Hwang GS, Giapis KP (1997) On the origin of the notching effect during etching in uniform high density plasmas. J Vac Sci Technol B Microelectron Nanometer Struct 15(1):70–87. http://link.aip.org/link/?JVB/15/70/1
Jiang H, Yoo K, Yeh JA, Li Z, Tien NC (2002) Fabrication of thick silicon dioxide sacrificial and isolation blocks in a silicon substrate. J Micromech Microeng 12:87–95
Kiang MH, Solgaard O, Lau KY, Muller R (1998) Electrostatic combdrive-actuated micromirrors for laser-beam scanning and positioning. Microelectromech Syst J 7(1):27–37. doi:10.1109/84.661381
Kiihamaki J, Franssila S (1999) Pattern shape effects and artifacts in deep silicon etching. J Vac Sci Technol A 17(4):2280–2285
Laermer F, Andrea S (1996) Method of anisotropically etching silicon. Patent US5501893
Larmer F et al (1992) Method of anisotropically etching silicon. German patent DE4241045C1
Lee S, Park S, il Cho D, Yongsoo O (1999) Surface/bulk micromachining (sbm) process and deep trench oxide isolation method for mems. In: Electron devices meeting, 1999. IEDM ’99. Technical digest. International, pp 701–704. doi:10.1109/IEDM.1999.824248
Lee S, Park S, Cho D (2002) Honeycomb-shaped deep-trench oxide posts combined with the sbm technology for micromachining single crystal silicon without using soi. Sens Actuators A 97–98:734–738. doi:10.1016/S0924-4247(02)00013-4
MacDonald NC (1996) {SCREAM} microelectromechanical systems. Microelectron Eng 32(1-4):49–73. doi:10.1016/0167-9317(96)00007-X, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/016793179600007X, Nanotechnology
Miao J, Sun J, Puech M (2005) Fabrication of thick SiO2 block with dry-released underneath cavity in silicon for rf mems. Electron Lett 41(11):662–664. doi:10.1049/el:20051305
Morozov OV, Amirov II (2007) Aspect-ratio-independent anisotropic silicon etching in a plasma chemical cyclic process. Russ Microelectron 36(5):333–341
Oehrlein G, Kurogi Y (1998) Sidewall surface chemistry in directional etching processes. Mater Sci Eng 24:153–183
Park S, Kwak D, Ko H, Song T, il Cho D (2005) Selective silicon-on-insulator (SOI) implant: a new micromachining method without footing and residual stress. J Micromech Microeng 15(9):1607–1613. http://www.iop.org/EJ/abstract/0960-1317/15/9/001
Rais-Zadeh M, Ayazi F (2005) Characterization of high-q spiral inductors on thick insulator-on-silicon. J Micromech Microeng 15:2105–2112
Sarajlic E, Berenschot E, Krijnen G, Elwenspoek M (2003) Versatile trench isolation technology for the fabrication of microactuators. Microelectron Eng 67-68:430–437
Schenk H, Durr P, Kunze D, Lakner H, Kuck H (2001) A resonantly excited 2d-micro-scanning mirror with large deflection. Sens Actuators A 104–111
Sridhar U, How LC, Jun LL, Bo MY, Khen-Sang T, Dow FP, Bergstrom J, Sooriakumar K, Hong LY, San LH, Kiat TC (1998) Trench oxide isolated single crystal silicon micromachined accelerometer. In: Electron devices meeting, 1998. IEDM ’98. technical digest., International, pp 475–478. doi:10.1109/IEDM.1998.746401
Sridhar U, Jun L, Dow F, Hong L, Bo M (1999) Isolation process for surface micromachined sensors and actuators. Patent US5930595, 1999
Tsai J, Chu HY, Hsieh, Fang JW (2004) The belst ii process for a silicon high-aspect-ratio micromaching vertical comb actuator and its applications. J Micromech Microeng. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/14/2/010
Zhu Y, Yan G, Fan J, Zhou J, Liu X, Li Z, Wang Y (2005) Fabrication of keyhole-free ultra-deep high-aspect-ratio isolation trench and its applications. J Micromech Microeng 15(3):636–642. http://stacks.iop.org/0960-1317/15/i=3/a=027
Acknowledgements
This work was performed at Facilities Sharing Center “Micro- and Nanostructures Diagnostics” and is supported by Ministry of Science and Education of Russian Federation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Postnikov, A., Morozov, O.V. & Amirov, I.I. Oxidized bridges technology for suspended MEMS fabrication using standard silicon wafer. Microsyst Technol 21, 669–674 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2080-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-014-2080-4