Abstract
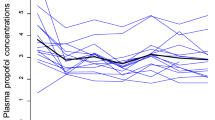
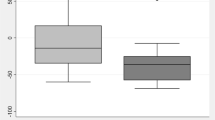
The purpose of this study was to assess the effect of gynecologic laparoscopy on propofol concentrations administered by the target-controlled infusion (TCI) system. Thirteen patients undergoing gynecologic laparoscopy (intraabdominal pressure of 10 mmHg) were enrolled in this study. Anesthesia was induced with vecuronium 0.1 mg·kg−1 and propofol, then maintained by 60% nitrous oxide and sevoflurane in oxygen and a constant infusion of propofol. Propofol was administered to all subjects by means of a target-controlled infusion to achieve propofol plasma concentration at 6.0 µg·ml−1 at intubation and 2.0 µg·ml−1 after intubation. Before and during laparoscopy, plasma propofol concentration was determined using high-performance liquid chromatograhy. Cardiac output (CO) and effective liver blood flow (LBF) were also measured using indocyanine green as an indicator. Before and during pneumoperitoneum, there were no significant differences in propofol concentations between each point. Propofol concentrations were well achieved to predicted concentrations administered by the TCI system during gynecologic laparoscopy under propofol and sevoflurane anesthesia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
PJ Simons ID Cockshott EJ Douglas EA Gordon K Hopkins M Rowland (1988) ArticleTitleDisposition in male volunteers of a subanaesthetic intravenous dose of an oil in water emulsion of 14C-propofol Xenobiotica 18 429–440 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXktFKmsLw%3D Occurrence Handle3261062
H Hiraoka K Yamamoto N Okano T Morita F Goto R Horiuchi (2004) ArticleTitleChanges in drug plasma concentrations of an extensively bound and highly extracted drug, propofol, in response to altered plasma binding Clin Pharmacol Ther 75 324–330 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.clpt.2003.12.004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXivVKgurY%3D Occurrence Handle15060510
D Takizawa H Hiraoka K Nakamura K Yamamoto R Horiuchi (2004) ArticleTitlePropofol concentrations during the anhepatic phase of living related donor liver transplantation Clin Pharmacol Ther 76 648–649 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.clpt.2004.09.003 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhtVKlt7vL Occurrence Handle15592336
D Takizawa H Hiraoka F Goto K Yamamoto R Horiuchi (2005) ArticleTitleHuman kidneys play an important role in the elimination of propofol Anesthesiology 102 327–330 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXosVaruw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle15681947
WE Gepts F Camu ID Cocksott EJ Douglas (1987) ArticleTitleDisposition of propofol administered as constant rate intravenous infusion in humans Anesth Analg 66 1256–1263 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXkvVKksQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle3500657
B Marsh M White M Morton (1991) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetic model driven infusion of propofol in children Br J Anaesth 67 41–48 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6A3MrptF0%3D Occurrence Handle1859758
C Are JM Hardacre MA Talamini K Murata S Frank (2003) ArticleTitleDecreased cardiac output in humans during laparoscopic antireflex surgery: direct measurements J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 13 139–146 Occurrence Handle10.1089/109264203766207645 Occurrence Handle12855094
MK Schilling C Redaelli L Krahenbuhl C Signer MW Buchler (1997) ArticleTitleSplanchnic microcirculatory changes during CO2 laparoscopy J Am Coll Surg 184 378–382 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB2MrjtlI%3D Occurrence Handle9100683
D Takizawa K Nishikawa E Sato H Hiraoka K Yamamoto S Saito R Horiuchi F Goto (2005) ArticleTitleDopamine decreases propofol concentrations during epidural blockade under general anesthesia Can J Anaesth 52 463–466 Occurrence Handle15872122
T Imai K Takahashi H Fukura Y Morishita (1997) ArticleTitleMeasurement of cardiac output by pulse dye densitometry using indocyanine green Anesthesiology 87 816–822 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FhvV2itw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9357883
SC Hoymork J Raeder B Grimsmo PA Steen (2003) ArticleTitleBispectral index, serum drug concentrations and emergence assciated with indivisually adjusted target-controlled infusions of remifentanil and propofol for laparoscopic surgery Br J Anaesth 91 773–780 Occurrence Handle10.1093/bja/aeg258 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXpvVSisb4%3D Occurrence Handle14633743
JA Myburgh RN Upton C Grant A Martinez (2001) ArticleTitleEpinephrine, norepinephrine and dopamine infusions decrease propofol concentrations during continuous propofol infusion in an ovine model Intens Care Med 27 276–282 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7ovVOlug%3D%3D
T Kurita K Morita T Kazama S Sato (2002) ArticleTitleInfluence of cardiac output on plasma propofol concentrations during constant infusion in swine Anesthesiology 96 1498–1503 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000542-200206000-00033 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XkvFGmtbw%3D Occurrence Handle12170066
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Takizawa, D., Hiraoka, H., Sato, E. et al. The effect of gynecologic laparoscopy on propofol concentrations administered by the target-controlled infusion system. J Anesth 20, 57–59 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-005-0355-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-005-0355-8