Abstract
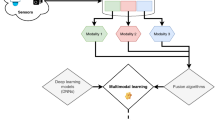
Multimodal emotion recognition is a challenging research topic which has recently started to attract the attention of the research community. To better recognize the video users’ emotion, the research of multimodal emotion recognition based on audio and video is essential. Multimodal emotion recognition performance heavily depends on finding good shared feature representation. The good shared representation needs to consider two aspects: (1) it has the character of each modality and (2) it can balance the effect of different modalities to make the decision optimal. In the light of these, we propose a novel Enhanced Sparse Local Discriminative Canonical Correlation Analysis approach (En-SLDCCA) to learn the multimodal shared feature representation. The shared feature representation learning involves two stages. In the first stage, we pretrain the Sparse Auto-Encoder with unimodal video (or audio), so that we can obtain the hidden feature representation of video and audio separately. In the second stage, we obtain the correlation coefficients of video and audio using our En-SLDCCA approach, then we form the shared feature representation which fuses the features from video and audio using the correlation coefficients. We evaluate the performance of our method on the challenging multimodal Enterface’05 database. Experimental results reveal that our method is superior to the unimodal video (or audio) and improves significantly the performance for multimodal emotion recognition when compared with the current state of the art.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, L., Yang, S., Bhanu, B.: Person re-identification by robust canonical correlation analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(8), 1103–1107 (2015). doi:10.1109/LSP.2015.2390222
Busso, C., Deng, Z., Yildirim, S., Bulut, M., Lee, C.M., Kazemzadeh, A., Lee, S., Neumann, U., Narayanan, S.: Analysis of emotion recognition using facial expressions, speech and multimodal information. In: International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces, vol. 38, No. 4, pp. 205–211 (2004). doi:10.1145/1027933.1027968
Chen, L.S., Huang, T.S., Miyasato, T., Nakatsu, R.: Multimodal human emotion/expression recognition. IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 366–371 (1998). doi:10.1109/AFGR.1998.670976
Chen, Y., Wiesel, A., Eldar, Y.C., Hero, A.O.: Shrinkage algorithms for mmse covariance estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(10), 5016–5029 (2010). doi:10.1109/TSP.2010.2053029
Datcu, D., Rothkrantz, L.J.M.: Multimodal recognition of emotions in car environments. In: DI & I Prague (2009)
Deng, J., Zhang, Z., Marchi, E., Schuller, B.: Sparse autoencoder-based feature transfer learning for speech emotion recognition. In: Humaine Association Conference on AVTective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, vol. 7971, pp. 511–516 (2013). doi:10.1109/ACII.2013.90
Dobrisek, S., Gajsek, R., Mihelic, F., Pavesic, N., Struc, V.: Towards efficient multi-modal emotion recognition. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 10(53), 53–53 (2013). doi:10.5772/54002
Gajsek, R., STruc V, Mihelic F, : Multi-modal emotion recognition using canonical correlations and acoustic features. In: International Conference on Pattern Recognition, vol. 82, No. 6, pp. 4133–4136 (2010). doi:10.1109/ICPR.2010.1005
Gunes, H., Piccardi, M., Pantic, M.: From the lab to the real world: affect recognition using multiple cues and modalities. InTech Education and Publishing, Croatia (2008)
Han, M.J., Hsu, I.H., Song, K.T., Chang, F.Y.: A new information fusion method for svm-based robotic audio-visual emotion recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, pp. 2656–2661 (2007). doi:10.1109/ICSMC.2007.4413990
Hardoon, D.R., Shawe-Taylor, J.: Sparse canonical correlation analysis. Mach. Learn. 83(3), 331–353 (2011). doi:10.1007/s10994-010-5222-7
Hardoon, D.R., Szedmak, S., Shawe-Taylor, J.: Canonical correlation analysis: an overview with application to learning methods. Neural Comput. 16(12), 2639–2664 (2004). doi:10.1162/0899766042321814
Huang, L., Xin, L., Zhao, L., Tao, J.: Combining audio and video by dominance in bimodal emotion recognition. In: Second International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, vo.l 4738, pp. 729–730 (2007). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-74889-2_71
Kapoor, A., Burleson, W., Picard, R.W.: Automatic prediction of frustration. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 65(8), 724–736 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.ijhcs.2007.02.003
Kim, Y., Lee, H., Provost, E.M.: Deep learning for robust feature generation in audiovisual emotion recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, vol. 32, No. 3, pp. 3687–3691 (2013). doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6638346
Le, D., Provost, E.M.: Emotion recognition from spontaneous speech using hidden markov models with deep belief networks. In: Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, pp. 216–221 (2013). doi:10.1109/ASRU.2013.6707732
Ledoit, O., Wolf, M.: Nonlinear shrinkage estimation of large-dimensional covariance matrices. Ann. Stat. 40(2), 1024–1060 (2012). doi:10.1214/12-AOS989
Li, Z., Tang, J.: Unsupervised feature selection via nonnegative spectral analysis and redundancy control. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(12), 5343–5355 (2015). doi:10.1109/TIP.2015.2479560
Li, Z., Tang, J.: Weakly-supervised deep matrix factorization for social image understanding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(99), 276–288 (2017). doi:10.1109/TIP.2016.2624140
Li, Z., Liu, J., Yang, Y., Zhou, X., Lu, H.: Clustering-guided sparse structural learning for unsupervised feature selection. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 26(9), 2138–2150 (2014). doi:10.1109/TKDE.2013.65
Li, Z., Liu, J., Tang, J., Lu, H.: Robust structured subspace learning for data representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(10), 2085–2098 (2015). doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2400461
Liu, M., Shan, S., Wang, R., Chen, X.: Learning expressionlets on spatio-temporal manifold for dynamic facial expression recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1749–1756 (2014). doi:10.1109/CVPR.2014.226
Lu J, Hu J, Zhou X, Shang Y: Activity-based person identification using sparse coding and discriminative metric learning. In: ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 1061–1064, (2012). doi:10.1145/2393347.2396383
Mansoorizadeh, M., Moghaddam Charkari, N.: Multimodal information fusion application to human emotion recognition from face and speech. Multimed. Tools Appl. 49(2), 277–297 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11042-009-0344-2
Martin O, Kotsia I, Macq B, Pitas I (2006) The enterface’05 audio-visual emotion database. In: International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops, pp. 8–8. doi:10.1109/ICDEW.2006.145
Mroueh, Y., Marcheret, E., Goel, V.: Deep multimodal learning for audio-visual speech recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing, vol. 22, pp. 1103–1107 (2015). doi:10.1109/LSP.2015.2390222
Nie, L., Zhang, L., Yang, Y., Wang, M., Hong, R., Chua, T.S.: Beyond doctors: future health prediction from multimedia and multimodal observations. In: The 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp. 591–600. (2015). doi:10.1145/2733373.2806217
Nie, L., Song, X., Chua, T.S.: Learning from Multiple Social Networks, pp. 118–118. Morgan & Claypool, San Rafael (2016). doi:10.2200/S00714ED1V01Y201603ICR048
Paleari, M., Huet, B.: Toward emotion indexing of multimedia excerpts. In: International Workshop on Content-Based Multimedia Indexing, pp. 425–432, (2008). doi:10.1109/CBMI.2008.4564978
Paleari, M., Benmokhtar, R., Huet, B.: Evidence theory-based multimodal emotion recognition. In: International Multimedia Modeling Conference on Advances in Multimedia Modeling, vol. 5371, pp. 435–446 (2009). doi:10.1007/978-3-540-92892-8_44
Paleari, M., Chellali, R., Huet, B.: Bimodal emotion recognition. In: International Conference on Social Robotics, vol. 6414, pp. 305–314 (2010). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-17248-9_32
Peng, Y., Zhang, D., Zhang, J.: A new canonical correlation analysis algorithm with local discrimination. Neural Process. Lett. 31(1), 1–15 (2010). doi:10.1007/s11063-009-9123-3
Pun, T., Alecu, T.I., Chanel, G., Kronegg, J.: Brain-computer interaction research at the computer vision and multimedia laboratory, university of geneva. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 14(2), 210–213 (2006). doi:10.1109/TNSRE.2006.875544
Schmidt, E.M.: Modeling and predicting emotion in music. Emotion 5, 6-6 (2012)
Schuller B, Vlasenko B, Eyben F, Rigoll G, Wendemuth A (2009) Acoustic emotion recognition: a benchmark comparison of performances. In: IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition & Understanding, pp. 552–557, doi:10.1109/ASRU.2009.5372886
Shan, C., Gong, S., Mcowan, P.W.: Beyond facial expressions: Learning human emotion from body gestures. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 43.1–43.10 (2007). doi:10.5244/C.21.43
Stuhlsatz, A., Lippel, J., Zielke, T.: Feature extraction with deep neural networks by a generalized discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 23(4), 596–608 (2012). doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2183645
Tang, J., Shu, X., Qi, G.J., Li, Z., Wang, M., Yan, S., Jain, R.: Tri-clustered tensor completion for social-aware image tag refinement. In: IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, pp. 1–1 (2016). doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2608882
Wang, H.: Local two-dimensional canonical correlation analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17(11), 921–924 (2010). doi:10.1109/LSP.2010.2071863
Wang, Y., Guan, L., Venetsanopoulos, A.N.: Audiovisual emotion recognition via cross-modal association in kernel space. In: IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, pp. 1–6 (2011). doi:10.1109/ICME.2011.6011949
Zeng, Z., Tu, J., Liu, M., Huang, T.S., Pianfetti, B., Roth, D., Levinson, S.: Audio-visual affect recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 9(2), 424–428 (2007). doi:10.1109/TMM.2006.886310
Zhao, G., Pietikainen, M.: Dynamic texture recognition using local binary patterns with an application to facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(6), 915–928 (2007). doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1110
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61272211 and 61672267) and the General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation 2015M570413.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, J., Mao, Q., Tu, J. et al. Multimodal shared features learning for emotion recognition by enhanced sparse local discriminative canonical correlation analysis. Multimedia Systems 25, 451–461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-017-0547-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-017-0547-8