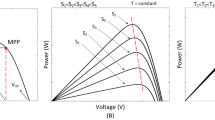
Abstract
In this paper, artificial neural network (ANN) based on a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithm is developed for a solar permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) drive system used without a boost converter and batteries. The discontinuous space vector PWM technique is used to drive two-level inverter which is directly fed by three parallel-connected Kyocera KD205GX-LP PV modules. The ANN-based MPPT algorithm estimates the voltages and currents corresponding to maximum powers produced by PV array at the maximum power point (MPP) for swiftly changing situations such as solar radiance and temperature. These maximum powers are given as input signal to vector control algorithm of PMSM. The PMSM is designed by using Infolytica/MotorSolve software so that the phase-to-phase maximum value of its operating voltage is 20 V. The use of three-phase PMSM presents more efficient solutions to the trading solar systems with dc motor or induction motor. Thus, an effective solar system is achieved. The performance of developed ANN-based MPPT algorithm, designed PMSM, vector-controlled driver and solar system is analyzed by using MATLAB/SimPowerSystems blocks under the rapidly changing environmental conditions.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rezvani A, Gandomkar M (2015) Simulation and control of intelligent photovoltaic system using new hybrid fuzzy-neural method. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-016-2210-2
Chen P (2015) An improved maximum power point tracking algorithm using fuzzy logic controller for photovoltaic applications. In: Master Thesis, August 2015, California State University, Fresno, USA
Ranjbar H, Behrouz M, Deihimi A (2015) Neural network based global maximum power point tracking under partially shaded conditions. In: 23rd Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Tehran, Iran, pp 1440–1445
Esram T, Chapman PL (2007) Comparison of photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking techniques. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 22(2):439–449
Jiang L, Maskell DL (2014) A simple hybrid MPPT technique for photovoltaic systems under rapidly changing partial shading conditions. IEEE 40th photovoltaic specialist conference (PVSC). Denver, USA, pp 782–787
Masoum MAS, Dehbonei H, Fuchs EF (2002) Theoretical and experimental analyses of photovoltaic systems with voltage and current-based maximum power-point tracking. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 17(4):514–522
Noh HJ, Lee DY, Hyun DS (2002) An improved MPPT converter with current compensation method for small scaled PV-applications. IEEE 28th annual conference of industrial electronic society. Seville, Spain, pp 1113–1118
Noguchi T, Togashi S, Nakamoto R (2000) Short-current pulse based adaptive maximum-power-point tracking for photovoltaic power generation system. IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics. Puebla, Mexico, pp 157–162
Mutoh N, Matuo T, Okada K (2002) Prediction-data-based maximum power-point-tracking method for photovoltaic power generation systems. EEE 33rd annual power electronics specialists conference. Queensland, Australia, pp 1489–1494
Kim Y, Jo H, Kim D (1996) A new peak power tracker for cost-effective photovoltaic power system. In: 31st intersociety energy conversion engineering conference, Washington DC, USA, pp 1673–1678
Hashimoto O, Shimizu T, Kimura G (2000) A novel high performance utility interactive photovoltaic inverter system. IEEE industry applications conference. Italy, Rome, pp 2225–2260
Koutroulis E, Kalaitzakis K, Voulgaris NC (2001) Development of a microcontroller-based, photovoltaic maximum power point tracking control system. IEEE Trans Power Electron 16(21):46–54
Zhang L, Al-Amoudi A, Bai Y (2000) Real-time maximum power point tracking for grid-connected photovoltaic systems. In: Eighth international conference on power electronics variable speed drives, London, UK, pp 124–129
Hua CC, Lin JR (2001) Fully digital control of distributed photovoltaic power systems. IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics. Pusan, Korea, pp 1–6
Chomsuwan K, Prisuwanna P, Monyakul V (2002) Photovoltaic grid connected inverter using two-switch buck-boost converter. In: IEEE twenty-ninth photovoltaic specialists conference, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, pp 1527–1530
Brambilla A, Gambarara M, Garutti A, Ronchi F (1999) New approach to photovoltaic arrays maximum power point tracking. 30th annual IEEE power electronics specialists conference. Charleston, SC, pp 632–637
Irisawa K, Saito T, Takano I, Sawada Y (2000) Maximum power point tracking control of photovoltaic generation system under non-uniform insolation by means of monitoring cells. IEEE twenty-eighth photovoltaic specialists conference. Anchorage, AK, pp 1707–1710
Aashoor FAO, Robinson FVP (2014) Maximum power point tracking of PV water pumping system using artificial neural based control. 3rd renewable power generation conference (RPG 2014). Naples, Italy, pp 1–5
Ranjani K, Raja M, Anitha B (2014) Maximum power point tracking by ANN controller for a standalone photovoltaic system. Int J Electr Comput Electron Commun Eng 8(3):592–596
Jiang LL, Nayanasiri DR, Maskel DL, Vilathgamuwa DM (2013) A simple and efficient hybrid maximum power point tracking method for PV systems under partially shaded condition. IEEE 39th annual conference of the industrial electronics society. Austria, Vienna, pp 1513–1518
Senjyu T, Uezato K (1994) Maximum power point tracker using fuzzy control for photovoltaic arrays. IEEE international conference on industrial technology. Guangzhou, China, pp 143–147
Syafaruddin E, Hiyama KT (2009) Polar coordinated fuzzy controller based real time maximum power point control of photovoltaic system. Renew Energy 34:2597–2606
Miyatake M, Toriumi F, Fujii N, Ko H (2011) Maximum power point tracking of multiple photovoltaic arrays: a PSO approach. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 47:367–380
Ishaque K, Salam Z (2013) A deterministic particle swarm optimization maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic system under partial shading condition. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 60:3195–3206
Hiyama T, Kitabayashi K (1997) Neural network based estimation of maximum power generation from PV module using environmental information. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 12:241–247
Bahgat ABG, Helwa NH, Ahmad GE, Shenawy ET (2005) Maximum power point tracking controller for PV systems using neural networks. Renew Energy 30(8):1257–1268
Kulaksız AA, Akkaya R (2012) Training data optimization for ANNs using genetic algorithms to enhance MPPT efficiency of a stand-alone PV system. Turk J Electr Eng Comput Sci 20(2):241–254
Mohamed AF, Elarini MM, Othman AM (2014) A new technique based on artificial bee colony algorithm for optimal sizing of stand-alone photovoltaic system. J Adv Res 5(3):397–408
Oshaba AS, Ali ES, Elazim Abd (2015) PI controller design using ABC algorithm for MPPT of PV system supplying DC motor pump load. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-015-2091-9
Elobaid LM, Abdelsalam AK, Zakzouk EE (2015) Artificial neural network-based photovoltaic maximum power point tracking techniques: a survey. IET Renew Power Gen 9(8):1043–1063
Caracas JVM, Farias GC, Teixeira LFM, Ribeiro LAS (2014) Implementation of a high-efficiency, high-lifetime, and low-cost converter for an autonomous photovoltaic water pumping system. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 50(1):631–641
Aydogmus O (2012) Design of a solar motor drive system fed by a direct connected photovoltaic array. Adv Electr Comput Eng 12(3):53–58
Essays UK (2007) Multiple boost converter based wind energy conversion system engineering essay. http://www.ukessays.com/essays/engineering/multiple-boost-converter-based-wind-energy-conversion-system-engineering-essay.php?cref=1. Accessed 10 November 2013
Aydogmus O, Deniz E, Kayisli K (2014) PMSM drive fed by sliding mode controlled PFC boost converter. Arab J Sci Eng 39(6):4765–4773
Kishor N, Villalva MG, Mohanty SR, Ruppert E (2010) Modeling of PV module with consideration of environmental factors. In: IEEE PES innovative smart grid technologies conference Europe, Gothenburg, Germany, pp 1–5
Villalva MG, Gazoli JR, Filho ER (2009) Comprehensive approach to modeling and simulation of photovoltaic arrays. IEEE Trans Power Electron 24(5):1198–1208
Aydogmus Z, Aydogmus O (2015) A comparison of artificial neural network and extended Kalman filter based sensorless speed estimation. Measurement 63:152–158
Deniz E, Aydogmus O, Aydogmus Z (2016) Implementation of ANN-based selective harmonic elimination PWM using hybrid genetic algorithm-based optimization. Measurement. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2016.02.012
Wallmark O (2001) Control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor with non-sinusoidal flux density distribution. In: Master thesis, December 2001, Chalmers University of Technology, Goteborg, Sweden
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deniz, E. ANN-based MPPT algorithm for solar PMSM drive system fed by direct-connected PV array. Neural Comput & Applic 28, 3061–3072 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2326-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2326-4