Abstract
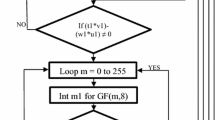
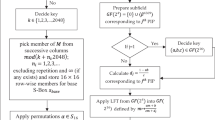
The substitution boxes are used in block ciphers with the purpose to induce confusion in data. The design of a substitution box determines the confusion ability of the cipher; therefore, many different types of boxes have been proposed by various authors in literature. In this paper, we present a novel method to design a new substitution box and compare its characteristics with some prevailing boxes used in cryptography. The algorithm proposed in this paper apply the action of projective linear group PGL(2, GF(28)) on Galois field GF(28). The new substitution box corresponds to a particular type of linear fractional transformation (35z + 15)/(9z + 5). In order to test the strength of the proposed substitution box, we apply non-linearity test, bit independence criterion, linear approximation probability method, differential approximation probability method, strict avalanche criterion, and majority logic criterion. This new technique to synthesize a substitution box offers a powerful algebraic complexity while keeping the software/hardware complexity within manageable parameters.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daemen J, Rijmen V (2002) The design of Rijndael-AES: the advanced encryption standard. Springer, Berlin
Hussain I, Shah T, Mahmood H, Afzal M (2010) Comparative analysis of S-boxes based on graphical SAC. Int J Comput Appl 2(5):5–8
Hussain I, Mahmood Z (2010) Graphical strict avalanche criterion for Kasumi S-box. Can J Comput Math Nat Sci Eng Med 1(5):132–136
Hussain I, Shah T, Aslam SK (2010) Graphical SAC analysis of S8 APA S-box. Adv Algebra 3(2):57–62
Shah T, Hussain I, Gondal MA, Mahmood H (2011) Statistical analysis of S-box in image encryption applications based on majority logic criterion. Int J Phys Sci 6(16):4110–4127
Hussain I, Shah T, Mahmood H, Gondal MA, Bhatti UY (2011) Some analysis of S-box based on residue of prime number. Proc Pak Acad Sci 48(2):111–115
Tran MT, Bui DK, Doung AD (2008) Gray S-box for advanced encryption standard. Int Conf Comp Intel Secur 253–256
Cui L, Cao Y (2007) A new S-box structure named Affine- Power-Affine. Int J Innov Comput I 3(3):45–53
Hussain I, Shah T, Mahmood H (2010) A new algorithm to construct secure keys for AES. Int J Cont Math Sci 5(26):1263–1270
Kim J, Phan RC-W (2009) Advanced differential-style cryptanalysis of the NSA’s skipjack block cipher. Cryptologia 33(3):246–270
Shi XY, Xiao Hu You XC, Lam KY (2002) A method for obtaining cryptographically strong 8 × 8 S-boxes. Int Conf Infor Network Appl 2(3):14–20
Feng D, Wu W (2000) Design and analysis of block ciphers. Tsinghua University Press
Matsui M (1994) Linear cryptanalysis method of DES cipher. Advances in cryptology, proceeding of the Eurocrypt’93. Lect Notes Comput Sci 765:386–397
Biham E, Shamir A (1991) Differential cryptanalysis of DES-like cryptosystems. J Cryptol 4(1):3–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hussain, I., Shah, T., Mahmood, H. et al. A projective general linear group based algorithm for the construction of substitution box for block ciphers. Neural Comput & Applic 22, 1085–1093 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-0870-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-012-0870-0