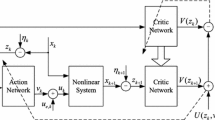
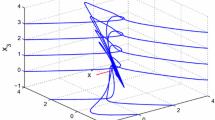
Abstract
In this paper, a novel neural-network-based iterative adaptive dynamic programming (ADP) algorithm is proposed. It aims at solving the optimal control problem of a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems with control constraints. By introducing a generalized nonquadratic functional, the iterative ADP algorithm through globalized dual heuristic programming technique is developed to design optimal controller with convergence analysis. Three neural networks are constructed as parametric structures to facilitate the implementation of the iterative algorithm. They are used for approximating at each iteration the cost function, the optimal control law, and the controlled nonlinear discrete-time system, respectively. A simulation example is also provided to verify the effectiveness of the control scheme in solving the constrained optimal control problem.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen D, Yang J, Mohler RR (2008) On near optimal neural control of multiple-input nonlinear systems. Neural Comput Appl 17(4):327–337
Lyshevski SE (1996) Constrained optimization and control of nonlinear systems: new results in optimal control. In: Proceedings of the 35th IEEE conference on decision and control, Kobe, Japan, pp 541–546
Lyshevski SE (1998) Nonlinear discrete-time systems: constrained optimization and application of nonquadratic costs. In: Proceedings of the American control conference, Philadelphia, pp 3699–3703
Bellman RE (1957) Dynamic programming. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Jagannathan S (2006) Neural network control of nonlinear discrete-time systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Yu W (2009) Recent advances in intelligent control systems. Springer, London
Werbos PJ (1992) Approximate dynamic programming for real-time control and neural modeling. In: White DA, Sofge DA (eds) Handbook of intelligent control: neural, fuzzy, and adaptive approaches. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp 493–525
Werbos PJ (2008) ADP: The key direction for future research in intelligent control and understanding brain intelligence. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 38(4):898–900
Werbos PJ (2009) Intelligence in the brain: a theory of how it works and how to build it. Neural Netw 22(3):200–212
Murray JJ, Cox CJ, Lendaris GG, Saeks R (2002) Adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern C Appl Rev 32(2):140–153
Wang FY, Zhang H, Liu D (2009) Adaptive dynamic programming: an introduction. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 4(2):39–47
Lewis FL, Vrabie D (2009) Reinforcement learning and adaptive dynamic programming for feedback control. IEEE Circuits Syst Mag 9(3):32–50
Si J, Barto AG, Powell WB, Wunsch DC (2004) Handbook of learning and approximate dynamic programming. IEEE Press/Wiley, New York
Bertsekas DP, Tsitsiklis JN (1996) Neuro-dynamic programming. Athena Scientific, Belmont
Si J, Wang YT (2001) On-line learning control by association and reinforcement. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 12(2):264–276
Liu D, Zhang H (2005) A neural dynamic programming approach for learning control of failure avoidance problems. Int J Intell Control Syst 10(1):21–32
Prokhorov DV, Wunsch DC (1997) Adaptive critic designs. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 8(5):997–1007
Sutton RS, Barto AG (1998) Reinforcement learning: an introduction. The MIT Press, Cambridge
Hagen ST, Krose B (2003) Neural Q-learning. Neural Comput Appl 12(2):81–88
Liu D, Xiong X, Zhang Y (2001) Action-dependent adaptive critic designs. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on neural networks, Washington, vol 2, pp 990–995
Venayagamoorthy GK, Harley RG, Wunsch DC (2002) Comparison of heuristic dynamic programming and dual heuristic programming adaptive critics for neurocontrol of a turbogenerator. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13(3):764–773
Venayagamoorthy GK, Harley RG, Wunsch DC (2003) Implementation of adaptive critic-based neurocontrollers for turbogenerators in a multimachine power system. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 14(5):1047–1064
Yen GG, Delima PG (2005) Improving the performance of globalized dual heuristic programming for fault tolerant control through an online learning supervisor. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 2(2):121–131
Jagannathan S, He P (2008) Neural-network-based state feedback control of a nonlinear discrete-time system in nonstrict feedback form. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 19(12):2073–2087
Cheng T, Lewis FL, Abu-Khalaf M (2007) A neural network solution for fixed-final time optimal control of nonlinear systems. Automatica 43(3):482–490
Balakrishnan SN, Biega V (1996) Adaptive-critic based neural networks for aircraft optimal control. J Guid Control Dyn 19(4):893–898
Balakrishnan SN, Ding J, Lewis FL (2008) Issues on stability of ADP feedback controllers for dynamic systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 38(4):913–917
Han D, Balakrishnan SN (2002) State-constrained agile missile control with adaptive critic-based neural networks. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 10(4):481–489
Al-Tamimi A, Lewis FL, Abu-Khalaf M (2008) Discrete-time nonlinear HJB solution using approximate dynamic programming: convergence proof. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 38(4):943–949
Zhang H, Wei Q, Luo Y (2008) A novel infinite-time optimal tracking control scheme for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems via the greedy HDP iteration algorithm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 38(4):937–942
Vrabie D, Pastravanu O, Abu-Khalaf M, Lewis FL (2009) Adaptive optimal control for continuous-time linear systems based on policy iteration. Automatica 45(2):477–484
Liu D, Jin N (2008) \(\varepsilon\)-adaptive dynamic programming for discrete-time systems. In: Proceedings of the international joint conference on neural networks, Hong Kong, pp 1417–1424
Abu-Khalaf M, Lewis FL (2005) Nearly optimal control laws for nonlinear systems with saturating actuators using a neural network HJB approach. Automatica 41(5):779–791
Zhang H, Luo Y, Liu D (2009) Neural-network-based near-optimal control for a class of discrete-time affine nonlinear systems with control constraints. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 20(9):1490–1503
Vamvoudakis KG, Lewis FL (2010) Online actor-critic algorithm to solve the continuous-time infinite horizon optimal control problem. Automatica 46(5):878–888
Zhang H, Wei Q, Liu D (2011) An iterative adaptive dynamic programming method for solving a class of nonlinear zero-sum differential games. Automatica 47(1):207–214
Song R, Zhang H, Luo Y, Wei Q (2010) Optimal control laws for time-delay systems with saturating actuators based on heuristic dynamic programming. Neurocomputing 73(16–18):3020–3027
Ma J, Yang T, Hou ZG, Tan M, Liu D (2008) Neurodynamic programming: a case study of the traveling salesman problem. Neural Comput Appl 17(4):347–355
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 60874043, 60904037, 60921061, and 61034002, by Beijing Natural Science Foundation under Grant 4102061, and by the National Science Foundation of USA under Grant ECCS-1027602.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Liu, D., Zhao, D. et al. A neural-network-based iterative GDHP approach for solving a class of nonlinear optimal control problems with control constraints. Neural Comput & Applic 22, 219–227 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0707-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0707-2