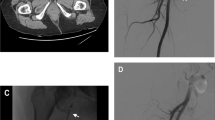
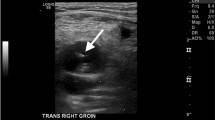
Summary
Objective
To investigate the efficacy of para-aneurysmal saline injection for closure of postcatheterization pseudo-aneurysm (PA) at the vascular access site.
Methods
Fifty-one consecutive patients with postcatheterization PA at the vascular access site were included to undergo percutaneous para-aneurysmal saline injection. In case of technical failure the day after, PA were treated by bovine thrombin injection. Anatomical properties of the PA were recorded as were details to injection.
Results
Initially all patients exhibited success which was reduced to 43 % at day one. A saline volume of median 7 ml (interquartile range 6–8 ml) has been injected. The amount of injected saline was not different in patients with and without treatment success at day one (P = 0.6). Several anatomical properties of the PA exhibited marked differences in patients with or without success. The length (10.3 mm (7.8–12.0) vs. 12.5 mm (10.3–15.0); P = 0.009) and the angulation (110° (100–118) vs. 140° (129–146); P < 0.001) of the fistula/vessel axis was statistically different between groups. The peak systolic velocity failed to show significance with a tendency to higher values in the ineffective study group (P = 0.07). No peripheral complications occurred.
Conclusion
Para-aneurysmal saline injection may be a therapeutic alternative to percutaneous thrombin injection in patients exhibiting favorable anatomical properties.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Funovics MA, Wolf F, Philipp MO, Kee S, Tichy B, Dirisamer A, Rand T, Lammer J. Feasibility study of NeoMend, a percutaneous arterial closure device that uses a nonthrombogenic bioadhesive. Am J Roentgenol. 2003;180:533–8.
Dick P, Barth B, Mlekusch W, Sabeti S, Amighi J, Schlager O, Koppensteiner R, Minar E, Schillinger M. Complications after peripheral vascular interventions in octagenerians. J Endovasc Ther. 2008;15:383–9.
Wyman RM, Safian RD, Portway V, Skillman JJ, McKay RG, Baim DS. Current complications of diagnostic and therapeutic cardiac catheterization. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988;12:1400–6.
Popma JJ, Satler LF, Pichard AD, Kent KM, Campbell A, Chuang YC, Clark C, Merritt AJ, Bucher TA, Leon MB. Vascular complications after balloon and new device angioplasty. Circulation. 1993;88:1569–78.
Katzenschlager R, Uguruoglu A, Ahmadi A, Hülsmann M, Koppensteiner R, Larch E, Maca T, Minar E, Stümpflen A, Ehringer H. Incidence of pseudoaneurysm after diagnostic and therapeutic angiography. Radiology. 1995;195:463–6.
Gurm HS, Hosman C, Share D, Moscucci M, Hansen BB. Comparative safety of vascular closure devices and manual closure among patients having percutaneous coronary intervention. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159:660–6.
Toursarkissian B, Allen BT, Petrinec D, Thompson RW, Rubin BG, Reilly JM, Anderson CB, Flye MW, Sicard GA, Sullivan TM. Spontaneous closure of selected iatrogenic pseudoaneurysms and arteriovenous fistulae. J Vasc Surg. 1997;25:803–9.
Kent KC, McArdle CR, Kennedy B, Baim DS, Anninos E, Skillman JJ, Perry MO, Smith RB, Cox GS, McCann RL, Kresowik TF, Hye RJ. A prospective study of the clinical outcome of femoral pseudoaneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas induced by arterial puncture. J Vasc Surg. 1993;17:125–33.
Coley BD, Roberts AC, Fellmeth BD, Valji K, Bookstein JJ, Hye RJ. Postangiographic femoral pseudoaneurysms: further experience with US-guided compression repair. Radiology. 1995;194:307–11.
Krueger K, Zaehringer M, Söhngen FD, Gossmann A, Schulte O, Feldmann C, Strohe D, Lackner K. Femoral pseudoaneurysms: management with percutaneous thrombin injections—success rates and effects on systemic coagulation. Radiology. 2003;226:452–8.
Reeder SB, Widlus DM, Lazinger M. Low-dose thrombin injection to treat latrogenic femoral artery pseudoaneurysms. Am J Roentgen. 2001;177:595–8.
Paulson EK, Nelson RC, Mayes CE, Sheafor DH, Sketch MH Jr, Kliewer MA. Sonographically guided thrombin injection of iatrogenic femoral pseudoaneurysms: further experience of a single institution. Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177:309–16.
Bronisz M, Rosc D, Bronisz A, Manitius J, Nartowicz E. The role of intrinsic fibrinolytic system activation in pathogenesis of hemostasis disturbances in hemodialyzed patients with chronic renal failure. Ren Fail. 2004;26:223–9.
Finkelstein A, Bazan S, Halkin A, Herz I, George J, Miller HI, Keren G, Banai S. Treatment of post-catheterization femoral artery pseudo-aneurysm with para-aneurysmal saline injection. Am J Cardiol. 2008;101:1418–22.
Gehling G, Ludwig J, Schmidt A, Daniel WG, Werner D. Percutaneous occlusion of femoral artery pseudoaneurysm by para-aneurysmal saline injection. Cath Cardiovasc Interv. 2003;58:500–4.
ElMahdy MF, Kassem HH, Ewis EB, Mahdy SG. Comparison between ultrasound-guided compression and para-aneurysmal saline injection in the treatment of postcatheterization femoral artery pseudoaneurysms. Am J Cardiol. 2014;113:871–6.
Sheldon PJ, Oglevie SB, Kaplan LA. Prolonged generalized urticarial reaction after percutaneous thrombin injection for treatment of a femoral artery pseudoaneurysm. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2000;11:759–61.
Périard D, Rey Meyer MA, Hayoz D, Cook S. Sealing pseudo-aneurysms of the femoral artery with saline injection: a new technique. EuroIntervention. 2012;7:1206–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
G.-A. Giurgea, I. Mlekusch, M. Hoke, A. Carls, S. Sabeti-Sandor, E. Minar, and W. Mlekusch declare that there are no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giurgea, GA., Mlekusch, I., Hoke, M. et al. Percutaneous instillation of physiological saline solution for the treatment of femoral pseudoaneuryms. Wien Klin Wochenschr 128, 421–425 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-016-0979-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-016-0979-8