Abstract
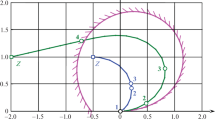
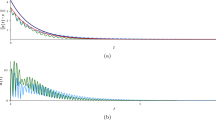
In this paper, we address the general problem of approximating, in a certain optimal way, non-admissible motions of a kinematic system with nonholonomic constraints. Since this kind of problems falls into the general subriemannian geometric setting, it is natural to consider optimality in the sense of approximating by means of subriemannian geodesics. We consider systems modeled by a subriemannian Goursat structure, a particular case being the well-known system of a car with trailers, along with the associated parallel parking problem. Several authors approximate the successive Lie brackets using trigonometric functions. By contrast, we show that more natural optimal motions are related with closed hyperelliptic plane curves with a certain number of loops.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sussmann HJ, Laferriere G (1991) Motion planning for controllable systems without drift. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on robotics and automation, Sacramento, CA, April 1991. IEEE Publications, New York, pp 109–148
Sussmann HJ, Liu WS (1993) Lie bracket extensions and averaging: the single bracket generating case. In: Li ZX, Canny JF (eds) Non-holonomic motion planning. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, pp 109–148
Tilbury D, Murray RM, Sastry S (1995) Trajectory generation for the n-trailer problem using Goursat normal form. IEEE Trans Automat Contr 40(5):802–819
Tilbury D, Laumond J, Murray R, Sastry S, Walsh G (1992) Steering car-like systems with trailers using sinusoids. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA) pp 1993–1998
Jean F (2001) Complexity of nonholonomic motion planning. Int J Control 74(8):776–782
Jean F (2003) Entropy and complexity of a path in subriemannian geometry. COCV 9:485–506
Jean F, Falbel E (2003) Measures and transverse paths in subriemannian geometry. J Anal Math 91:231–246
Boizot N, Gauthier JP (2013) Motion planning for kinematic systems. IEEE TAC 58(6):1430–1442
Boizot N, Gauthier JP (2013) On the motion planning of the ball with a trailer. Math Control Relat Fields 3(3):269–286
Gauthier JP, Zakalyukin V (2006) On the motion planning problem, complexity, entropy and nonholonomic interpolation. J Dyn Control Syst 12(3):371–404
Gauthier JP, Jakubczyk B, Zakalyukin V (2010) Motion planning and fastly oscillating controls. SIAM J Control Optic 48(5):3433–3448
Romero-melendez C, Gauthier JP, Monroy-Perez F (2004) On complexity and motion planning for corank one sub-riemannian metrics. COCV 10:634–655
Gauthier JP, Zakalyukin V (2005) On the codimension one motion planning problem. J Dyn Control Syst 11(1):73–89
Gauthier JP, Zakalyukin V (2005) On the one-step-bracket-generating motion planning problem. J Dyn Control Syst 11(2):215–235
Laumond JP, Sekhavat S, Lamiraux F (1998) Guidelines in nonholonomic motion planning for mobile robots. In: Robot motion planning and control, Springer, Berlin
Morin P, Samson C (2003) Practical stabilization of driftless systems on lie groups: the transverse function approach. IEEE Trans Automat Control 48:1496–1508
Fliess M, Levine J, Martin P, Rouchon P (1995) Flatness and defect of non-linear systems: introductory theory and examples. Int J Control 61:1327–1361
Montgomery R, Zhitomirskii MY (2001) Geometric approach to Goursat flags. Ann Inst H Poincaré, Anal Non Linéaire 18:459–493
Love AEH (1944) A treatise on the mathematical theory of elasticity. Dover, New York
Anzaldo-Meneses A, Monroy-Perez F (2003) Goursat distributions and subriemannian structures. J Math Phys 44(12):6101–6111
Gauthier JP, Kawski M (2014) Minimal complexity sinusoidal controls for path planning. In: Proceedings of the 53th IEEE, CDC conference, pp 3731–3736
Bellaiche A (1997) The tangent space in sub-Riemannian geometry. J Math Sci 83(4):461–476
Bianchini RM, Stefani G (1990) Graded approximations and controllability along a trajectory. SIAM J Control Optim 28:903–924
Bressan A (1985) Local asymptotic approximation of non linear control systems. Int J Control 41:1331–1336
von Weber E (1898) Zur Invariantentheorie der Systeme Pfaff’scher Gleichungen. Berichte über die Verhandlungen der Königlich Sächsischen Gesellshaft der Wissenshaften. Math Phys Klasse Leipzig 50:207–229
Teel AR, Murray RM, Walsh G (1992) Non-holonomic control systems: from steering to stabilization with sinusoids, IEEE conference on decision and control, pp 1603–1609
Agrachev AA, Sachkov YuL (2004) A control theory from the geometric viewpoint. Springer, Berlin
Acknowledgments
This paper was prepared during the sabbatical leave of the second author at the Laboratoire des Sciences de l’Information et des Systèmes (LSIS, UMR 7296) in the Université du Sud Toulon-Var, France. The author was financially supported by the CONACYT under the program of sabbatical leaves abroad for the reinforcement of the research groups, project number 204051.
Conflict of interest
Herewith I confirm, on behalf of all authors, that the information provided is accurate, and that we have no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gauthier, JP., Monroy-Pérez, F. On certain hyperelliptic signals that are natural controls for nonholonomic motion planning. Math. Control Signals Syst. 27, 415–437 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00498-015-0145-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00498-015-0145-2