Abstract
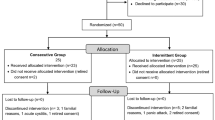
The aim of this randomized controlled single-blind study is to explore whether addition of mud-pack and hot pool treatments to patient education make a significant difference in short and mild term outcomes of the patients with fibromyalgia. Seventy women with fibromyalgia syndrome were randomly assigned to either balneotherapy with mud-pack and hot pool treatments (35) or control (35) groups. After randomization, five patients from balneotherapy group and five patients from control group were dropped out from the study with different excuses. All patients had 6-h patient education programme about fibromyalgia syndrome and were given a home exercise programme. The patients in balneotherapy group had heated pool treatment at 38 °C for 20 min a day, and mud-pack treatment afterwards on back region at 45 °C. Balneotherapy was applied on weekdays for 2 weeks. All patients continued to take their medical treatment. An investigator who was blinded to the intervention assessed all the patients before and after the treatment, at the first and the third months of follow-up. Outcome measures were FIQ, BDI and both patient’s and physician’s global assessments. Balneotherapy group was significantly better than control group at after the treatment and at the end of the first month follow-up assessments in terms of patient’s and physician’s global assessment, total FIQ score, and pain intensity, fatigue, non-refreshed awaking, stiffness, anxiety and depression subscales of FIQ. No significant difference was found between the groups in terms of BDI scores. It is concluded that patient education combined with 2 weeks balneotherapy application has more beneficial effects in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome as compared to patient education alone.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardiç F, Ozgen M, Aybek H et al (2007) Effect of balneotherapy on serum IL-1, PGE2 and LTB4 levels in fibromyalgia patients. Rheumatol Int 27:441–446
Arnold B, Häuser W, Arnold M, Bernateck M, Bernardy K, Brückle W, Friedel E, Hesselschwerdt HJ, Jäckel W, Köllner V, Kühn E, Petzke F, Settan M, Weigl M, Winter (2012) Multicomponent therapy of fibromyalgia syndrome. Systematic review, meta-analysis and guideline. Schmerz 26(3):287–290
Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561–571
Buckhardt CS, Goldenberg D, Crofford L et al (2005) Guideline for the management of fibromyalgia syndrome pain in adults and children. APS Clinical Practice Guideline Series. American Pain Society, Glenview
Burckhardt CS, Clark SR, Bennet RM (1991) The fibromyalgia impact questionnaire: development and validition. J Rheumatol 18:728–733
Busch AJ, Barber KA, Overend TJ, Peloso PMJ, Schachter CL (2007) Exercise for treating fibromyalgia syndrome. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev. Issue 4. Art. No.: CD003786. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003786.pub2
Buskila D, Shakra MA, Neumann L, Odes L, Shneider E, Flusser D, Sukenik S (2001) Balneotherapy for fibromyalgia at Dead Sea. Rheumatol Int 20:105–108
Carville SF, Arendt-Nielsen S, Bliddal H et al (2008) EULAR evidence based recommendations for the management of fibromyalgia syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 67:536–541
Cozzi F, Lazzarin I, Todesco S, Cima L (1995) Hypotalamic pituary-adrenal axis dysregulation in healthy subjects undergoing mud-bath-applications. Arthritis Rheum 38:724–725
Donmez A, Karagulle MZ, Tercan N, Dinler M, Işsever H, Karagülle M, Turan M (2005) Spa therapy in fibromyalgia: a randomised controlled clinic study. Rheumatol Int 26:168–172
Eich W, Häuser W, Arnold B, Bernardy K, Brückle W, Eidmann U, Klimczyk K, Köllner V, Kühn-Becker H, Offenbächer M, Settan M, von Wachter M, Petzke F (2012) Fibromyalgia syndrome. General principles and coordination of clinical care and patient education. Schmerz 26:268–275
Evcik D, Kızılay B, Gökcen E (2002) The effects of balneotherapy on fibromyalgia patients. Rheumatol Int 22:56–59
Falagas ME, Zarkadoulia E, Rafailidis PI (2009) The therapeutic effect of balneotherapy: evaluation of the evidence from randomised controlled trials. Int J Clin Pract 63:1068–1084
Fioravanti A, Perpignano G, Tirri G et al (2007) Effects of mud-bath treatment on fibromyalgia patients: a randomized clinical trial. Rheumatol Int 27:1157–1161
Fioravanti A, Cantarini L, Guidelli GM, Galeazzi M (2011) Mechanisms of action of spa therapies in rheumatic diseases: what scientific evidence is there? Rheumatol Int 31:1–8
Fraioli A, Grassi M, Mennuni G, Geraci A, Petraccia L, Fontana M, Conte S, Serio A (2013) Clinical researches on the efficacy of spa therapy in fibromyalgia. A systematic review. Ann Ist Super Sanita 49(2):219–229
Häuser W, Thieme K, Turk DC (2010) Guidelines on the management of fibromyalgia syndrome—a systematic review. Eur J Pain 14:5–10
Kesiktas N, Karagülle Z, Erdogan N, Yazıcıoglu K, Yılmaz H, Paker N (2011) The efficacy of balneotherapy and physical modalities on the pulmonary system of patients with fibromyalgia. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 24(1):57–65
Langhorst J, Musial F, Klose P, Hauser W (2009) Efficacy of hydrotherapy in fibromyalgia syndrome—a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Rheumatology 48:1155–1159
Mc Veigh JG, Mc Gaughey H, Hall M, Kane P (2008) The effectiveness of hydrotherapy in the management of fibromyalgia syndrome: a systematic review. Rheumatol Int 29:119–130
Oral A, Ilieva EM, Küçükdeveci AA, Varela E, Valero R, Berteanu M, Christodoulou N (2013) Generalised and regional soft tissue pain syndromes. The role of physical and rehabilitation medicine physicians. The European perspective based on the best evidence. A paper by the UEMS-PRM Section Professional Practice Committee. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 49(4):535–549
Ozkurt S, Dönmez A, Zeki Karagülle M, Uzunoğlu E, Turan M, Erdoğan N (2012) Balneotherapy in fibromyalgia: a single blind randomized controlled clinical study. Rheumatol Int 32:1949–1954
van Tubergen A, Hidding A (2002) Spa and exercise treatment in ankylosing spondylitis: fact or fancy? Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 16(4):653–666
Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J, Russell IJ, Hebert L (1995) The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis Rheum 38:19–28
Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles M-A et al (2010) The American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis Care Res 62:600–610
Zijlstra TR, van de Laar MAFJ, Bernelot Moens HJ, Taal E, Zakraoui L, Rasker JJ (2005) Spa treatment for primary fibromyalgia syndrome: a combination of thalassotherapy, exercise and patient education improves symptoms and quality of life. Rheumatology 44:539–546
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bağdatlı, A.O., Donmez, A., Eröksüz, R. et al. Does addition of ‘mud-pack and hot pool treatment’ to patient education make a difference in fibromyalgia patients? A randomized controlled single blind study. Int J Biometeorol 59, 1905–1911 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-015-0997-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-015-0997-7