Abstract.
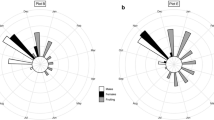
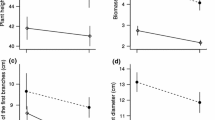
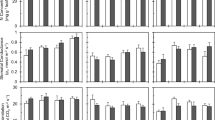
Clusia hilariana Schlechtendal is a dioecious tree performing crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM). It grows in the sandy coastal restinga of Brazil. As pioneers and 'nurse plants' individual trees become surrounded by other vegetation forming isolated vegetation islands on the sand plain. The female plants produce large and heavy fleshy fruits suggesting a particular demand for resources. Frugivores may introduce nutrients (faeces) and diaspores into the stands of female plants. Thus, the hypothesis was advanced that sex expression in C. hilariana has important general consequences for the physiology of the trees themselves and also determines aspects of the vegetation around them. Field work in the restinga of Macaé (Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil) showed that morphological leaf characteristics, the expression of CAM and the species diversity and species composition of their respective vegetation islands were similar for both sexes. The female plants had somewhat higher chlorophyll levels. Differences in effective quantum yield of photosystem II (PS II) and non-photochemical quenching of chlorophyll a fluorescence between female and male plants were very small. Female plants were a little less subject to acute photoinhibition at noon. Maximum fluorescence (Fm), variable fluorescence (Fv) and minimum fluorescence (F 0) were significantly lower in female plants. However, maximum quantum yield ratio of male to female plants as well as fluorescence yield ratio and minimum fluorescence ratio of male to female plants related to chlorophyll content were all close to unity. Therefore, although there may be some fine-tuned differences in the light reactions of photosynthesis, PS II of male and female plants are not different. Hence, the hypothesis of possible important consequences of sex determination for expression of morphological and physiological traits of the plants and for the composition of the 'nursed' vegetation underneath them must be rejected.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liebig, M., Scarano, F., de Mattos, E. et al. Ecophysiological and floristic implications of sex expression in the dioecious neotropical CAM tree Clusia hilariana Schltdl.. Trees 15, 278–288 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004680100096
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004680100096