Abstract
Key message
Pithecellobium dulce has a huge repository of morphological and genetic diversity within the species which has been documented for further tree research and breeding programmes.
Abstract
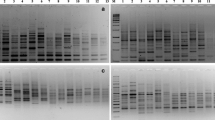
A total of 40 accessions of a multipurpose leguminous tree, Pithecellobium dulce, differing in morphological and phenological characteristics was collected from different locations in Rajasthan and genetic diversity assessed using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Out of 60 RAPD primers, 43 decamer primers produced 311 scorable bands of which 223 bands were polymorphic. Polymorphic banding patterns with the number of amplified fragments varied from 1 (OPA-12 and OPF-17) to 12 (OPF-04, OPT-07, OPT-17, OPT-20). Percent polymorphism ranged from 33.3 % (OPF-07, OPA-20, OPT-05) to 89 % (OPA-13) with an average of 64.34 %. Out of the 20 ISSR primers screened, 8 primers produced 77 amplification products of which 55 were polymorphic. The number of bands amplified per primer varied between 6 (UBC-820) and 13 (UBC-808 and UBC-816) with average band size between 300 and 4,500 bp. Percent polymorphism ranged from 38 % (UBC-817) to 100 % (UBC-811) with an average of 71 %. Dendrogram constructed on the basis of combined RAPD and ISSR markers separated the accessions into five distinct clusters at 53 % variation with Jaccard’s similarity coefficient ranging from minimum similarity (0.35) between Karoli (K) and Malviya Nagar, Jaipur (MN1) to maximum similarity (0.81) between two populations of Kota (K1 and K2). The matrices for two markers, RAPD and ISSR, were also compared using Mantel’s test. The correlation value between the matrices is high (r = 0.83) indicating good correlation between the two molecular marker systems. The study indicated a high level of morphological and genetic diversity in P. dulce.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arif M, Zaidi NW, Singh YP, Haq QMR, Singh US (2009) A comparative analysis of ISSR and RAPD markers for study of genetic diversity in Shisham (Dalbergia sissoo). Plant Mol Biol Rep 27:488–495
Arnau G, Lallemand J, Bourgoin M (2003) Fast and reliable strawberry cultivar identification using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) amplification. Euphytica 129:69–79
Bachmann K (1997) Nuclear DNA markers in plant biosystematic research. Opera Botanica 132:137–148
Barrera-Necha L, Bautista-Baños S, Bravo-Luna L, Bermudez-Torres K, Garcia-Suarez F, Jimenez-Estrada M, Reyes-Chilpa R (2003) Antifungal activity against postharvest fungi by extracts and compounds of Pithecellobium dulce seeds (huamuchil). Acta Hortic 29:81–92
Basha S, Sujatha M (2007) Inter and intra-population variability of Jatropha curcas (L.) characterized by RAPD and ISSR markers and development of population-specific SCAR markers. Euphytica 156:375–386
Basha SD, Francis G, Makkar HPS, Becker K, Sujatha M (2009) A comparative study of biochemical traits and molecular markers for assessment of genetic relationships between Jatropha curcas L. germplasm from different countries. Plant Sci 176:812–823
Bhandari MM (1995) Flora of the Indian desert. MPS Repros, Jodhpur
Blair MW, Panaud O, McCouch SR (1999) Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) amplification for analysis of microsatellite motif frequency and fingerprinting in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 98:780–792
Brake M, Migdadi H, Al-Gharaibeh M, Ayoub S, Haddad N, Oqlah AE (2014) Characterization of Jordanian olive cultivars (Olea europaea L.) using RAPD and ISSR molecular markers. Sci Hortic 176:282–289
Chen J-M, Gituru WR, Wang Y-H, Wang Q-F (2006) The extent of clonality and genetic diversity in the rare Caldesia grandis Alismataceae): comparative results for RAPD and ISSR markers. Aquat Bot 84:301–307
Dangi RS, Lagu MD, Choudhary LB, Ranjekar PK, Gupta VS (2004) Assessment of genetic diversity in Trigonella foenum-graecum and Trigonella caerulea using ISSR and RAPD markers. BMC Plant Biol 4:13–24
Dangi B, Jain R, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2012) Assessment of diversity in Terminalia bellerica Roxb. using morphological, phytochemical and molecular markers. Natl Acad Sci Lett 35:27–35
Duke JA Handbook of energy crops (1983). http://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/duke_energy/arundo_donax
Duke JA, Wain KK (1981) Medicinal plants of the world. Computer index with more than 85000 entries, vol 3. Longman group UK Limited, p 1654
Dwivedi SL, Gurtu S, Chandra S, Yuejin W, Nigam SN (2001) Assessment of genetic diversity among selected groundnut germplasm. I: RAPD analysis. Plant Breed 120:345–349
Esselman EJ, Jianqiang L, Crawford DJ, Windus JL, Wolfe AD (1999) Clonal diversity in the rare Calamagrostis porteri ssp. insperata (Poaceae): comparative results for allozymes and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and intersimple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Mol Ecol 8:443–451
Gajera BB, Kumar N, Singh AS, Punvar BS, Ravikiran R, Subhash N, Jadeja GC (2010) Assessment of genetic diversity in castor (Ricinus communis L.) using RAPD and ISSR markers. Ind Crops Prod 32:491–498
Gomez SM, Ramasubramanian T, Mohankumar S (2011) Potential RAPD markers for population studies in tree legumes. Pak J Bot 43:1879–1883
Goulão L, Oliveira CM (2001) Molecular characterisation of cultivars of apple (Malus×domestica Borkh.) using microsatellite (SSR and ISSR) markers. Euphytica 122:81–89
Gupta M, Chyi YS, Romero-Severson J, Owen JL (1994) Amplification of DNA markers from evolutionarily diverse genomes using single primers of simple-sequence repeats. Theor Appl Genet 89:998–1006
Gupta S, Srivastava M, Mishra GP, Naik PK, Chauhan RS, Tiwari SK, Kumar M, Singh R (2008) Analogy of ISSR and RAPD markers for comparative analysis of genetic diversity among different Jatropha curcas genotypes. Afr J Biotechnol 7:4230–4243
Joshi SP, Gupta VS, Aggarwal RK, Ranjekar PK, Brar DS (2000) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship as revealed by inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism in the genus Oryza. Theor Appl Genet 100:1311–1320
Kalpana D, Choi SH, Choi TK, Senthil K, Lee YS (2012) Assessment of genetic diversity among varieties of mulberry using RAPD and ISSR fingerprinting. Sci Hortic 134:79–87
Karp A, Edwards KJ (eds) (1997) DNA markers: a global overview. Wiler-VCH, New York
Karthikeyan A, Madhanraj A, Pandian SK, Ramesh M (2011) Genetic variation among highly endangered Bacopa monnieri (L.) Pennell from Southern India as detected using RAPD analysis. Genet Resour Crop Evol 58:769–782
Khatri LM, Nasir MKA, Saleem R, Valhari MU (1994) The fatty acid composition of Pithecellobium dulce seed oil. Pak J Sci Ind Res 37:216
Khurana-Kaul V, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2012) Characterization of genetic diversity in Jatropha curcas L. germplasm using RAPD and ISSR markers. Indian J Biotechnol 11:54–61
Kumar RV, Tripathi YK, Shukla P, Ahlawat SP, Gupta VK (2009) Genetic diversity and relationships among germplasm of Jatropha curcas L. revealed by RAPDs. Trees 23:1075–1079
Landergott U, Holderegger R, Kozlowski G, Schneller JJ (2001) Historical bottlenecks decrease genetic diversity in natural populations of Dryopteris cristata. Heredity 87:344–355
Little EL, Woodbury RO, Wadsworth FH (1988) Trees of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands. Agric Handb 449. USDA Forest Service, Washington, DC, p 1177
Loarce Y, Gallego R, Ferrer E (1996) A comparative analysis of the genetic relationships between rye cultivars using RFLP and RAPD markers. Euphytica 88:107–115
Mana S, Singhal S, Sharma NK, Singh D (2010) Hypoglycemic effect of Holarrhena antidysenterica seeds on streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Int J Pharm Tech Res 2:1325–1329
Mantel N (1967) The detection of disease clustering and generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Mary S, Nair NV, Chaturvedi PK, Selvi A (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity among Saccharum spontaneum L. from four geographical regions of India, using molecular markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:1221–1231
Moreno S, Martín JP, Ortiz JM (1998) Inter-simple sequence repeats PCR for characterization of closely related grapevine germplasm. Euphytica 101:117–125
Nagaoka T, Ogihara Y (1997) Applicability of inter-simple sequence repeat polymorphisms in wheat for use as DNA markers in comparison to RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 94:597–602
Parrotta J (1991) Performance of thirteen tropical tree species at a coastal plantation site in Puerto Rico. Nitrogen Fixing Tree Res Rep 9:47–49
Penner GA (ed) (1996) RAPD analysis of plant genomes. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Phong DT, Hien VTT, Thanh TTV, Tang DV (2011) Comparison of RAPD and ISSR markers for assessment of genetic diversity among endangered rare Dalbergia oliveri (Fabaceae) genotypes in Vietnam. Genet Mol Res 10:2382–2393
Pithayanukul P, Ruenraroengsak P, Bavovada R, Pakmanee N, Suttisri R, Saen-oon S (2005) Inhibition of Naja kaouthia venom activities by plant polyphenols. J Ethnopharmacol 97:527–533
Porebski S, Bailey LG, Baum BR (1997) Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Mol Biol Rep 15:8–15
Rajasab AH, Isaq M (2004) Documentation of folk knowledge on edible wild plants of north Karnataka. Indian J Tradit Knowl 3:419–429
Sarwat M, Das S, Srivastava PS (2008) Analysis of genetic diversity through AFLP, SAMPL, ISSR and RAPD markers in Tribulus terrestris, a medicinal herb. Plant Cell Rep 27:519–528
Sheidai M, Afshar F, Keshavarzi M, Talebi S-M, Noormohammadi Z, Shafaf T (2014) Genetic diversity and genome size variability in Linum austriacum (Lineaceae) populations. Biochem Syst Ecol 57:20–26
Shilpha J, Silambarasan T, Pandian SK, Ramesh M (2013) Assessment of genetic diversity in Solanum trilobatum L., an important medicinal plant from South India using RAPD and ISSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 60:807–818
Singh S, Panda MK, Nayak S (2012) Evaluation of genetic diversity in turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) using RAPD and ISSR markers. Ind Crops Prod 37:284–291
Sivakumar A, Murugesan M (2005) Ethnobotanical studies on the wild edible plants used by the tribals of Anaimalai Hills, the Western Ghats. Anc Sci Life 25:69
Thimmappaiah WG, Santhosh DS, Melwyn GS (2009) Assessment of genetic diversity in cashew germplasm using RAPD and ISSR markers. Sci Hortic 120:411–417
Vicente MJ, Segura F, Aguado M, Migliaro D, Franco JA, Martínez-Sánchez JJ (2011) Genetic diversity of Astragalus nitidiflorus, a critically endangered endemic of SE Spain, and implications for its conservation. Biochem Syst Ecol 39:175–182
Yee E, Kidwell KK, Sills GR, Lumpkin TA (1999) Diversity among selected Vigna angularis (Azuki) accessions on the basis of RAPD and AFLP markers. Crop Sci 39:268–275
Zhao WG, Zhang JQ, Wang YH, Chen TT, Yin YL, Huang YP, Pan YL, Yang YH (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity in wild populations of mulberry from western part of Northeast China determined by ISSR markers. J Genet Mol Biol 17:196–203
Author contribution statement
Each author has contributed equally.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi in the form of R&D project 33-154/2007(SR) is gratefully acknowledged. Pooja Goyal thanks Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), for the award of SRF.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Carlson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, P., Jain, R., Kachhwaha, S. et al. Assessment of genetic diversity in Pithecellobium dulce (Roxb.) Benth. germplasm using RAPD and ISSR markers. Trees 29, 637–653 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-014-1141-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-014-1141-8