Abstract
Background
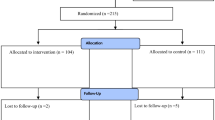
Irritation of inguinal nerves with laparoscopic hernia repair may cause chronic neuralgia and hypoesthesia. Hypoesthesia in particular is generally not assessed objectively. We objectively investigated hypoesthesia and chronic pain after transabdominal preperitoneal inguinal hernia repair (TAPP) with titanium spiral tacks (STs) compared with tissue adhesive (TA) for mesh fixation.
Methods
Mesh fixation in 80 TAPP procedures was randomized to fixation with ST (n = 40) or TA (n = 40). The outcome parameters included hypoesthesia assessed with von Frey monofilaments, early postoperative and chronic pain with the visual analog scale (VAS), morbidity (surgical-site infection, hematoma/seroma, relapse of hernia, trocar hernia), and recovery time to normal activity.
Results
Median (range) follow-up was 38 (13–56) months. Demographic and baseline parameters were similar in the two groups. Prevalence of hypoesthesia was significantly higher at all postoperative times in the ST group (6 weeks: 32 vs. 6%; 6 months: 38 vs. 14%; 12 months: 34 vs. 13%; 13–56 months: 32 vs. 4%). Mean hypoesthesia scores over all time points were significantly higher in the ST group. The percentages of regions with hypoesthesia (abdominal, inguinal, or genitofemoral) following all procedures were higher in the ST group after 6 weeks (14 vs. 2%), 6 months (15 vs. 5%), and 13–56 months (22 vs. 4%). The intensity of pain decreased significantly in both groups over time.
Conclusions
Postoperative hypoesthesia depends on the method of mesh fixation during TAPP and is significantly reduced with TA compared with stapling.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
EU Hernia Trialists Collaboration (2002) Repair of groin hernia with synthetic mesh: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Surg 235:322–332
McCormack K, Scott NW, Go PM, Ross S, Grant AM (2003) Laparoscopic techniques versus open techniques for inguinal hernia repair. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD001785
Pokorny H, Klingler A, Schmid T, Fortelny R, Hollinsky C, Kawji R, Steiner E, Pernthaler H, Fugger R, Scheyer M (2008) Recurrence and complications after laparoscopic versus open inguinal hernia repair: results of a prospective randomized multicenter trial. Hernia 12:385–389
Schmedt CG, Sauerland S, Bittner R (2005) Comparison of endoscopic procedures vs. Lichtenstein and other open mesh techniques for inguinal hernia repair: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Surg Endosc 19:188–199
Memon MA, Cooper NJ, Memon B, Memon MI, Abrams KR (2003) Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials comparing open and laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 90:1479–1492
Butters M, Redecke J, Koninger J (2007) Long-term results of a randomized clinical trial of shouldice, lichtenstein and transabdominal preperitoneal hernia repairs. Br J Surg 94:562–565
Eklund A, Carlsson P, Rosenblad A, Montgomery A, Bergkvist L, Rudberg C (2010) Long-term cost-minimization analysis comparing laparoscopic with open (lichtenstein) inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 97:765–771
Eklund A, Montgomery A, Bergkvist L, Rudberg C (2010) Chronic pain 5 years after randomized comparison of laparoscopic and lichtenstein inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 97:600–608
The MRC Laparoscopic Groin Hernia Trial Group (1999) Laparoscopic versus open repair of groin hernia: a randomised comparison. Lancet 354:185–190
Hindmarsh AC, Cheong E, Lewis MP, Rhodes M (2003) Attendance at a pain clinic with severe chronic pain after open and laparoscopic inguinal hernia repairs. Br J Surg 90:1152–1154
Kumar S, Wilson RG, Nixon SJ, Macintyre IM (2002) Chronic pain after laparoscopic and open mesh repair of groin hernia. Br J Surg 89:1476–1479
Lau H (2005) Fibrin sealant versus mechanical stapling for mesh fixation during endoscopic extraperitoneal inguinal hernioplasty: a randomized prospective trial. Ann Surg 242:670–675
Lovisetto F, Zonta S, Rota E, Mazzilli M, Bardone M, Bottero L, Faillace G, Longoni M (2007) Use of human fibrin glue (Tissucol) versus staples for mesh fixation in laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal hernioplasty: a prospective, randomized study. Ann Surg 245:222–231
Schwab R, Willms A, Kroger A, Becker HP (2006) Less chronic pain following mesh fixation using a fibrin sealant in TEP inguinal hernia repair. Hernia 10:272–277
Topart P, Vandenbroucke F, Lozac’h P (2005) Tisseel versus tack staples as mesh fixation in totally extraperitoneal laparoscopic repair of groin hernias: a retrospective analysis. Surg Endosc 19:724–727
Andrew DR, Gregory RP, Richardson DR (1994) Meralgia paraesthetica following laparoscopic inguinal herniorrhaphy. Br J Surg 81:715
Broin EO, Horner C, Mealy K, Kerin MJ, Gillen P, O’Brien M, Tanner WA (1995) Meralgia paraesthetica following laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. An anatomical analysis. Surg Endosc 9:76–78
Stark E, Oestreich K, Wendl K, Rumstadt B, Hagmuller E (1999) Nerve irritation after laparoscopic hernia repair. Surg Endosc 13:878–881
Beattie GC, Kumar S, Nixon SJ (2000) Laparoscopic total extraperitoneal hernia repair: mesh fixation is unnecessary. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 10:71–73
Poobalan AS, Bruce J, Smith WC, King PM, Krukowski ZH, Chambers WA (2003) A review of chronic pain after inguinal herniorrhaphy. Clin J Pain 19:48–54
Hollinsky C, Gobl S (1999) Bursting strength evaluation after different types of mesh fixation in laparoscopic herniorrhaphy. Surg Endosc 13:958–961
Katkhouda N, Mavor E, Friedlander MH, Mason RJ, Kiyabu M, Grant SW, Achanta K, Kirkman EL, Narayanan K, Essani R (2001) Use of fibrin sealant for prosthetic mesh fixation in laparoscopic extraperitoneal inguinal hernia repair. Ann Surg 233:18–25
Fortelny RH, Petter-Puchner AH, Walder N, Mittermayr R, Ohlinger W, Heinze A, Redl H (2007) Cyanoacrylate tissue sealant impairs tissue integration of macroporous mesh in experimental hernia repair. Surg Endosc 21:1781–1785
Jourdan IC, Bailey ME (1998) Initial experience with the use of N-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate glue for the fixation of polypropylene mesh in laparoscopic hernia repair. Surg Laparosc Endosc 8:291–293
Ceccarelli G, Casciola L, Pisanelli MC, Bartoli A, Di Zitti L, Spaziani A, Biancafarina A, Stefanoni M, Patriti A (2008) Comparing fibrin sealant with staples for mesh fixation in laparoscopic transabdominal hernia repair: a case control-study. Surg Endosc 22:668–673
Olmi S, Scaini A, Erba L, Guaglio M, Croce E (2007) Quantification of pain in laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) inguinal hernioplasty identifies marked differences between prosthesis fixation systems. Surgery 142:40–46
Aasvang E, Kehlet H (2005) Chronic postoperative pain: the case of inguinal herniorrhaphy. Br J Anaesth 95:69–76
Mikkelsen T, Werner MU, Lassen B, Kehlet H (2004) Pain and sensory dysfunction 6 to 12 months after inguinal herniotomy. Anesth Analg 99:146–151
Beldi G, Haupt N, Ipaktchi R, Wagner M, Candinas D (2008) Postoperative hypoesthesia and pain: qualitative assessment after open and laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. Surg Endosc 22:129–133
Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, Olkin I, Pitkin R, Rennie D, Schulz KF, Simel D, Stroup DF (1996) Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials. The CONSORT statement. JAMA 276:637–639
Gerber S, Hammerli PA, Glattli A (2000) Laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal hernioplasty. Evaluation of complications due to transabdominal approach. Chirurg 71:824–828
Cunningham J, Temple WJ, Mitchell P, Nixon JA, Preshaw RM, Hagen NA (1996) Cooperative hernia study. Pain in the postrepair patient. Ann Surg 224:598–602
Gillion JF, Fagniez PL (1999) Chronic pain and cutaneous sensory changes after inguinal hernia repair: comparison between open and laparoscopic techniques. Hernia 3:5
Heikkinen T, Bringman S, Ohtonen P, Kunelius P, Haukipuro K, Hulkko A (2004) Five-year outcome of laparoscopic and Lichtenstein hernioplasties. Surg Endosc 18:518–522
Acknowledgements
We thank Brigitte Wanner for meticulous data collection and Dr. Stephan Vorburger for advice with statistical analysis. This study was supported by a grant from Anklin AG, 4102 Binningen, Switzerland.
Disclosures
Authors Lukas Brügger, Martina Boesch, Ramin Ipaktchi, Anita Kurmann, Daniel Candinas, and Guido Beldi have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brügger, L., Bloesch, M., Ipaktchi, R. et al. Objective hypoesthesia and pain after transabdominal preperitoneal hernioplasty: a prospective, randomized study comparing tissue adhesive versus spiral tacks. Surg Endosc 26, 1079–1085 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-011-2003-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-011-2003-8