Abstract
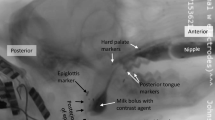
Simultaneous videoradiography and solid-state manometry (videomanometry) were performed in 8 patients (4 women, 4 men; age range = 46–81 years, mean age = 70 years) with pharyngeal dysfunction in order to disclose any changes in intrabolus pressure during swallowing maneuvers. Five of the patients had severe pharyngeal dysfunction with frequent misdirected swallows. Three of the patients had moderate pharyngeal dysfunction with delayed initiation of pharyngeal swallow. Three different swallowing techniques were applied: supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck. Pharyngeal intrabolus pressure was analyzed at the level of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor. Supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck did not alter peak amplitude or duration of the intrabolus pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bülow, M., Olsson, R. & Ekberg, O. Supraglottic Swallow, Effortful Swallow, and Chin Tuck Did Not Alter Hypopharyngeal Intrabolus Pressure in Patients with Pharyngeal Dysfunction . Dysphagia 17, 197–201 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-002-0050-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-002-0050-y