Abstract
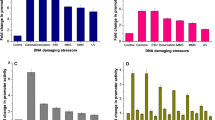
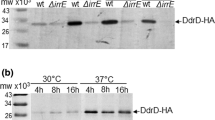
Bacteria are able to adapt to changes in the environment using two-component signal transduction systems (TCSs) composed of a histidine kinase (HK) and a response regulator (RR). Deinococcus radiodurans, one of the most resistant organisms to ionizing radiation, has 20 putative HKs and 25 putative RRs. In this study, we constructed 12 D. radiodurans mutant strains lacking a gene encoding a HK and surveyed their resistance to γ-radiation, UV-B radiation (302 nm), mitomycin C (MMC), and H2O2. Five (dr0860 −, dr1174 −, dr1556 −, dr2244 −, and dr2419 −) of the 12 mutant strains showed at least a one-log cycle reduction in γ-radiation resistance. The mutations (1) dr1174, dr1227, and dr2244 and (2) dr0860, dr2416, and dr2419 caused decreases in resistance to UV radiation and MMC, respectively. Only the dr2416 and dr2419 mutant strains showed higher sensitivity to H2O2 than the wild-type. Reductions in the resistance to γ-radiation and H2O2, but not to UV and MMC, were observed in the absence of DR2415, which seems to be a cognate RR of DR2416. This result suggests that DR2415/DR2416 (DrtR/S: DNA damage response TCS) may be another TCS responsible for the extreme resistance of D. radiodurans to DNA-damaging agents.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calva E, Oropeza R (2006) Two-component signal transduction systems, environmental signals, and virulence. Microb Ecol 51:166–176
Laub MT, Goulian M (2007) Specificity in two-component signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Genet 41:121–145
Pirrung MC (1999) Histidine kinases and two-component signal transduction systems. Chem Biol 6:167–175
Perry J, Koteva K, Wright G (2011) Receptor domains of two-component signal transduction systems. Mol Biosyst 7:1388–1398
Galperin MY (2010) Diversity of structure and function of response regulator output domains. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:150–159
Cox MM, Battista JR (2005) Deinococcus radiodurans—the consummate survivor. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:882–892
Riley PA (1994) Free radicals in biology: oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 65:27–33
Slade D, Radman M (2011) Oxidative stress resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans. Microbiol Mol Rev 75:133–191
Shashidhar R, Kumar SA, Misra HS, Bandekar JR (2010) Evaluation of the role of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidant systems in the radiation resistance of Deinococcus. Can J Microbiol 56:195–201
Bentchikou E, Servant P, Coste G, Sommer S (2010) A major role of the RecFOR pathway in DNA double-strand-break repair through ESDSA in Deinococcus radiodurans. PLoS Genet 6:e1000774
Slade D, Lindner AB, Paul G, Radman M (2009) Recombination and replication in DNA repair of heavily irradiated Deinococcus radiodurans. Cell 136:1044–1055
Mattimore V, Battista JR (1996) Radioresistance of Deinococcus radiodurans: functions necessary to survive ionizing radiation are also necessary to survive prolonged desiccation. J Bacteriol 178:633–637
Makarova KS, Aravind L, Wolf YI, Tatusov RL, Minton KW, Koonin EV, Daly MJ (2001) Genome of the extremely radiation-resistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans viewed from the perspective of comparative genomics. Microbiol Mol Biol R 65:44–79
Wang L, Xu G, Chen H, Zhao Y, Xu N, Tian B, Hua Y (2008) DrRRA: a novel response regulator essential for the extreme radioresistance of Deinococcus radiodurans. Mol Microbiol 67:1211–1222
Desai SS, Rajpurohit YS, Misra HS, Deobagkar DN (2011) Characterization of the role of the RadS/RadR two-component system in the radiation resistance of Deinococcus radiodurans. Microbiology 157:2974–2982
Funayama T, Narumi I, Kikuchi M, Kitayama S, Watanabe H, Yamamoto K (1999) Identification and disruption analysis of the recN gene in the extremely radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. Mutat Res 435:151–161
Khairnar NP, Kamble VA, Misra HS (2008) RecBC enzyme overproduction affects UV and gamma radiation survival of Deinococcus radiodurans. DNA Repair 7:40–47
de Been M, Bart MJ, Abee T, Siezen RJ, Francke C (2008) The identification of response regulator-specific binding sites reveals new roles of two-component systems in Bacillus cereus and closely related low-GC gram-positives. Environ Microbiol 10:2796–2809
Bhoo SH, Davis SJ, Walker J, Karniol B, Vierstra RD (2001) Bacteriophytochromes are photochromic histidine kinases using a biliverdin chromophore. Nature 414:776–779
Confalonieri F, Sommer S (2011) Bacterial and archaeal resistance to ionizing radiation. J Physics 261. Article ID 012005
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Nuclear R&D program of Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Im, S., Song, D., Joe, M. et al. Comparative survival analysis of 12 histidine kinase mutants of Deinococcus radiodurans after exposure to DNA-damaging agents. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36, 781–789 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0904-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-0904-8