Abstract
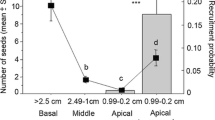
Although mistletoe is typically viewed as a parasite of juniper in a two-way interaction, its role may become neutral or even mutualistic when their common avian seed dispersing agents are considered as a three-way interaction. In the study area, wintering avian frugivores forage on both one-seed juniper (Juniperus monosperma) berries and on the fruit of its associated mistletoe (Phoradendron juniperinum). Three major findings emerged from our studies that support a three-way interaction and the hypothesis of conditional interactions. First, mistletoes provide a stable resource for shared avian seed dispersers; junipers do not. Whereas juniper berry production varied 10- to 15-fold over the 3 years of our study, mistletoe fruit abundance did not vary significantly. Second, the abundance of avian seed dispersal agents, such as Townsend's solitaires (Myadestes townsendi), is strongly tied to the abundance of juniper berries in mast years and mistletoe fruits in all years. In fact, the best overall predictor of their common avian seed dispersal agents was the abundance of mistletoe; stands with mistletoe attracted up to 3 times more avian frugivores than stands with little or no mistletoe. Thus, mistletoe berries can serve as the main attractor for birds that disperse juniper berries. Third, in agreement with the hypothesis that mistletoe can benefit junipers by attracting and supporting greater populations of avian seed dispersal agents, the number of juniper seedlings was more than 2-fold greater in stands with high mistletoe density compared with stands that had little or no mistletoe. Results suggest that the occurrence of a three-way interaction, in the presence of environmental variation (in this case, annual variation in juniper berry crops), may change the ecological roles of associated species. A conceptual model is presented to illustrate how the role of mistletoe may range from parasitic to mutualistic, while the role of avian seed dispersers may conversely range from mutualistic to parasitic, the latter by acting as vectors for the spread of mistletoe.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Ommeren, R.J., Whitham, T.G. Changes in interactions between juniper and mistletoe mediated by shared avian frugivores: parasitism to potential mutualism. Oecologia 130, 281–288 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100792
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100792