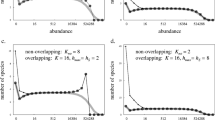
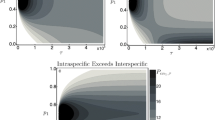
Abstract
Elucidating the mechanisms underlying the assembly and dynamics of ecological communities is a fundamental goal of ecology. Two conceptual approaches have emerged in this respect: the niche-assembly view and the neutral perspective. The debate as to which approach best explains the biodiversity patterns observed in nature is becoming outdated, as ecologists increasingly agree on the existence of a niche-neutral continuum of community dynamical behaviors. However, attempts to make the continuum idea operational and measurable remain sparse. Here, we propose a model-based approach to achieving this. The proposed methodology consists of separating out fluctuations in species abundances into niche-mediated and stochastic factors, linking the niche configuration to community dynamics through competition, and adding demographic stochasticity. This results in a comprehensive framework including neutrality and strict niche segregation as extreme cases. We develop an index of departure from neutral drift as a surrogate for community position on the niche-neutral continuum. We evaluate the performance of our modeling approach with simulated data, and subsequently use the model to analyze rodent web-trapping data from a real-world system. The model fitting is carried out with a Bayesian approach using Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams P (1980) Some comments on measuring niche overlap. Ecology 61:44–49
Adler PB, HilleRisLambers J, Levine JM (2007) A niche for neutrality. Ecol Lett 10:95–104
Armstrong RA, McGehee R (1980) Competitive exclusion. Am Nat 115:151–170
Bell G (2000) Distribution of abundance in neutral communities. Am Nat 155:606–617
Benedetti-Cecchi L, Bertocci I, Vasseli S, Maggi E, Bulleri F (2008) Neutrality and the response of rare species to environmental variance. PLoS One 3(7):e2777
Bjørnstad ON, Grinfell BT (2001) Noisy clockwork: time series analysis of population fluctuations in animals. Science 293:638–643
Brown J (1984) Relationship between abundance and distribution of species. Am Nat 124:255–279
Buckland ST, Newman KB, Thomas L, Koesters NB (2004) State-space models for the dynamics of wild animal populations. Ecol Modell 171:157–175
Bush GL (1969) Sympatric host race formation and speciation in frugivorous flies of the genus Rhagoletis (Diptera, Tephritidae). Evolution 23:237–251
Cadotte MW (2007) Concurrent niche and neutral processes in the competition-colonization model of species coexistence. Proc R Soc Lond B 274:2739–2744
Cannon CH, Leighton M (2004) Tree species distribution across five habitat in the Bornean rain forest. J Veg Sci 15:257–266
Chave J, Muller-Landau HC, Levin SA (2002) Comparing classical community models: theoretical consequences for patterns of diversity. Am Nat 159:1–23
Chesson P (2000) Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 31:343–366
Colwell RK, Futuyma DJ (1971) On the measurement of the niche breadth and overlap. Ecology 52:567–576
Coomes DA, Rees M, Grubb PJ, Turnbull L (2002) Are differences in seed mass among species important in structuring plant communities? Evidence from analyses of spatial and temporal variation in dune-annual populations. Oikos 96:421–432
de Valpine P, Hastings A (2002) Fitting population models incorporating process noise and observation error. Ecol Monogr 72:57–76
Dennis B, Ponciano JM, Lele SR, Taper ML, Staples DF (2006) Estimating density dependence, process noise and observation error. Ecology 76:323–341
Dornelas M, Connoly SR, Hughes TP (2006) Coral reef diversity refutes the neutral theory of biodiversity. Nature 440:80–82
Etienne RS, Alonso D, McKane AJ (2007) The zero-sum assumption in the neutral theory. J Theor Biol 248:522–536
Friggens M (2006) Sevilleta small mammal population data SEV008. http://sevilleta.unm.edu/data/
Gange AC, Brown VK (2009) Multitrophic interactions in terrestrial systems, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gause GF (1934) The struggle for existence. Hafner, New York
Gause GF (1935) Experimental demonstration of Volterra’s periodic oscillations in the numbers of animals. J Exp Biol 12:44–48
Gelman A (2006) Prior distributions for variance parameters in hierarchical models. Bayes Anal 1:515–533
Gelman A, Meng XL, Stern H (1996) Posterior predictive assessment of model fitness via realized discrepancies. Stat Sin 6:733–760
Gelman A, Carlin JB, Stern HS, Rubin DB (2003) Bayesian data analysis, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall, New York
Gilks WR, Richardson S, Spiegelhalter DJ (eds) (1996) Markov chain Monte Carlo in practice. Chapman and Hall, London
Gravel D, Canham CD, Beaudet M, Messier C (2006) Reconciling niche and neutrality: the continuum hypothesis. Ecol Lett 9:399–409
Grinnell J (1917) The niche relationships of the California thraster. Auk 34:427–433
Hanski I, Koskela H (1978) Stability, abundance, and niche width in beetle community inhabiting cow dung. Oikos 31:290–298
Hardin G (1960) The competitive exclusion principle. Science 131:1292–1297
Hartner EJ, Whitmore RC (1977) Multivariate measures of niche overlap using discriminant analysis. Theor Pop Biol 12:21–36
Hastings A (1980) Disturbance, coexistence, history, and competition for space. Theor Pop Biol 18:363–373
Hastings A, Wolin CL (1989) Within-patch dynamics in a metapopulation. Ecology 70:1261–1266
Holyoak M, Loreau M (2006) Reconciling empirical ecology with neutral community models. Ecology 87:1370–1377
Houlahan JE, Currie DJ, Cottenie K, Cumming JS, Ernest SKM, Findlay CS, Fuhlendorf SD, Gaedke U, Legendre P, Magnuson JJ, McArdle BH, Muldavin EH, Noble D, Russel R, Stevens RD, Willis TJ, Woiwod IP, Wondzell SM (2007) Compensatory dynamics are rare in natural ecological communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3273–3277
Hubbell SP (2001) The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography. Princeton University Press, New Jersey
Hughes JB (2000) The scale of resource specialization and the distribution and abundance of lycaenid butterflies. Oecologia 123:375–383
Hurlbert SH (1978) The measurement of the niche overlap and some relatives. Ecology 59:67–77
Hurlbert SH (2004) Species-energy relationships and habitat complexity in bird communities. Ecol Lett 7:714–720
Hutchinson GE (1957) Concluding remarks. Cold spring harbor symposium on quantitative biology 22:415–427
Hutchinson GE (1961) The paradox of the plankton. Am Nat 95:137–145
Ings TC, Montoya JM, Bascompte J, Bluthgen N, Brown L, Dormann CF, Edwards F, Figueroa D, Jacob U, Jones JI, Lauridsen RB, Ledger ME, Lewis HM, Olesen JM, van Veen FJF, Warren PH, Woodward G (2009) Ecological networks––beyond food webs. J Anim Ecol 78:253–269
Jabot F, Etienne RS, Chave J (2008) Reconciling neutral community model and environmental filtering: theory and an empirical test. Oikos 117:1308–1320
Jacobson AR, Provenzale A, von Hardenberg A, Bassano B, Festa-Bianchet M (2004) Climate forcing and density dependence in a mountain ungulate population. Ecology 85:1598–1610
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lande R, Engen S, Saether B-E (2003) Stochastic population dynamics in ecology and conservation. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Levine JM, HilleRisLambers J (2009) The importance of niches for the maintenance of diversity. Nature 461:254–257
Levins R (1968) Evolution in changing environments: some theoretical explanations. Princeton University Press, Princeton
MacArthur RH, Levins R (1967) The limiting similarity, convergence and divergence of coexisting species. Am Nat 101:377–385
McGill BJ (2003) A test of the unified neutral theory. Nature 422:881–885
McGill BJ, Maurer BA, Weiser M (2006) Empirical evaluation of neutral theory. Ecology 87:1411–1423
McNaughton SJ, Wolf LL (1970) Dominance and niche in ecological systems. Science 167:131–139
Mutshinda CM, O’Hara RB, Woiwod IP (2008) Species abundance dynamics under neutral assumptions: a Bayesian approach to the controversy. Funct Ecol 22:340–347
Mutshinda CM, O’Hara RB, Woiwod IP (2009) What drives community dynamics? Proc R Soc Lond B 276:2923–2929
Mutshinda CM, O’Hara RB, Woiwod IP (2010) A multispecies perspective on ecological impacts of climatic forcing. J Anim Ecol. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2656.2010.01743.x
Pianka ER (1974) Niche overlap and diffuse competition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:2141–2145
Redfearn A, Pimm S (1988) Population variability and polyphagy in herbivorous insects. Ecol Monogr 58:39–55
Ross HH (1957) Principles of natural coexistence indicated by leafhopper populations. Evolution 11:113–129
Royle JA, Dorazio RM (2006) Hierarchical models of animal abundance and occurrence. J Agr Biol Env Stat 11:249–263
Saether B-E, Tufto J, Engen S, Jerstad K, Røstad OW, Skåtan JE (2000) Population dynamical consequences of climate change for a small temperate songbird. Science 287:854–856
Saitoh T, Stenseth NC, Bjonstad ON (1997) Density dependence in fluctuating grey-sided vole populations. J Anim Ecol 66:14–24
Simberloff D (1982) The status of competition theory in ecology. Ann Zool Fenn 19:241–253
Solé RV, Alonso D, Sadana J (2004) Habitat fragmentation and biodiversity collapse in neutral communities. Ecol Complex 1:65–75
Thomas A, O’Hara RB, Ligges U, Sturtz S (2006) Making BUGS Open. R News 6:12–17
Tokeshi M (1993) Species abundance patterns and community structure. Adv Ecol Res 24:112–186
Turnbull LA, Manley L, Rees M (2005) Niches, rather than neutrality, structure a grassland pioneer guild. Proc R Soc Lond B 272:1357–1364
Volkov I, Banavar JR, Hubbell SP, Martian A (2003) Neutral theory and relative species abundance in ecology. Nature 424:1035–1037
Wilson DS (1992) Complex interactions in metacommunities with implications to biodiversity and higher level of selection. Ecology 73:1984–2000
Yamamoto N, Yokoyama J, Kawata M (2007) Relative resource abundance explains butterfly biodiversity in island communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10524–10529
Zhou S, Zhang D (2008) Neutral theory in community ecology. Front Biol China 30:1–8
Acknowledgments
We thank Otso Ovaskainen, Craig Loehle, Lasse Ruokolainen, and Mike Fowler for their helpful comments on an early version of the manuscript. We are grateful to the Sevilleta Long-Term Ecological Research Program (LTER) for making the rodent data available. The financial support for this research was provided by the Academy of Finland (project no. 205371) and the research funding programme “LOEWE–Landes-Offensive zur Entwicklung Wissenschaftlich-ökonomischer Exzellenz” of Hesse’s Ministry of Higher Education, Research, and the Arts. The authors declare that the experiments reported in this study comply with the laws of the country in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Scott Collins.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mutshinda, C.M., O’Hara, R.B. Integrating the niche and neutral perspectives on community structure and dynamics. Oecologia 166, 241–251 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-010-1831-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-010-1831-x